Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 1.4.0 |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2025-07-09 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- mripperger
Authors
- mripperger
REACH ROS Plugins
This package contains the ROS2-based plugin implemenations of REACH kinematics, evaluation, and display interfaces
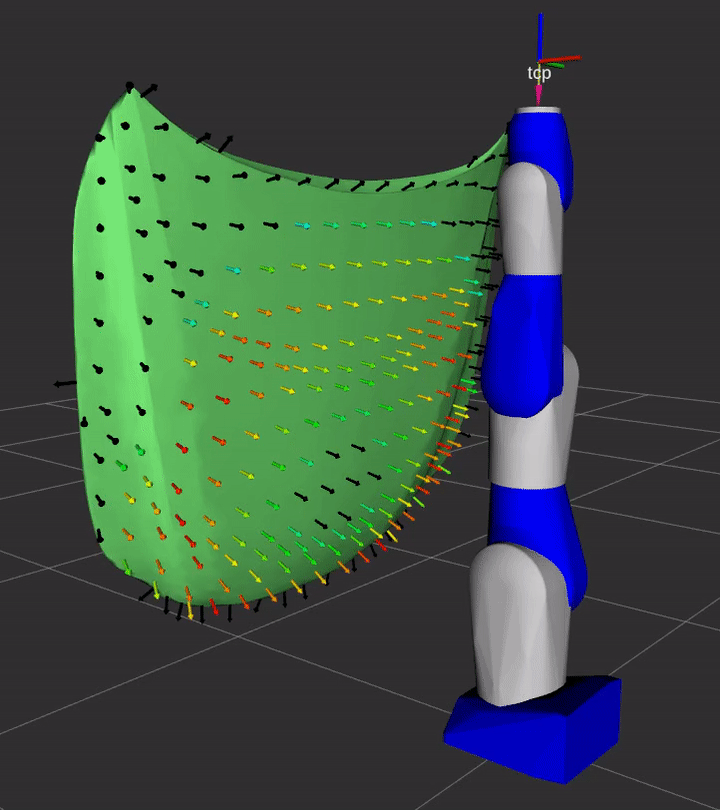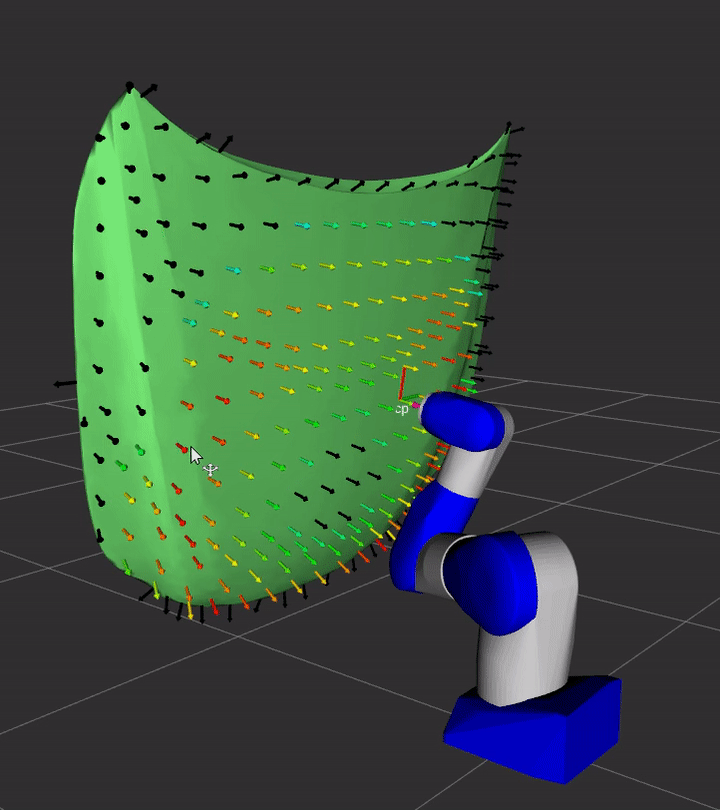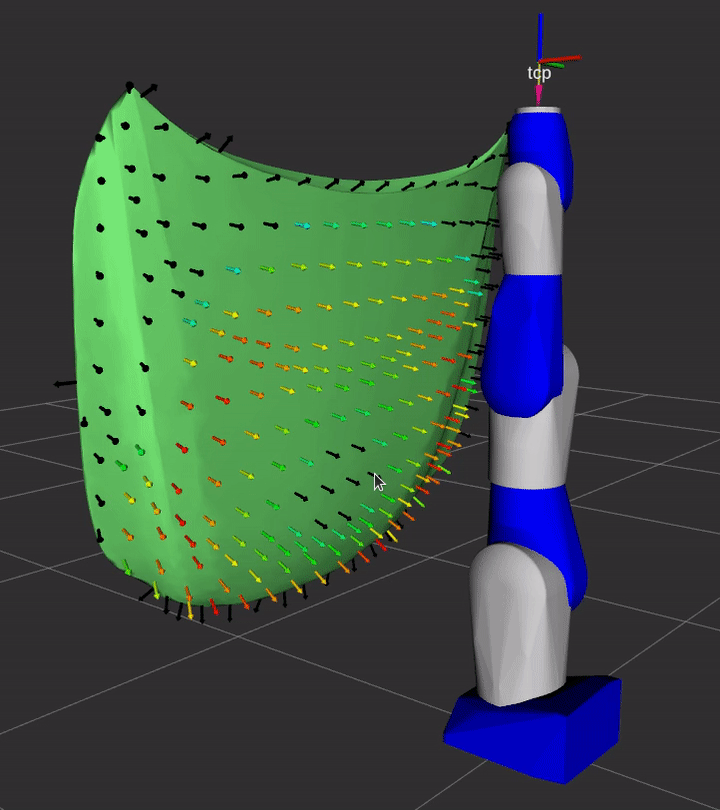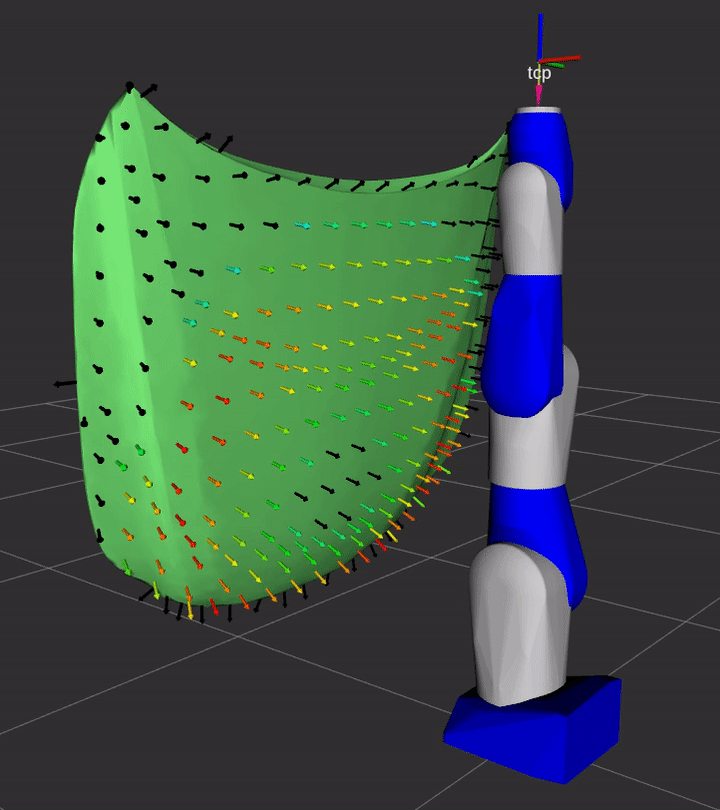
Installation
First, clone the repository into a colcon workspace
cd ~/reach_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git
cd ..
Install the dependencies
vcs import src < src/reach_ros2/dependencies.repos
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Build the repository
colcon build --symlink-install
Demo
A simple demonstration of the capability of this repository is provided in the demo sub-directory.
See the instructions for details on how to launch the demo from ROS 2 and see the Python instructions to see how you can use the Python interface to launch studies.
Usage
Use the following steps to run a reach study with a robot using the ROS1 infrastructure and plugins.
- Create any files describing your robot system required by the REACH plugins (e.g., URDF, SRDF, kinematics file, joint limits file, etc.)
- Create a mesh model of the workpiece
Note: the origin of this model should align with the kinematic base frame of the robot
- Create a point cloud of the target points on the workpiece
- This point cloud can be generated using a command line tool from PCL 1.8:
pcl_mesh_sampling <workpiece_mesh>.ply <output_cloud>.pcd -n_samples <number of samples> -leaf_size <leaf_size> -write_normals true
- Create a configuration YAML file defining the parameters of the reach study and the configuration of the interface plugins (see this demo example)
- Run the setup launch file
ros2 launch reach_ros setup.launch robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF>
- Run the reach study analysis
ros2 launch reach_ros start.launch \
robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF> \
robot_description_semantic_file:=<path_to_SRDF> \
robot_description_kinematics_file:=<path_to_kinematics.yaml> \
robot_description_joint_limits_file:=<path_to_joint_limits.yaml> \
config_file:=<config_file.yaml> \
config_name:=<arbitrary_config> \
results_dir:=<arbitrary_results_directory>
Evaluation Plugins
Manipulability
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose. Higher manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
Manipulability Scaled
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose divided by the characteristic length of the motion group. The characteristic length is computed by walking from the base link to the tip link of the motion group and summing the distances between adjacent links. Higher scaled manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
-
excluded_links(optional)- The names of links contained in the motion group that should not contribute to the characteristic length
Manipulability Ratio
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose and evaluate a score. The score is calculated as the ratio of the smallest manipulability value to the largest manipulability value. The larger this ratio, the more uniform the dexterity and the higher the score. Range [0, 1]
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package reach_ros
1.4.0 (2023-10-04)
- IK Solver Update
(#30)
- Migrate utility function to reach
- Replace deprecated function
- Check that IK solver has been loaded for move group
- Run format jobs on 20.04
- Ran clang format
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.5 (2023-10-04)
- Export dependency on reach (#29)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.4 (2023-09-25)
- Python CMake Update
(#27)
- Ensure PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR is set by ament
- Replace ROS version compile definition with preprocessor check
- CI Update (#26)
- Push docker image on ref_type tag
- Added AFTER_SCRIPT to CI
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.3 (2023-09-22)
- Use YAML anchors in reach study config files to simplify (#24)
- Run CI workflow on tag push and workflow dispatch (#25)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.2 (2023-09-14)
- Updated CMake version for if STRGREATER_EQUAL command (#23)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.1 (2023-09-07)
- Updated python module install (#22)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.0 (2023-08-16)
- Add customizable color scale for visualization (#18)
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann
1.2.0 (2023-08-16)
- Added Python equivalent of the c++ reach study node
- Added a Python interface to allow usage of ROS2 plugins in Python
- Revised ROS node singleton pattern
- Remove the plugin library from ament_target_export so downstream packages cannot link against it
- Link executable against main library instead of plugin library
- Fixed typo in plugin export
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.1.0 (2023-06-13)
- Updated to REACH 1.3.0
- Clean up config/launch files
- Updated demo results
- Updated distance penalty to cap at 1.0
- Updated collision distance evaluator to optionally accept collision mesh; updated README
- Added comments about collision_mesh_frame parameter
- Fix deps install in README
- Updated to reach 1.2.0
- Updated README
- Added transformed point cloud target pose generator
- Exposed interface implementations separately from plugin library
- Fixed collision mesh frame key
- Fixed docker commit name in CI configuration
- Updated node to join executor thread properly
- Added reach plugin library name to environment variable for discovery by the plugin loader
- Updated to reach 1.1.0
- Updated to reach 0.1.1
- Merge pull request #2 from marip8/ros2 ROS2 Support
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.0.0 (2023-05-10)
- Move ROS1 components (#44)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged reach_ros at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 1.4.0 |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2025-07-09 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- mripperger
Authors
- mripperger
REACH ROS Plugins
This package contains the ROS2-based plugin implemenations of REACH kinematics, evaluation, and display interfaces

Installation
First, clone the repository into a colcon workspace
cd ~/reach_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git
cd ..
Install the dependencies
vcs import src < src/reach_ros2/dependencies.repos
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Build the repository
colcon build --symlink-install
Demo
A simple demonstration of the capability of this repository is provided in the demo sub-directory.
See the instructions for details on how to launch the demo from ROS 2 and see the Python instructions to see how you can use the Python interface to launch studies.
Usage
Use the following steps to run a reach study with a robot using the ROS1 infrastructure and plugins.
- Create any files describing your robot system required by the REACH plugins (e.g., URDF, SRDF, kinematics file, joint limits file, etc.)
- Create a mesh model of the workpiece
Note: the origin of this model should align with the kinematic base frame of the robot
- Create a point cloud of the target points on the workpiece
- This point cloud can be generated using a command line tool from PCL 1.8:
pcl_mesh_sampling <workpiece_mesh>.ply <output_cloud>.pcd -n_samples <number of samples> -leaf_size <leaf_size> -write_normals true
- Create a configuration YAML file defining the parameters of the reach study and the configuration of the interface plugins (see this demo example)
- Run the setup launch file
ros2 launch reach_ros setup.launch robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF>
- Run the reach study analysis
ros2 launch reach_ros start.launch \
robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF> \
robot_description_semantic_file:=<path_to_SRDF> \
robot_description_kinematics_file:=<path_to_kinematics.yaml> \
robot_description_joint_limits_file:=<path_to_joint_limits.yaml> \
config_file:=<config_file.yaml> \
config_name:=<arbitrary_config> \
results_dir:=<arbitrary_results_directory>
Evaluation Plugins
Manipulability
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose. Higher manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
Manipulability Scaled
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose divided by the characteristic length of the motion group. The characteristic length is computed by walking from the base link to the tip link of the motion group and summing the distances between adjacent links. Higher scaled manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
-
excluded_links(optional)- The names of links contained in the motion group that should not contribute to the characteristic length
Manipulability Ratio
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose and evaluate a score. The score is calculated as the ratio of the smallest manipulability value to the largest manipulability value. The larger this ratio, the more uniform the dexterity and the higher the score. Range [0, 1]
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package reach_ros
1.4.0 (2023-10-04)
- IK Solver Update
(#30)
- Migrate utility function to reach
- Replace deprecated function
- Check that IK solver has been loaded for move group
- Run format jobs on 20.04
- Ran clang format
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.5 (2023-10-04)
- Export dependency on reach (#29)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.4 (2023-09-25)
- Python CMake Update
(#27)
- Ensure PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR is set by ament
- Replace ROS version compile definition with preprocessor check
- CI Update (#26)
- Push docker image on ref_type tag
- Added AFTER_SCRIPT to CI
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.3 (2023-09-22)
- Use YAML anchors in reach study config files to simplify (#24)
- Run CI workflow on tag push and workflow dispatch (#25)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.2 (2023-09-14)
- Updated CMake version for if STRGREATER_EQUAL command (#23)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.1 (2023-09-07)
- Updated python module install (#22)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.0 (2023-08-16)
- Add customizable color scale for visualization (#18)
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann
1.2.0 (2023-08-16)
- Added Python equivalent of the c++ reach study node
- Added a Python interface to allow usage of ROS2 plugins in Python
- Revised ROS node singleton pattern
- Remove the plugin library from ament_target_export so downstream packages cannot link against it
- Link executable against main library instead of plugin library
- Fixed typo in plugin export
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.1.0 (2023-06-13)
- Updated to REACH 1.3.0
- Clean up config/launch files
- Updated demo results
- Updated distance penalty to cap at 1.0
- Updated collision distance evaluator to optionally accept collision mesh; updated README
- Added comments about collision_mesh_frame parameter
- Fix deps install in README
- Updated to reach 1.2.0
- Updated README
- Added transformed point cloud target pose generator
- Exposed interface implementations separately from plugin library
- Fixed collision mesh frame key
- Fixed docker commit name in CI configuration
- Updated node to join executor thread properly
- Added reach plugin library name to environment variable for discovery by the plugin loader
- Updated to reach 1.1.0
- Updated to reach 0.1.1
- Merge pull request #2 from marip8/ros2 ROS2 Support
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.0.0 (2023-05-10)
- Move ROS1 components (#44)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged reach_ros at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 1.4.0 |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2025-07-09 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- mripperger
Authors
- mripperger
REACH ROS Plugins
This package contains the ROS2-based plugin implemenations of REACH kinematics, evaluation, and display interfaces

Installation
First, clone the repository into a colcon workspace
cd ~/reach_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git
cd ..
Install the dependencies
vcs import src < src/reach_ros2/dependencies.repos
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Build the repository
colcon build --symlink-install
Demo
A simple demonstration of the capability of this repository is provided in the demo sub-directory.
See the instructions for details on how to launch the demo from ROS 2 and see the Python instructions to see how you can use the Python interface to launch studies.
Usage
Use the following steps to run a reach study with a robot using the ROS1 infrastructure and plugins.
- Create any files describing your robot system required by the REACH plugins (e.g., URDF, SRDF, kinematics file, joint limits file, etc.)
- Create a mesh model of the workpiece
Note: the origin of this model should align with the kinematic base frame of the robot
- Create a point cloud of the target points on the workpiece
- This point cloud can be generated using a command line tool from PCL 1.8:
pcl_mesh_sampling <workpiece_mesh>.ply <output_cloud>.pcd -n_samples <number of samples> -leaf_size <leaf_size> -write_normals true
- Create a configuration YAML file defining the parameters of the reach study and the configuration of the interface plugins (see this demo example)
- Run the setup launch file
ros2 launch reach_ros setup.launch robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF>
- Run the reach study analysis
ros2 launch reach_ros start.launch \
robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF> \
robot_description_semantic_file:=<path_to_SRDF> \
robot_description_kinematics_file:=<path_to_kinematics.yaml> \
robot_description_joint_limits_file:=<path_to_joint_limits.yaml> \
config_file:=<config_file.yaml> \
config_name:=<arbitrary_config> \
results_dir:=<arbitrary_results_directory>
Evaluation Plugins
Manipulability
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose. Higher manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
Manipulability Scaled
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose divided by the characteristic length of the motion group. The characteristic length is computed by walking from the base link to the tip link of the motion group and summing the distances between adjacent links. Higher scaled manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
-
excluded_links(optional)- The names of links contained in the motion group that should not contribute to the characteristic length
Manipulability Ratio
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose and evaluate a score. The score is calculated as the ratio of the smallest manipulability value to the largest manipulability value. The larger this ratio, the more uniform the dexterity and the higher the score. Range [0, 1]
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package reach_ros
1.4.0 (2023-10-04)
- IK Solver Update
(#30)
- Migrate utility function to reach
- Replace deprecated function
- Check that IK solver has been loaded for move group
- Run format jobs on 20.04
- Ran clang format
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.5 (2023-10-04)
- Export dependency on reach (#29)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.4 (2023-09-25)
- Python CMake Update
(#27)
- Ensure PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR is set by ament
- Replace ROS version compile definition with preprocessor check
- CI Update (#26)
- Push docker image on ref_type tag
- Added AFTER_SCRIPT to CI
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.3 (2023-09-22)
- Use YAML anchors in reach study config files to simplify (#24)
- Run CI workflow on tag push and workflow dispatch (#25)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.2 (2023-09-14)
- Updated CMake version for if STRGREATER_EQUAL command (#23)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.1 (2023-09-07)
- Updated python module install (#22)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.0 (2023-08-16)
- Add customizable color scale for visualization (#18)
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann
1.2.0 (2023-08-16)
- Added Python equivalent of the c++ reach study node
- Added a Python interface to allow usage of ROS2 plugins in Python
- Revised ROS node singleton pattern
- Remove the plugin library from ament_target_export so downstream packages cannot link against it
- Link executable against main library instead of plugin library
- Fixed typo in plugin export
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.1.0 (2023-06-13)
- Updated to REACH 1.3.0
- Clean up config/launch files
- Updated demo results
- Updated distance penalty to cap at 1.0
- Updated collision distance evaluator to optionally accept collision mesh; updated README
- Added comments about collision_mesh_frame parameter
- Fix deps install in README
- Updated to reach 1.2.0
- Updated README
- Added transformed point cloud target pose generator
- Exposed interface implementations separately from plugin library
- Fixed collision mesh frame key
- Fixed docker commit name in CI configuration
- Updated node to join executor thread properly
- Added reach plugin library name to environment variable for discovery by the plugin loader
- Updated to reach 1.1.0
- Updated to reach 0.1.1
- Merge pull request #2 from marip8/ros2 ROS2 Support
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.0.0 (2023-05-10)
- Move ROS1 components (#44)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged reach_ros at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 1.4.0 |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2025-07-09 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- mripperger
Authors
- mripperger
REACH ROS Plugins
This package contains the ROS2-based plugin implemenations of REACH kinematics, evaluation, and display interfaces

Installation
First, clone the repository into a colcon workspace
cd ~/reach_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git
cd ..
Install the dependencies
vcs import src < src/reach_ros2/dependencies.repos
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Build the repository
colcon build --symlink-install
Demo
A simple demonstration of the capability of this repository is provided in the demo sub-directory.
See the instructions for details on how to launch the demo from ROS 2 and see the Python instructions to see how you can use the Python interface to launch studies.
Usage
Use the following steps to run a reach study with a robot using the ROS1 infrastructure and plugins.
- Create any files describing your robot system required by the REACH plugins (e.g., URDF, SRDF, kinematics file, joint limits file, etc.)
- Create a mesh model of the workpiece
Note: the origin of this model should align with the kinematic base frame of the robot
- Create a point cloud of the target points on the workpiece
- This point cloud can be generated using a command line tool from PCL 1.8:
pcl_mesh_sampling <workpiece_mesh>.ply <output_cloud>.pcd -n_samples <number of samples> -leaf_size <leaf_size> -write_normals true
- Create a configuration YAML file defining the parameters of the reach study and the configuration of the interface plugins (see this demo example)
- Run the setup launch file
ros2 launch reach_ros setup.launch robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF>
- Run the reach study analysis
ros2 launch reach_ros start.launch \
robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF> \
robot_description_semantic_file:=<path_to_SRDF> \
robot_description_kinematics_file:=<path_to_kinematics.yaml> \
robot_description_joint_limits_file:=<path_to_joint_limits.yaml> \
config_file:=<config_file.yaml> \
config_name:=<arbitrary_config> \
results_dir:=<arbitrary_results_directory>
Evaluation Plugins
Manipulability
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose. Higher manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
Manipulability Scaled
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose divided by the characteristic length of the motion group. The characteristic length is computed by walking from the base link to the tip link of the motion group and summing the distances between adjacent links. Higher scaled manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
-
excluded_links(optional)- The names of links contained in the motion group that should not contribute to the characteristic length
Manipulability Ratio
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose and evaluate a score. The score is calculated as the ratio of the smallest manipulability value to the largest manipulability value. The larger this ratio, the more uniform the dexterity and the higher the score. Range [0, 1]
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package reach_ros
1.4.0 (2023-10-04)
- IK Solver Update
(#30)
- Migrate utility function to reach
- Replace deprecated function
- Check that IK solver has been loaded for move group
- Run format jobs on 20.04
- Ran clang format
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.5 (2023-10-04)
- Export dependency on reach (#29)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.4 (2023-09-25)
- Python CMake Update
(#27)
- Ensure PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR is set by ament
- Replace ROS version compile definition with preprocessor check
- CI Update (#26)
- Push docker image on ref_type tag
- Added AFTER_SCRIPT to CI
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.3 (2023-09-22)
- Use YAML anchors in reach study config files to simplify (#24)
- Run CI workflow on tag push and workflow dispatch (#25)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.2 (2023-09-14)
- Updated CMake version for if STRGREATER_EQUAL command (#23)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.1 (2023-09-07)
- Updated python module install (#22)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.0 (2023-08-16)
- Add customizable color scale for visualization (#18)
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann
1.2.0 (2023-08-16)
- Added Python equivalent of the c++ reach study node
- Added a Python interface to allow usage of ROS2 plugins in Python
- Revised ROS node singleton pattern
- Remove the plugin library from ament_target_export so downstream packages cannot link against it
- Link executable against main library instead of plugin library
- Fixed typo in plugin export
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.1.0 (2023-06-13)
- Updated to REACH 1.3.0
- Clean up config/launch files
- Updated demo results
- Updated distance penalty to cap at 1.0
- Updated collision distance evaluator to optionally accept collision mesh; updated README
- Added comments about collision_mesh_frame parameter
- Fix deps install in README
- Updated to reach 1.2.0
- Updated README
- Added transformed point cloud target pose generator
- Exposed interface implementations separately from plugin library
- Fixed collision mesh frame key
- Fixed docker commit name in CI configuration
- Updated node to join executor thread properly
- Added reach plugin library name to environment variable for discovery by the plugin loader
- Updated to reach 1.1.0
- Updated to reach 0.1.1
- Merge pull request #2 from marip8/ros2 ROS2 Support
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.0.0 (2023-05-10)
- Move ROS1 components (#44)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged reach_ros at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 1.4.0 |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2025-07-09 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- mripperger
Authors
- mripperger
REACH ROS Plugins
This package contains the ROS2-based plugin implemenations of REACH kinematics, evaluation, and display interfaces

Installation
First, clone the repository into a colcon workspace
cd ~/reach_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git
cd ..
Install the dependencies
vcs import src < src/reach_ros2/dependencies.repos
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Build the repository
colcon build --symlink-install
Demo
A simple demonstration of the capability of this repository is provided in the demo sub-directory.
See the instructions for details on how to launch the demo from ROS 2 and see the Python instructions to see how you can use the Python interface to launch studies.
Usage
Use the following steps to run a reach study with a robot using the ROS1 infrastructure and plugins.
- Create any files describing your robot system required by the REACH plugins (e.g., URDF, SRDF, kinematics file, joint limits file, etc.)
- Create a mesh model of the workpiece
Note: the origin of this model should align with the kinematic base frame of the robot
- Create a point cloud of the target points on the workpiece
- This point cloud can be generated using a command line tool from PCL 1.8:
pcl_mesh_sampling <workpiece_mesh>.ply <output_cloud>.pcd -n_samples <number of samples> -leaf_size <leaf_size> -write_normals true
- Create a configuration YAML file defining the parameters of the reach study and the configuration of the interface plugins (see this demo example)
- Run the setup launch file
ros2 launch reach_ros setup.launch robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF>
- Run the reach study analysis
ros2 launch reach_ros start.launch \
robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF> \
robot_description_semantic_file:=<path_to_SRDF> \
robot_description_kinematics_file:=<path_to_kinematics.yaml> \
robot_description_joint_limits_file:=<path_to_joint_limits.yaml> \
config_file:=<config_file.yaml> \
config_name:=<arbitrary_config> \
results_dir:=<arbitrary_results_directory>
Evaluation Plugins
Manipulability
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose. Higher manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
Manipulability Scaled
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose divided by the characteristic length of the motion group. The characteristic length is computed by walking from the base link to the tip link of the motion group and summing the distances between adjacent links. Higher scaled manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
-
excluded_links(optional)- The names of links contained in the motion group that should not contribute to the characteristic length
Manipulability Ratio
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose and evaluate a score. The score is calculated as the ratio of the smallest manipulability value to the largest manipulability value. The larger this ratio, the more uniform the dexterity and the higher the score. Range [0, 1]
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package reach_ros
1.4.0 (2023-10-04)
- IK Solver Update
(#30)
- Migrate utility function to reach
- Replace deprecated function
- Check that IK solver has been loaded for move group
- Run format jobs on 20.04
- Ran clang format
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.5 (2023-10-04)
- Export dependency on reach (#29)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.4 (2023-09-25)
- Python CMake Update
(#27)
- Ensure PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR is set by ament
- Replace ROS version compile definition with preprocessor check
- CI Update (#26)
- Push docker image on ref_type tag
- Added AFTER_SCRIPT to CI
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.3 (2023-09-22)
- Use YAML anchors in reach study config files to simplify (#24)
- Run CI workflow on tag push and workflow dispatch (#25)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.2 (2023-09-14)
- Updated CMake version for if STRGREATER_EQUAL command (#23)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.1 (2023-09-07)
- Updated python module install (#22)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.0 (2023-08-16)
- Add customizable color scale for visualization (#18)
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann
1.2.0 (2023-08-16)
- Added Python equivalent of the c++ reach study node
- Added a Python interface to allow usage of ROS2 plugins in Python
- Revised ROS node singleton pattern
- Remove the plugin library from ament_target_export so downstream packages cannot link against it
- Link executable against main library instead of plugin library
- Fixed typo in plugin export
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.1.0 (2023-06-13)
- Updated to REACH 1.3.0
- Clean up config/launch files
- Updated demo results
- Updated distance penalty to cap at 1.0
- Updated collision distance evaluator to optionally accept collision mesh; updated README
- Added comments about collision_mesh_frame parameter
- Fix deps install in README
- Updated to reach 1.2.0
- Updated README
- Added transformed point cloud target pose generator
- Exposed interface implementations separately from plugin library
- Fixed collision mesh frame key
- Fixed docker commit name in CI configuration
- Updated node to join executor thread properly
- Added reach plugin library name to environment variable for discovery by the plugin loader
- Updated to reach 1.1.0
- Updated to reach 0.1.1
- Merge pull request #2 from marip8/ros2 ROS2 Support
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.0.0 (2023-05-10)
- Move ROS1 components (#44)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged reach_ros at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 1.4.0 |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2025-07-09 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- mripperger
Authors
- mripperger
REACH ROS Plugins
This package contains the ROS2-based plugin implemenations of REACH kinematics, evaluation, and display interfaces

Installation
First, clone the repository into a colcon workspace
cd ~/reach_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git
cd ..
Install the dependencies
vcs import src < src/reach_ros2/dependencies.repos
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Build the repository
colcon build --symlink-install
Demo
A simple demonstration of the capability of this repository is provided in the demo sub-directory.
See the instructions for details on how to launch the demo from ROS 2 and see the Python instructions to see how you can use the Python interface to launch studies.
Usage
Use the following steps to run a reach study with a robot using the ROS1 infrastructure and plugins.
- Create any files describing your robot system required by the REACH plugins (e.g., URDF, SRDF, kinematics file, joint limits file, etc.)
- Create a mesh model of the workpiece
Note: the origin of this model should align with the kinematic base frame of the robot
- Create a point cloud of the target points on the workpiece
- This point cloud can be generated using a command line tool from PCL 1.8:
pcl_mesh_sampling <workpiece_mesh>.ply <output_cloud>.pcd -n_samples <number of samples> -leaf_size <leaf_size> -write_normals true
- Create a configuration YAML file defining the parameters of the reach study and the configuration of the interface plugins (see this demo example)
- Run the setup launch file
ros2 launch reach_ros setup.launch robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF>
- Run the reach study analysis
ros2 launch reach_ros start.launch \
robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF> \
robot_description_semantic_file:=<path_to_SRDF> \
robot_description_kinematics_file:=<path_to_kinematics.yaml> \
robot_description_joint_limits_file:=<path_to_joint_limits.yaml> \
config_file:=<config_file.yaml> \
config_name:=<arbitrary_config> \
results_dir:=<arbitrary_results_directory>
Evaluation Plugins
Manipulability
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose. Higher manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
Manipulability Scaled
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose divided by the characteristic length of the motion group. The characteristic length is computed by walking from the base link to the tip link of the motion group and summing the distances between adjacent links. Higher scaled manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
-
excluded_links(optional)- The names of links contained in the motion group that should not contribute to the characteristic length
Manipulability Ratio
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose and evaluate a score. The score is calculated as the ratio of the smallest manipulability value to the largest manipulability value. The larger this ratio, the more uniform the dexterity and the higher the score. Range [0, 1]
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package reach_ros
1.4.0 (2023-10-04)
- IK Solver Update
(#30)
- Migrate utility function to reach
- Replace deprecated function
- Check that IK solver has been loaded for move group
- Run format jobs on 20.04
- Ran clang format
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.5 (2023-10-04)
- Export dependency on reach (#29)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.4 (2023-09-25)
- Python CMake Update
(#27)
- Ensure PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR is set by ament
- Replace ROS version compile definition with preprocessor check
- CI Update (#26)
- Push docker image on ref_type tag
- Added AFTER_SCRIPT to CI
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.3 (2023-09-22)
- Use YAML anchors in reach study config files to simplify (#24)
- Run CI workflow on tag push and workflow dispatch (#25)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.2 (2023-09-14)
- Updated CMake version for if STRGREATER_EQUAL command (#23)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.1 (2023-09-07)
- Updated python module install (#22)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.0 (2023-08-16)
- Add customizable color scale for visualization (#18)
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann
1.2.0 (2023-08-16)
- Added Python equivalent of the c++ reach study node
- Added a Python interface to allow usage of ROS2 plugins in Python
- Revised ROS node singleton pattern
- Remove the plugin library from ament_target_export so downstream packages cannot link against it
- Link executable against main library instead of plugin library
- Fixed typo in plugin export
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.1.0 (2023-06-13)
- Updated to REACH 1.3.0
- Clean up config/launch files
- Updated demo results
- Updated distance penalty to cap at 1.0
- Updated collision distance evaluator to optionally accept collision mesh; updated README
- Added comments about collision_mesh_frame parameter
- Fix deps install in README
- Updated to reach 1.2.0
- Updated README
- Added transformed point cloud target pose generator
- Exposed interface implementations separately from plugin library
- Fixed collision mesh frame key
- Fixed docker commit name in CI configuration
- Updated node to join executor thread properly
- Added reach plugin library name to environment variable for discovery by the plugin loader
- Updated to reach 1.1.0
- Updated to reach 0.1.1
- Merge pull request #2 from marip8/ros2 ROS2 Support
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.0.0 (2023-05-10)
- Move ROS1 components (#44)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged reach_ros at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 1.4.0 |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2025-07-09 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- mripperger
Authors
- mripperger
REACH ROS Plugins
This package contains the ROS2-based plugin implemenations of REACH kinematics, evaluation, and display interfaces

Installation
First, clone the repository into a colcon workspace
cd ~/reach_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git
cd ..
Install the dependencies
vcs import src < src/reach_ros2/dependencies.repos
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Build the repository
colcon build --symlink-install
Demo
A simple demonstration of the capability of this repository is provided in the demo sub-directory.
See the instructions for details on how to launch the demo from ROS 2 and see the Python instructions to see how you can use the Python interface to launch studies.
Usage
Use the following steps to run a reach study with a robot using the ROS1 infrastructure and plugins.
- Create any files describing your robot system required by the REACH plugins (e.g., URDF, SRDF, kinematics file, joint limits file, etc.)
- Create a mesh model of the workpiece
Note: the origin of this model should align with the kinematic base frame of the robot
- Create a point cloud of the target points on the workpiece
- This point cloud can be generated using a command line tool from PCL 1.8:
pcl_mesh_sampling <workpiece_mesh>.ply <output_cloud>.pcd -n_samples <number of samples> -leaf_size <leaf_size> -write_normals true
- Create a configuration YAML file defining the parameters of the reach study and the configuration of the interface plugins (see this demo example)
- Run the setup launch file
ros2 launch reach_ros setup.launch robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF>
- Run the reach study analysis
ros2 launch reach_ros start.launch \
robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF> \
robot_description_semantic_file:=<path_to_SRDF> \
robot_description_kinematics_file:=<path_to_kinematics.yaml> \
robot_description_joint_limits_file:=<path_to_joint_limits.yaml> \
config_file:=<config_file.yaml> \
config_name:=<arbitrary_config> \
results_dir:=<arbitrary_results_directory>
Evaluation Plugins
Manipulability
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose. Higher manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
Manipulability Scaled
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose divided by the characteristic length of the motion group. The characteristic length is computed by walking from the base link to the tip link of the motion group and summing the distances between adjacent links. Higher scaled manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
-
excluded_links(optional)- The names of links contained in the motion group that should not contribute to the characteristic length
Manipulability Ratio
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose and evaluate a score. The score is calculated as the ratio of the smallest manipulability value to the largest manipulability value. The larger this ratio, the more uniform the dexterity and the higher the score. Range [0, 1]
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package reach_ros
1.4.0 (2023-10-04)
- IK Solver Update
(#30)
- Migrate utility function to reach
- Replace deprecated function
- Check that IK solver has been loaded for move group
- Run format jobs on 20.04
- Ran clang format
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.5 (2023-10-04)
- Export dependency on reach (#29)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.4 (2023-09-25)
- Python CMake Update
(#27)
- Ensure PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR is set by ament
- Replace ROS version compile definition with preprocessor check
- CI Update (#26)
- Push docker image on ref_type tag
- Added AFTER_SCRIPT to CI
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.3 (2023-09-22)
- Use YAML anchors in reach study config files to simplify (#24)
- Run CI workflow on tag push and workflow dispatch (#25)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.2 (2023-09-14)
- Updated CMake version for if STRGREATER_EQUAL command (#23)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.1 (2023-09-07)
- Updated python module install (#22)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.0 (2023-08-16)
- Add customizable color scale for visualization (#18)
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann
1.2.0 (2023-08-16)
- Added Python equivalent of the c++ reach study node
- Added a Python interface to allow usage of ROS2 plugins in Python
- Revised ROS node singleton pattern
- Remove the plugin library from ament_target_export so downstream packages cannot link against it
- Link executable against main library instead of plugin library
- Fixed typo in plugin export
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.1.0 (2023-06-13)
- Updated to REACH 1.3.0
- Clean up config/launch files
- Updated demo results
- Updated distance penalty to cap at 1.0
- Updated collision distance evaluator to optionally accept collision mesh; updated README
- Added comments about collision_mesh_frame parameter
- Fix deps install in README
- Updated to reach 1.2.0
- Updated README
- Added transformed point cloud target pose generator
- Exposed interface implementations separately from plugin library
- Fixed collision mesh frame key
- Fixed docker commit name in CI configuration
- Updated node to join executor thread properly
- Added reach plugin library name to environment variable for discovery by the plugin loader
- Updated to reach 1.1.0
- Updated to reach 0.1.1
- Merge pull request #2 from marip8/ros2 ROS2 Support
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.0.0 (2023-05-10)
- Move ROS1 components (#44)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged reach_ros at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 1.4.0 |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2025-07-09 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- mripperger
Authors
- mripperger
REACH ROS Plugins
This package contains the ROS2-based plugin implemenations of REACH kinematics, evaluation, and display interfaces

Installation
First, clone the repository into a colcon workspace
cd ~/reach_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git
cd ..
Install the dependencies
vcs import src < src/reach_ros2/dependencies.repos
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Build the repository
colcon build --symlink-install
Demo
A simple demonstration of the capability of this repository is provided in the demo sub-directory.
See the instructions for details on how to launch the demo from ROS 2 and see the Python instructions to see how you can use the Python interface to launch studies.
Usage
Use the following steps to run a reach study with a robot using the ROS1 infrastructure and plugins.
- Create any files describing your robot system required by the REACH plugins (e.g., URDF, SRDF, kinematics file, joint limits file, etc.)
- Create a mesh model of the workpiece
Note: the origin of this model should align with the kinematic base frame of the robot
- Create a point cloud of the target points on the workpiece
- This point cloud can be generated using a command line tool from PCL 1.8:
pcl_mesh_sampling <workpiece_mesh>.ply <output_cloud>.pcd -n_samples <number of samples> -leaf_size <leaf_size> -write_normals true
- Create a configuration YAML file defining the parameters of the reach study and the configuration of the interface plugins (see this demo example)
- Run the setup launch file
ros2 launch reach_ros setup.launch robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF>
- Run the reach study analysis
ros2 launch reach_ros start.launch \
robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF> \
robot_description_semantic_file:=<path_to_SRDF> \
robot_description_kinematics_file:=<path_to_kinematics.yaml> \
robot_description_joint_limits_file:=<path_to_joint_limits.yaml> \
config_file:=<config_file.yaml> \
config_name:=<arbitrary_config> \
results_dir:=<arbitrary_results_directory>
Evaluation Plugins
Manipulability
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose. Higher manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
Manipulability Scaled
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose divided by the characteristic length of the motion group. The characteristic length is computed by walking from the base link to the tip link of the motion group and summing the distances between adjacent links. Higher scaled manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
-
excluded_links(optional)- The names of links contained in the motion group that should not contribute to the characteristic length
Manipulability Ratio
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose and evaluate a score. The score is calculated as the ratio of the smallest manipulability value to the largest manipulability value. The larger this ratio, the more uniform the dexterity and the higher the score. Range [0, 1]
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package reach_ros
1.4.0 (2023-10-04)
- IK Solver Update
(#30)
- Migrate utility function to reach
- Replace deprecated function
- Check that IK solver has been loaded for move group
- Run format jobs on 20.04
- Ran clang format
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.5 (2023-10-04)
- Export dependency on reach (#29)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.4 (2023-09-25)
- Python CMake Update
(#27)
- Ensure PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR is set by ament
- Replace ROS version compile definition with preprocessor check
- CI Update (#26)
- Push docker image on ref_type tag
- Added AFTER_SCRIPT to CI
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.3 (2023-09-22)
- Use YAML anchors in reach study config files to simplify (#24)
- Run CI workflow on tag push and workflow dispatch (#25)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.2 (2023-09-14)
- Updated CMake version for if STRGREATER_EQUAL command (#23)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.1 (2023-09-07)
- Updated python module install (#22)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.0 (2023-08-16)
- Add customizable color scale for visualization (#18)
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann
1.2.0 (2023-08-16)
- Added Python equivalent of the c++ reach study node
- Added a Python interface to allow usage of ROS2 plugins in Python
- Revised ROS node singleton pattern
- Remove the plugin library from ament_target_export so downstream packages cannot link against it
- Link executable against main library instead of plugin library
- Fixed typo in plugin export
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.1.0 (2023-06-13)
- Updated to REACH 1.3.0
- Clean up config/launch files
- Updated demo results
- Updated distance penalty to cap at 1.0
- Updated collision distance evaluator to optionally accept collision mesh; updated README
- Added comments about collision_mesh_frame parameter
- Fix deps install in README
- Updated to reach 1.2.0
- Updated README
- Added transformed point cloud target pose generator
- Exposed interface implementations separately from plugin library
- Fixed collision mesh frame key
- Fixed docker commit name in CI configuration
- Updated node to join executor thread properly
- Added reach plugin library name to environment variable for discovery by the plugin loader
- Updated to reach 1.1.0
- Updated to reach 0.1.1
- Merge pull request #2 from marip8/ros2 ROS2 Support
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.0.0 (2023-05-10)
- Move ROS1 components (#44)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged reach_ros at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 1.4.0 |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2025-07-09 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- mripperger
Authors
- mripperger
REACH ROS Plugins
This package contains the ROS2-based plugin implemenations of REACH kinematics, evaluation, and display interfaces

Installation
First, clone the repository into a colcon workspace
cd ~/reach_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git
cd ..
Install the dependencies
vcs import src < src/reach_ros2/dependencies.repos
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Build the repository
colcon build --symlink-install
Demo
A simple demonstration of the capability of this repository is provided in the demo sub-directory.
See the instructions for details on how to launch the demo from ROS 2 and see the Python instructions to see how you can use the Python interface to launch studies.
Usage
Use the following steps to run a reach study with a robot using the ROS1 infrastructure and plugins.
- Create any files describing your robot system required by the REACH plugins (e.g., URDF, SRDF, kinematics file, joint limits file, etc.)
- Create a mesh model of the workpiece
Note: the origin of this model should align with the kinematic base frame of the robot
- Create a point cloud of the target points on the workpiece
- This point cloud can be generated using a command line tool from PCL 1.8:
pcl_mesh_sampling <workpiece_mesh>.ply <output_cloud>.pcd -n_samples <number of samples> -leaf_size <leaf_size> -write_normals true
- Create a configuration YAML file defining the parameters of the reach study and the configuration of the interface plugins (see this demo example)
- Run the setup launch file
ros2 launch reach_ros setup.launch robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF>
- Run the reach study analysis
ros2 launch reach_ros start.launch \
robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF> \
robot_description_semantic_file:=<path_to_SRDF> \
robot_description_kinematics_file:=<path_to_kinematics.yaml> \
robot_description_joint_limits_file:=<path_to_joint_limits.yaml> \
config_file:=<config_file.yaml> \
config_name:=<arbitrary_config> \
results_dir:=<arbitrary_results_directory>
Evaluation Plugins
Manipulability
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose. Higher manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
Manipulability Scaled
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose divided by the characteristic length of the motion group. The characteristic length is computed by walking from the base link to the tip link of the motion group and summing the distances between adjacent links. Higher scaled manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
-
excluded_links(optional)- The names of links contained in the motion group that should not contribute to the characteristic length
Manipulability Ratio
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose and evaluate a score. The score is calculated as the ratio of the smallest manipulability value to the largest manipulability value. The larger this ratio, the more uniform the dexterity and the higher the score. Range [0, 1]
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package reach_ros
1.4.0 (2023-10-04)
- IK Solver Update
(#30)
- Migrate utility function to reach
- Replace deprecated function
- Check that IK solver has been loaded for move group
- Run format jobs on 20.04
- Ran clang format
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.5 (2023-10-04)
- Export dependency on reach (#29)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.4 (2023-09-25)
- Python CMake Update
(#27)
- Ensure PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR is set by ament
- Replace ROS version compile definition with preprocessor check
- CI Update (#26)
- Push docker image on ref_type tag
- Added AFTER_SCRIPT to CI
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.3 (2023-09-22)
- Use YAML anchors in reach study config files to simplify (#24)
- Run CI workflow on tag push and workflow dispatch (#25)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.2 (2023-09-14)
- Updated CMake version for if STRGREATER_EQUAL command (#23)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.1 (2023-09-07)
- Updated python module install (#22)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.0 (2023-08-16)
- Add customizable color scale for visualization (#18)
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann
1.2.0 (2023-08-16)
- Added Python equivalent of the c++ reach study node
- Added a Python interface to allow usage of ROS2 plugins in Python
- Revised ROS node singleton pattern
- Remove the plugin library from ament_target_export so downstream packages cannot link against it
- Link executable against main library instead of plugin library
- Fixed typo in plugin export
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.1.0 (2023-06-13)
- Updated to REACH 1.3.0
- Clean up config/launch files
- Updated demo results
- Updated distance penalty to cap at 1.0
- Updated collision distance evaluator to optionally accept collision mesh; updated README
- Added comments about collision_mesh_frame parameter
- Fix deps install in README
- Updated to reach 1.2.0
- Updated README
- Added transformed point cloud target pose generator
- Exposed interface implementations separately from plugin library
- Fixed collision mesh frame key
- Fixed docker commit name in CI configuration
- Updated node to join executor thread properly
- Added reach plugin library name to environment variable for discovery by the plugin loader
- Updated to reach 1.1.0
- Updated to reach 0.1.1
- Merge pull request #2 from marip8/ros2 ROS2 Support
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.0.0 (2023-05-10)
- Move ROS1 components (#44)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged reach_ros at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 1.4.0 |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2025-07-09 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- mripperger
Authors
- mripperger
REACH ROS Plugins
This package contains the ROS2-based plugin implemenations of REACH kinematics, evaluation, and display interfaces

Installation
First, clone the repository into a colcon workspace
cd ~/reach_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git
cd ..
Install the dependencies
vcs import src < src/reach_ros2/dependencies.repos
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Build the repository
colcon build --symlink-install
Demo
A simple demonstration of the capability of this repository is provided in the demo sub-directory.
See the instructions for details on how to launch the demo from ROS 2 and see the Python instructions to see how you can use the Python interface to launch studies.
Usage
Use the following steps to run a reach study with a robot using the ROS1 infrastructure and plugins.
- Create any files describing your robot system required by the REACH plugins (e.g., URDF, SRDF, kinematics file, joint limits file, etc.)
- Create a mesh model of the workpiece
Note: the origin of this model should align with the kinematic base frame of the robot
- Create a point cloud of the target points on the workpiece
- This point cloud can be generated using a command line tool from PCL 1.8:
pcl_mesh_sampling <workpiece_mesh>.ply <output_cloud>.pcd -n_samples <number of samples> -leaf_size <leaf_size> -write_normals true
- Create a configuration YAML file defining the parameters of the reach study and the configuration of the interface plugins (see this demo example)
- Run the setup launch file
ros2 launch reach_ros setup.launch robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF>
- Run the reach study analysis
ros2 launch reach_ros start.launch \
robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF> \
robot_description_semantic_file:=<path_to_SRDF> \
robot_description_kinematics_file:=<path_to_kinematics.yaml> \
robot_description_joint_limits_file:=<path_to_joint_limits.yaml> \
config_file:=<config_file.yaml> \
config_name:=<arbitrary_config> \
results_dir:=<arbitrary_results_directory>
Evaluation Plugins
Manipulability
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose. Higher manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
Manipulability Scaled
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose divided by the characteristic length of the motion group. The characteristic length is computed by walking from the base link to the tip link of the motion group and summing the distances between adjacent links. Higher scaled manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
-
excluded_links(optional)- The names of links contained in the motion group that should not contribute to the characteristic length
Manipulability Ratio
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose and evaluate a score. The score is calculated as the ratio of the smallest manipulability value to the largest manipulability value. The larger this ratio, the more uniform the dexterity and the higher the score. Range [0, 1]
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package reach_ros
1.4.0 (2023-10-04)
- IK Solver Update
(#30)
- Migrate utility function to reach
- Replace deprecated function
- Check that IK solver has been loaded for move group
- Run format jobs on 20.04
- Ran clang format
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.5 (2023-10-04)
- Export dependency on reach (#29)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.4 (2023-09-25)
- Python CMake Update
(#27)
- Ensure PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR is set by ament
- Replace ROS version compile definition with preprocessor check
- CI Update (#26)
- Push docker image on ref_type tag
- Added AFTER_SCRIPT to CI
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.3 (2023-09-22)
- Use YAML anchors in reach study config files to simplify (#24)
- Run CI workflow on tag push and workflow dispatch (#25)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.2 (2023-09-14)
- Updated CMake version for if STRGREATER_EQUAL command (#23)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.1 (2023-09-07)
- Updated python module install (#22)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.0 (2023-08-16)
- Add customizable color scale for visualization (#18)
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann
1.2.0 (2023-08-16)
- Added Python equivalent of the c++ reach study node
- Added a Python interface to allow usage of ROS2 plugins in Python
- Revised ROS node singleton pattern
- Remove the plugin library from ament_target_export so downstream packages cannot link against it
- Link executable against main library instead of plugin library
- Fixed typo in plugin export
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.1.0 (2023-06-13)
- Updated to REACH 1.3.0
- Clean up config/launch files
- Updated demo results
- Updated distance penalty to cap at 1.0
- Updated collision distance evaluator to optionally accept collision mesh; updated README
- Added comments about collision_mesh_frame parameter
- Fix deps install in README
- Updated to reach 1.2.0
- Updated README
- Added transformed point cloud target pose generator
- Exposed interface implementations separately from plugin library
- Fixed collision mesh frame key
- Fixed docker commit name in CI configuration
- Updated node to join executor thread properly
- Added reach plugin library name to environment variable for discovery by the plugin loader
- Updated to reach 1.1.0
- Updated to reach 0.1.1
- Merge pull request #2 from marip8/ros2 ROS2 Support
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.0.0 (2023-05-10)
- Move ROS1 components (#44)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged reach_ros at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 1.4.0 |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2025-07-09 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- mripperger
Authors
- mripperger
REACH ROS Plugins
This package contains the ROS2-based plugin implemenations of REACH kinematics, evaluation, and display interfaces

Installation
First, clone the repository into a colcon workspace
cd ~/reach_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git
cd ..
Install the dependencies
vcs import src < src/reach_ros2/dependencies.repos
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Build the repository
colcon build --symlink-install
Demo
A simple demonstration of the capability of this repository is provided in the demo sub-directory.
See the instructions for details on how to launch the demo from ROS 2 and see the Python instructions to see how you can use the Python interface to launch studies.
Usage
Use the following steps to run a reach study with a robot using the ROS1 infrastructure and plugins.
- Create any files describing your robot system required by the REACH plugins (e.g., URDF, SRDF, kinematics file, joint limits file, etc.)
- Create a mesh model of the workpiece
Note: the origin of this model should align with the kinematic base frame of the robot
- Create a point cloud of the target points on the workpiece
- This point cloud can be generated using a command line tool from PCL 1.8:
pcl_mesh_sampling <workpiece_mesh>.ply <output_cloud>.pcd -n_samples <number of samples> -leaf_size <leaf_size> -write_normals true
- Create a configuration YAML file defining the parameters of the reach study and the configuration of the interface plugins (see this demo example)
- Run the setup launch file
ros2 launch reach_ros setup.launch robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF>
- Run the reach study analysis
ros2 launch reach_ros start.launch \
robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF> \
robot_description_semantic_file:=<path_to_SRDF> \
robot_description_kinematics_file:=<path_to_kinematics.yaml> \
robot_description_joint_limits_file:=<path_to_joint_limits.yaml> \
config_file:=<config_file.yaml> \
config_name:=<arbitrary_config> \
results_dir:=<arbitrary_results_directory>
Evaluation Plugins
Manipulability
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose. Higher manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
Manipulability Scaled
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose divided by the characteristic length of the motion group. The characteristic length is computed by walking from the base link to the tip link of the motion group and summing the distances between adjacent links. Higher scaled manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
-
excluded_links(optional)- The names of links contained in the motion group that should not contribute to the characteristic length
Manipulability Ratio
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose and evaluate a score. The score is calculated as the ratio of the smallest manipulability value to the largest manipulability value. The larger this ratio, the more uniform the dexterity and the higher the score. Range [0, 1]
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package reach_ros
1.4.0 (2023-10-04)
- IK Solver Update
(#30)
- Migrate utility function to reach
- Replace deprecated function
- Check that IK solver has been loaded for move group
- Run format jobs on 20.04
- Ran clang format
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.5 (2023-10-04)
- Export dependency on reach (#29)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.4 (2023-09-25)
- Python CMake Update
(#27)
- Ensure PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR is set by ament
- Replace ROS version compile definition with preprocessor check
- CI Update (#26)
- Push docker image on ref_type tag
- Added AFTER_SCRIPT to CI
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.3 (2023-09-22)
- Use YAML anchors in reach study config files to simplify (#24)
- Run CI workflow on tag push and workflow dispatch (#25)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.2 (2023-09-14)
- Updated CMake version for if STRGREATER_EQUAL command (#23)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.1 (2023-09-07)
- Updated python module install (#22)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.0 (2023-08-16)
- Add customizable color scale for visualization (#18)
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann
1.2.0 (2023-08-16)
- Added Python equivalent of the c++ reach study node
- Added a Python interface to allow usage of ROS2 plugins in Python
- Revised ROS node singleton pattern
- Remove the plugin library from ament_target_export so downstream packages cannot link against it
- Link executable against main library instead of plugin library
- Fixed typo in plugin export
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.1.0 (2023-06-13)
- Updated to REACH 1.3.0
- Clean up config/launch files
- Updated demo results
- Updated distance penalty to cap at 1.0
- Updated collision distance evaluator to optionally accept collision mesh; updated README
- Added comments about collision_mesh_frame parameter
- Fix deps install in README
- Updated to reach 1.2.0
- Updated README
- Added transformed point cloud target pose generator
- Exposed interface implementations separately from plugin library
- Fixed collision mesh frame key
- Fixed docker commit name in CI configuration
- Updated node to join executor thread properly
- Added reach plugin library name to environment variable for discovery by the plugin loader
- Updated to reach 1.1.0
- Updated to reach 0.1.1
- Merge pull request #2 from marip8/ros2 ROS2 Support
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.0.0 (2023-05-10)
- Move ROS1 components (#44)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged reach_ros at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 1.4.0 |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2025-07-09 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- mripperger
Authors
- mripperger
REACH ROS Plugins
This package contains the ROS2-based plugin implemenations of REACH kinematics, evaluation, and display interfaces

Installation
First, clone the repository into a colcon workspace
cd ~/reach_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git
cd ..
Install the dependencies
vcs import src < src/reach_ros2/dependencies.repos
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Build the repository
colcon build --symlink-install
Demo
A simple demonstration of the capability of this repository is provided in the demo sub-directory.
See the instructions for details on how to launch the demo from ROS 2 and see the Python instructions to see how you can use the Python interface to launch studies.
Usage
Use the following steps to run a reach study with a robot using the ROS1 infrastructure and plugins.
- Create any files describing your robot system required by the REACH plugins (e.g., URDF, SRDF, kinematics file, joint limits file, etc.)
- Create a mesh model of the workpiece
Note: the origin of this model should align with the kinematic base frame of the robot
- Create a point cloud of the target points on the workpiece
- This point cloud can be generated using a command line tool from PCL 1.8:
pcl_mesh_sampling <workpiece_mesh>.ply <output_cloud>.pcd -n_samples <number of samples> -leaf_size <leaf_size> -write_normals true
- Create a configuration YAML file defining the parameters of the reach study and the configuration of the interface plugins (see this demo example)
- Run the setup launch file
ros2 launch reach_ros setup.launch robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF>
- Run the reach study analysis
ros2 launch reach_ros start.launch \
robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF> \
robot_description_semantic_file:=<path_to_SRDF> \
robot_description_kinematics_file:=<path_to_kinematics.yaml> \
robot_description_joint_limits_file:=<path_to_joint_limits.yaml> \
config_file:=<config_file.yaml> \
config_name:=<arbitrary_config> \
results_dir:=<arbitrary_results_directory>
Evaluation Plugins
Manipulability
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose. Higher manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
Manipulability Scaled
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose divided by the characteristic length of the motion group. The characteristic length is computed by walking from the base link to the tip link of the motion group and summing the distances between adjacent links. Higher scaled manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
-
excluded_links(optional)- The names of links contained in the motion group that should not contribute to the characteristic length
Manipulability Ratio
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose and evaluate a score. The score is calculated as the ratio of the smallest manipulability value to the largest manipulability value. The larger this ratio, the more uniform the dexterity and the higher the score. Range [0, 1]
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package reach_ros
1.4.0 (2023-10-04)
- IK Solver Update
(#30)
- Migrate utility function to reach
- Replace deprecated function
- Check that IK solver has been loaded for move group
- Run format jobs on 20.04
- Ran clang format
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.5 (2023-10-04)
- Export dependency on reach (#29)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.4 (2023-09-25)
- Python CMake Update
(#27)
- Ensure PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR is set by ament
- Replace ROS version compile definition with preprocessor check
- CI Update (#26)
- Push docker image on ref_type tag
- Added AFTER_SCRIPT to CI
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.3 (2023-09-22)
- Use YAML anchors in reach study config files to simplify (#24)
- Run CI workflow on tag push and workflow dispatch (#25)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.2 (2023-09-14)
- Updated CMake version for if STRGREATER_EQUAL command (#23)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.1 (2023-09-07)
- Updated python module install (#22)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.0 (2023-08-16)
- Add customizable color scale for visualization (#18)
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann
1.2.0 (2023-08-16)
- Added Python equivalent of the c++ reach study node
- Added a Python interface to allow usage of ROS2 plugins in Python
- Revised ROS node singleton pattern
- Remove the plugin library from ament_target_export so downstream packages cannot link against it
- Link executable against main library instead of plugin library
- Fixed typo in plugin export
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.1.0 (2023-06-13)
- Updated to REACH 1.3.0
- Clean up config/launch files
- Updated demo results
- Updated distance penalty to cap at 1.0
- Updated collision distance evaluator to optionally accept collision mesh; updated README
- Added comments about collision_mesh_frame parameter
- Fix deps install in README
- Updated to reach 1.2.0
- Updated README
- Added transformed point cloud target pose generator
- Exposed interface implementations separately from plugin library
- Fixed collision mesh frame key
- Fixed docker commit name in CI configuration
- Updated node to join executor thread properly
- Added reach plugin library name to environment variable for discovery by the plugin loader
- Updated to reach 1.1.0
- Updated to reach 0.1.1
- Merge pull request #2 from marip8/ros2 ROS2 Support
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.0.0 (2023-05-10)
- Move ROS1 components (#44)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged reach_ros at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 1.4.0 |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2025-07-09 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- mripperger
Authors
- mripperger
REACH ROS Plugins
This package contains the ROS2-based plugin implemenations of REACH kinematics, evaluation, and display interfaces

Installation
First, clone the repository into a colcon workspace
cd ~/reach_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git
cd ..
Install the dependencies
vcs import src < src/reach_ros2/dependencies.repos
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Build the repository
colcon build --symlink-install
Demo
A simple demonstration of the capability of this repository is provided in the demo sub-directory.
See the instructions for details on how to launch the demo from ROS 2 and see the Python instructions to see how you can use the Python interface to launch studies.
Usage
Use the following steps to run a reach study with a robot using the ROS1 infrastructure and plugins.
- Create any files describing your robot system required by the REACH plugins (e.g., URDF, SRDF, kinematics file, joint limits file, etc.)
- Create a mesh model of the workpiece
Note: the origin of this model should align with the kinematic base frame of the robot
- Create a point cloud of the target points on the workpiece
- This point cloud can be generated using a command line tool from PCL 1.8:
pcl_mesh_sampling <workpiece_mesh>.ply <output_cloud>.pcd -n_samples <number of samples> -leaf_size <leaf_size> -write_normals true
- Create a configuration YAML file defining the parameters of the reach study and the configuration of the interface plugins (see this demo example)
- Run the setup launch file
ros2 launch reach_ros setup.launch robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF>
- Run the reach study analysis
ros2 launch reach_ros start.launch \
robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF> \
robot_description_semantic_file:=<path_to_SRDF> \
robot_description_kinematics_file:=<path_to_kinematics.yaml> \
robot_description_joint_limits_file:=<path_to_joint_limits.yaml> \
config_file:=<config_file.yaml> \
config_name:=<arbitrary_config> \
results_dir:=<arbitrary_results_directory>
Evaluation Plugins
Manipulability
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose. Higher manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
Manipulability Scaled
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose divided by the characteristic length of the motion group. The characteristic length is computed by walking from the base link to the tip link of the motion group and summing the distances between adjacent links. Higher scaled manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
-
excluded_links(optional)- The names of links contained in the motion group that should not contribute to the characteristic length
Manipulability Ratio
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose and evaluate a score. The score is calculated as the ratio of the smallest manipulability value to the largest manipulability value. The larger this ratio, the more uniform the dexterity and the higher the score. Range [0, 1]
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package reach_ros
1.4.0 (2023-10-04)
- IK Solver Update
(#30)
- Migrate utility function to reach
- Replace deprecated function
- Check that IK solver has been loaded for move group
- Run format jobs on 20.04
- Ran clang format
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.5 (2023-10-04)
- Export dependency on reach (#29)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.4 (2023-09-25)
- Python CMake Update
(#27)
- Ensure PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR is set by ament
- Replace ROS version compile definition with preprocessor check
- CI Update (#26)
- Push docker image on ref_type tag
- Added AFTER_SCRIPT to CI
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.3 (2023-09-22)
- Use YAML anchors in reach study config files to simplify (#24)
- Run CI workflow on tag push and workflow dispatch (#25)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.2 (2023-09-14)
- Updated CMake version for if STRGREATER_EQUAL command (#23)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.1 (2023-09-07)
- Updated python module install (#22)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.0 (2023-08-16)
- Add customizable color scale for visualization (#18)
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann
1.2.0 (2023-08-16)
- Added Python equivalent of the c++ reach study node
- Added a Python interface to allow usage of ROS2 plugins in Python
- Revised ROS node singleton pattern
- Remove the plugin library from ament_target_export so downstream packages cannot link against it
- Link executable against main library instead of plugin library
- Fixed typo in plugin export
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.1.0 (2023-06-13)
- Updated to REACH 1.3.0
- Clean up config/launch files
- Updated demo results
- Updated distance penalty to cap at 1.0
- Updated collision distance evaluator to optionally accept collision mesh; updated README
- Added comments about collision_mesh_frame parameter
- Fix deps install in README
- Updated to reach 1.2.0
- Updated README
- Added transformed point cloud target pose generator
- Exposed interface implementations separately from plugin library
- Fixed collision mesh frame key
- Fixed docker commit name in CI configuration
- Updated node to join executor thread properly
- Added reach plugin library name to environment variable for discovery by the plugin loader
- Updated to reach 1.1.0
- Updated to reach 0.1.1
- Merge pull request #2 from marip8/ros2 ROS2 Support
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.0.0 (2023-05-10)
- Move ROS1 components (#44)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged reach_ros at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 1.4.0 |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2025-07-09 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- mripperger
Authors
- mripperger
REACH ROS Plugins
This package contains the ROS2-based plugin implemenations of REACH kinematics, evaluation, and display interfaces

Installation
First, clone the repository into a colcon workspace
cd ~/reach_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git
cd ..
Install the dependencies
vcs import src < src/reach_ros2/dependencies.repos
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Build the repository
colcon build --symlink-install
Demo
A simple demonstration of the capability of this repository is provided in the demo sub-directory.
See the instructions for details on how to launch the demo from ROS 2 and see the Python instructions to see how you can use the Python interface to launch studies.
Usage
Use the following steps to run a reach study with a robot using the ROS1 infrastructure and plugins.
- Create any files describing your robot system required by the REACH plugins (e.g., URDF, SRDF, kinematics file, joint limits file, etc.)
- Create a mesh model of the workpiece
Note: the origin of this model should align with the kinematic base frame of the robot
- Create a point cloud of the target points on the workpiece
- This point cloud can be generated using a command line tool from PCL 1.8:
pcl_mesh_sampling <workpiece_mesh>.ply <output_cloud>.pcd -n_samples <number of samples> -leaf_size <leaf_size> -write_normals true
- Create a configuration YAML file defining the parameters of the reach study and the configuration of the interface plugins (see this demo example)
- Run the setup launch file
ros2 launch reach_ros setup.launch robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF>
- Run the reach study analysis
ros2 launch reach_ros start.launch \
robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF> \
robot_description_semantic_file:=<path_to_SRDF> \
robot_description_kinematics_file:=<path_to_kinematics.yaml> \
robot_description_joint_limits_file:=<path_to_joint_limits.yaml> \
config_file:=<config_file.yaml> \
config_name:=<arbitrary_config> \
results_dir:=<arbitrary_results_directory>
Evaluation Plugins
Manipulability
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose. Higher manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
Manipulability Scaled
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose divided by the characteristic length of the motion group. The characteristic length is computed by walking from the base link to the tip link of the motion group and summing the distances between adjacent links. Higher scaled manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
-
excluded_links(optional)- The names of links contained in the motion group that should not contribute to the characteristic length
Manipulability Ratio
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose and evaluate a score. The score is calculated as the ratio of the smallest manipulability value to the largest manipulability value. The larger this ratio, the more uniform the dexterity and the higher the score. Range [0, 1]
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package reach_ros
1.4.0 (2023-10-04)
- IK Solver Update
(#30)
- Migrate utility function to reach
- Replace deprecated function
- Check that IK solver has been loaded for move group
- Run format jobs on 20.04
- Ran clang format
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.5 (2023-10-04)
- Export dependency on reach (#29)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.4 (2023-09-25)
- Python CMake Update
(#27)
- Ensure PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR is set by ament
- Replace ROS version compile definition with preprocessor check
- CI Update (#26)
- Push docker image on ref_type tag
- Added AFTER_SCRIPT to CI
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.3 (2023-09-22)
- Use YAML anchors in reach study config files to simplify (#24)
- Run CI workflow on tag push and workflow dispatch (#25)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.2 (2023-09-14)
- Updated CMake version for if STRGREATER_EQUAL command (#23)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.1 (2023-09-07)
- Updated python module install (#22)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.0 (2023-08-16)
- Add customizable color scale for visualization (#18)
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann
1.2.0 (2023-08-16)
- Added Python equivalent of the c++ reach study node
- Added a Python interface to allow usage of ROS2 plugins in Python
- Revised ROS node singleton pattern
- Remove the plugin library from ament_target_export so downstream packages cannot link against it
- Link executable against main library instead of plugin library
- Fixed typo in plugin export
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.1.0 (2023-06-13)
- Updated to REACH 1.3.0
- Clean up config/launch files
- Updated demo results
- Updated distance penalty to cap at 1.0
- Updated collision distance evaluator to optionally accept collision mesh; updated README
- Added comments about collision_mesh_frame parameter
- Fix deps install in README
- Updated to reach 1.2.0
- Updated README
- Added transformed point cloud target pose generator
- Exposed interface implementations separately from plugin library
- Fixed collision mesh frame key
- Fixed docker commit name in CI configuration
- Updated node to join executor thread properly
- Added reach plugin library name to environment variable for discovery by the plugin loader
- Updated to reach 1.1.0
- Updated to reach 0.1.1
- Merge pull request #2 from marip8/ros2 ROS2 Support
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.0.0 (2023-05-10)
- Move ROS1 components (#44)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged reach_ros at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 1.4.0 |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2025-07-09 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- mripperger
Authors
- mripperger
REACH ROS Plugins
This package contains the ROS2-based plugin implemenations of REACH kinematics, evaluation, and display interfaces

Installation
First, clone the repository into a colcon workspace
cd ~/reach_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git
cd ..
Install the dependencies
vcs import src < src/reach_ros2/dependencies.repos
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Build the repository
colcon build --symlink-install
Demo
A simple demonstration of the capability of this repository is provided in the demo sub-directory.
See the instructions for details on how to launch the demo from ROS 2 and see the Python instructions to see how you can use the Python interface to launch studies.
Usage
Use the following steps to run a reach study with a robot using the ROS1 infrastructure and plugins.
- Create any files describing your robot system required by the REACH plugins (e.g., URDF, SRDF, kinematics file, joint limits file, etc.)
- Create a mesh model of the workpiece
Note: the origin of this model should align with the kinematic base frame of the robot
- Create a point cloud of the target points on the workpiece
- This point cloud can be generated using a command line tool from PCL 1.8:
pcl_mesh_sampling <workpiece_mesh>.ply <output_cloud>.pcd -n_samples <number of samples> -leaf_size <leaf_size> -write_normals true
- Create a configuration YAML file defining the parameters of the reach study and the configuration of the interface plugins (see this demo example)
- Run the setup launch file
ros2 launch reach_ros setup.launch robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF>
- Run the reach study analysis
ros2 launch reach_ros start.launch \
robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF> \
robot_description_semantic_file:=<path_to_SRDF> \
robot_description_kinematics_file:=<path_to_kinematics.yaml> \
robot_description_joint_limits_file:=<path_to_joint_limits.yaml> \
config_file:=<config_file.yaml> \
config_name:=<arbitrary_config> \
results_dir:=<arbitrary_results_directory>
Evaluation Plugins
Manipulability
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose. Higher manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
Manipulability Scaled
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose divided by the characteristic length of the motion group. The characteristic length is computed by walking from the base link to the tip link of the motion group and summing the distances between adjacent links. Higher scaled manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
-
excluded_links(optional)- The names of links contained in the motion group that should not contribute to the characteristic length
Manipulability Ratio
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose and evaluate a score. The score is calculated as the ratio of the smallest manipulability value to the largest manipulability value. The larger this ratio, the more uniform the dexterity and the higher the score. Range [0, 1]
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package reach_ros
1.4.0 (2023-10-04)
- IK Solver Update
(#30)
- Migrate utility function to reach
- Replace deprecated function
- Check that IK solver has been loaded for move group
- Run format jobs on 20.04
- Ran clang format
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.5 (2023-10-04)
- Export dependency on reach (#29)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.4 (2023-09-25)
- Python CMake Update
(#27)
- Ensure PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR is set by ament
- Replace ROS version compile definition with preprocessor check
- CI Update (#26)
- Push docker image on ref_type tag
- Added AFTER_SCRIPT to CI
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.3 (2023-09-22)
- Use YAML anchors in reach study config files to simplify (#24)
- Run CI workflow on tag push and workflow dispatch (#25)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.2 (2023-09-14)
- Updated CMake version for if STRGREATER_EQUAL command (#23)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.1 (2023-09-07)
- Updated python module install (#22)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.0 (2023-08-16)
- Add customizable color scale for visualization (#18)
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann
1.2.0 (2023-08-16)
- Added Python equivalent of the c++ reach study node
- Added a Python interface to allow usage of ROS2 plugins in Python
- Revised ROS node singleton pattern
- Remove the plugin library from ament_target_export so downstream packages cannot link against it
- Link executable against main library instead of plugin library
- Fixed typo in plugin export
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.1.0 (2023-06-13)
- Updated to REACH 1.3.0
- Clean up config/launch files
- Updated demo results
- Updated distance penalty to cap at 1.0
- Updated collision distance evaluator to optionally accept collision mesh; updated README
- Added comments about collision_mesh_frame parameter
- Fix deps install in README
- Updated to reach 1.2.0
- Updated README
- Added transformed point cloud target pose generator
- Exposed interface implementations separately from plugin library
- Fixed collision mesh frame key
- Fixed docker commit name in CI configuration
- Updated node to join executor thread properly
- Added reach plugin library name to environment variable for discovery by the plugin loader
- Updated to reach 1.1.0
- Updated to reach 0.1.1
- Merge pull request #2 from marip8/ros2 ROS2 Support
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.0.0 (2023-05-10)
- Move ROS1 components (#44)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged reach_ros at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 1.4.0 |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2025-07-09 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- mripperger
Authors
- mripperger
REACH ROS Plugins
This package contains the ROS2-based plugin implemenations of REACH kinematics, evaluation, and display interfaces

Installation
First, clone the repository into a colcon workspace
cd ~/reach_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git
cd ..
Install the dependencies
vcs import src < src/reach_ros2/dependencies.repos
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Build the repository
colcon build --symlink-install
Demo
A simple demonstration of the capability of this repository is provided in the demo sub-directory.
See the instructions for details on how to launch the demo from ROS 2 and see the Python instructions to see how you can use the Python interface to launch studies.
Usage
Use the following steps to run a reach study with a robot using the ROS1 infrastructure and plugins.
- Create any files describing your robot system required by the REACH plugins (e.g., URDF, SRDF, kinematics file, joint limits file, etc.)
- Create a mesh model of the workpiece
Note: the origin of this model should align with the kinematic base frame of the robot
- Create a point cloud of the target points on the workpiece
- This point cloud can be generated using a command line tool from PCL 1.8:
pcl_mesh_sampling <workpiece_mesh>.ply <output_cloud>.pcd -n_samples <number of samples> -leaf_size <leaf_size> -write_normals true
- Create a configuration YAML file defining the parameters of the reach study and the configuration of the interface plugins (see this demo example)
- Run the setup launch file
ros2 launch reach_ros setup.launch robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF>
- Run the reach study analysis
ros2 launch reach_ros start.launch \
robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF> \
robot_description_semantic_file:=<path_to_SRDF> \
robot_description_kinematics_file:=<path_to_kinematics.yaml> \
robot_description_joint_limits_file:=<path_to_joint_limits.yaml> \
config_file:=<config_file.yaml> \
config_name:=<arbitrary_config> \
results_dir:=<arbitrary_results_directory>
Evaluation Plugins
Manipulability
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose. Higher manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
Manipulability Scaled
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose divided by the characteristic length of the motion group. The characteristic length is computed by walking from the base link to the tip link of the motion group and summing the distances between adjacent links. Higher scaled manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
-
excluded_links(optional)- The names of links contained in the motion group that should not contribute to the characteristic length
Manipulability Ratio
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose and evaluate a score. The score is calculated as the ratio of the smallest manipulability value to the largest manipulability value. The larger this ratio, the more uniform the dexterity and the higher the score. Range [0, 1]
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package reach_ros
1.4.0 (2023-10-04)
- IK Solver Update
(#30)
- Migrate utility function to reach
- Replace deprecated function
- Check that IK solver has been loaded for move group
- Run format jobs on 20.04
- Ran clang format
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.5 (2023-10-04)
- Export dependency on reach (#29)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.4 (2023-09-25)
- Python CMake Update
(#27)
- Ensure PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR is set by ament
- Replace ROS version compile definition with preprocessor check
- CI Update (#26)
- Push docker image on ref_type tag
- Added AFTER_SCRIPT to CI
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.3 (2023-09-22)
- Use YAML anchors in reach study config files to simplify (#24)
- Run CI workflow on tag push and workflow dispatch (#25)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.2 (2023-09-14)
- Updated CMake version for if STRGREATER_EQUAL command (#23)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.1 (2023-09-07)
- Updated python module install (#22)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.0 (2023-08-16)
- Add customizable color scale for visualization (#18)
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann
1.2.0 (2023-08-16)
- Added Python equivalent of the c++ reach study node
- Added a Python interface to allow usage of ROS2 plugins in Python
- Revised ROS node singleton pattern
- Remove the plugin library from ament_target_export so downstream packages cannot link against it
- Link executable against main library instead of plugin library
- Fixed typo in plugin export
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.1.0 (2023-06-13)
- Updated to REACH 1.3.0
- Clean up config/launch files
- Updated demo results
- Updated distance penalty to cap at 1.0
- Updated collision distance evaluator to optionally accept collision mesh; updated README
- Added comments about collision_mesh_frame parameter
- Fix deps install in README
- Updated to reach 1.2.0
- Updated README
- Added transformed point cloud target pose generator
- Exposed interface implementations separately from plugin library
- Fixed collision mesh frame key
- Fixed docker commit name in CI configuration
- Updated node to join executor thread properly
- Added reach plugin library name to environment variable for discovery by the plugin loader
- Updated to reach 1.1.0
- Updated to reach 0.1.1
- Merge pull request #2 from marip8/ros2 ROS2 Support
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.0.0 (2023-05-10)
- Move ROS1 components (#44)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged reach_ros at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 1.4.0 |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2025-07-09 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- mripperger
Authors
- mripperger
REACH ROS Plugins
This package contains the ROS2-based plugin implemenations of REACH kinematics, evaluation, and display interfaces

Installation
First, clone the repository into a colcon workspace
cd ~/reach_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git
cd ..
Install the dependencies
vcs import src < src/reach_ros2/dependencies.repos
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Build the repository
colcon build --symlink-install
Demo
A simple demonstration of the capability of this repository is provided in the demo sub-directory.
See the instructions for details on how to launch the demo from ROS 2 and see the Python instructions to see how you can use the Python interface to launch studies.
Usage
Use the following steps to run a reach study with a robot using the ROS1 infrastructure and plugins.
- Create any files describing your robot system required by the REACH plugins (e.g., URDF, SRDF, kinematics file, joint limits file, etc.)
- Create a mesh model of the workpiece
Note: the origin of this model should align with the kinematic base frame of the robot
- Create a point cloud of the target points on the workpiece
- This point cloud can be generated using a command line tool from PCL 1.8:
pcl_mesh_sampling <workpiece_mesh>.ply <output_cloud>.pcd -n_samples <number of samples> -leaf_size <leaf_size> -write_normals true
- Create a configuration YAML file defining the parameters of the reach study and the configuration of the interface plugins (see this demo example)
- Run the setup launch file
ros2 launch reach_ros setup.launch robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF>
- Run the reach study analysis
ros2 launch reach_ros start.launch \
robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF> \
robot_description_semantic_file:=<path_to_SRDF> \
robot_description_kinematics_file:=<path_to_kinematics.yaml> \
robot_description_joint_limits_file:=<path_to_joint_limits.yaml> \
config_file:=<config_file.yaml> \
config_name:=<arbitrary_config> \
results_dir:=<arbitrary_results_directory>
Evaluation Plugins
Manipulability
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose. Higher manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
Manipulability Scaled
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose divided by the characteristic length of the motion group. The characteristic length is computed by walking from the base link to the tip link of the motion group and summing the distances between adjacent links. Higher scaled manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
-
excluded_links(optional)- The names of links contained in the motion group that should not contribute to the characteristic length
Manipulability Ratio
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose and evaluate a score. The score is calculated as the ratio of the smallest manipulability value to the largest manipulability value. The larger this ratio, the more uniform the dexterity and the higher the score. Range [0, 1]
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package reach_ros
1.4.0 (2023-10-04)
- IK Solver Update
(#30)
- Migrate utility function to reach
- Replace deprecated function
- Check that IK solver has been loaded for move group
- Run format jobs on 20.04
- Ran clang format
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.5 (2023-10-04)
- Export dependency on reach (#29)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.4 (2023-09-25)
- Python CMake Update
(#27)
- Ensure PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR is set by ament
- Replace ROS version compile definition with preprocessor check
- CI Update (#26)
- Push docker image on ref_type tag
- Added AFTER_SCRIPT to CI
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.3 (2023-09-22)
- Use YAML anchors in reach study config files to simplify (#24)
- Run CI workflow on tag push and workflow dispatch (#25)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.2 (2023-09-14)
- Updated CMake version for if STRGREATER_EQUAL command (#23)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.1 (2023-09-07)
- Updated python module install (#22)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.0 (2023-08-16)
- Add customizable color scale for visualization (#18)
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann
1.2.0 (2023-08-16)
- Added Python equivalent of the c++ reach study node
- Added a Python interface to allow usage of ROS2 plugins in Python
- Revised ROS node singleton pattern
- Remove the plugin library from ament_target_export so downstream packages cannot link against it
- Link executable against main library instead of plugin library
- Fixed typo in plugin export
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.1.0 (2023-06-13)
- Updated to REACH 1.3.0
- Clean up config/launch files
- Updated demo results
- Updated distance penalty to cap at 1.0
- Updated collision distance evaluator to optionally accept collision mesh; updated README
- Added comments about collision_mesh_frame parameter
- Fix deps install in README
- Updated to reach 1.2.0
- Updated README
- Added transformed point cloud target pose generator
- Exposed interface implementations separately from plugin library
- Fixed collision mesh frame key
- Fixed docker commit name in CI configuration
- Updated node to join executor thread properly
- Added reach plugin library name to environment variable for discovery by the plugin loader
- Updated to reach 1.1.0
- Updated to reach 0.1.1
- Merge pull request #2 from marip8/ros2 ROS2 Support
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.0.0 (2023-05-10)
- Move ROS1 components (#44)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged reach_ros at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 1.4.0 |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2025-07-09 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- mripperger
Authors
- mripperger
REACH ROS Plugins
This package contains the ROS2-based plugin implemenations of REACH kinematics, evaluation, and display interfaces

Installation
First, clone the repository into a colcon workspace
cd ~/reach_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros2.git
cd ..
Install the dependencies
vcs import src < src/reach_ros2/dependencies.repos
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Build the repository
colcon build --symlink-install
Demo
A simple demonstration of the capability of this repository is provided in the demo sub-directory.
See the instructions for details on how to launch the demo from ROS 2 and see the Python instructions to see how you can use the Python interface to launch studies.
Usage
Use the following steps to run a reach study with a robot using the ROS1 infrastructure and plugins.
- Create any files describing your robot system required by the REACH plugins (e.g., URDF, SRDF, kinematics file, joint limits file, etc.)
- Create a mesh model of the workpiece
Note: the origin of this model should align with the kinematic base frame of the robot
- Create a point cloud of the target points on the workpiece
- This point cloud can be generated using a command line tool from PCL 1.8:
pcl_mesh_sampling <workpiece_mesh>.ply <output_cloud>.pcd -n_samples <number of samples> -leaf_size <leaf_size> -write_normals true
- Create a configuration YAML file defining the parameters of the reach study and the configuration of the interface plugins (see this demo example)
- Run the setup launch file
ros2 launch reach_ros setup.launch robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF>
- Run the reach study analysis
ros2 launch reach_ros start.launch \
robot_description_file:=<path_to_URDF> \
robot_description_semantic_file:=<path_to_SRDF> \
robot_description_kinematics_file:=<path_to_kinematics.yaml> \
robot_description_joint_limits_file:=<path_to_joint_limits.yaml> \
config_file:=<config_file.yaml> \
config_name:=<arbitrary_config> \
results_dir:=<arbitrary_results_directory>
Evaluation Plugins
Manipulability
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose. Higher manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
Manipulability Scaled
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose divided by the characteristic length of the motion group. The characteristic length is computed by walking from the base link to the tip link of the motion group and summing the distances between adjacent links. Higher scaled manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
-
excluded_links(optional)- The names of links contained in the motion group that should not contribute to the characteristic length
Manipulability Ratio
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose and evaluate a score. The score is calculated as the ratio of the smallest manipulability value to the largest manipulability value. The larger this ratio, the more uniform the dexterity and the higher the score. Range [0, 1]
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package reach_ros
1.4.0 (2023-10-04)
- IK Solver Update
(#30)
- Migrate utility function to reach
- Replace deprecated function
- Check that IK solver has been loaded for move group
- Run format jobs on 20.04
- Ran clang format
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.5 (2023-10-04)
- Export dependency on reach (#29)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.4 (2023-09-25)
- Python CMake Update
(#27)
- Ensure PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR is set by ament
- Replace ROS version compile definition with preprocessor check
- CI Update (#26)
- Push docker image on ref_type tag
- Added AFTER_SCRIPT to CI
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.3 (2023-09-22)
- Use YAML anchors in reach study config files to simplify (#24)
- Run CI workflow on tag push and workflow dispatch (#25)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.2 (2023-09-14)
- Updated CMake version for if STRGREATER_EQUAL command (#23)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.1 (2023-09-07)
- Updated python module install (#22)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.3.0 (2023-08-16)
- Add customizable color scale for visualization (#18)
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann
1.2.0 (2023-08-16)
- Added Python equivalent of the c++ reach study node
- Added a Python interface to allow usage of ROS2 plugins in Python
- Revised ROS node singleton pattern
- Remove the plugin library from ament_target_export so downstream packages cannot link against it
- Link executable against main library instead of plugin library
- Fixed typo in plugin export
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.1.0 (2023-06-13)
- Updated to REACH 1.3.0
- Clean up config/launch files
- Updated demo results
- Updated distance penalty to cap at 1.0
- Updated collision distance evaluator to optionally accept collision mesh; updated README
- Added comments about collision_mesh_frame parameter
- Fix deps install in README
- Updated to reach 1.2.0
- Updated README
- Added transformed point cloud target pose generator
- Exposed interface implementations separately from plugin library
- Fixed collision mesh frame key
- Fixed docker commit name in CI configuration
- Updated node to join executor thread properly
- Added reach plugin library name to environment variable for discovery by the plugin loader
- Updated to reach 1.1.0
- Updated to reach 0.1.1
- Merge pull request #2 from marip8/ros2 ROS2 Support
- Contributors: Marc Bestmann, Michael Ripperger
1.0.0 (2023-05-10)
- Move ROS1 components (#44)
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged reach_ros at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 1.1.4 |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Build type | CATKIN |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2024-06-15 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- mripperger
Authors
- mripperger
REACH ROS Plugins
This package contains the ROS1-based plugin implemenations of REACH kinematics, evaluation, and display interfaces
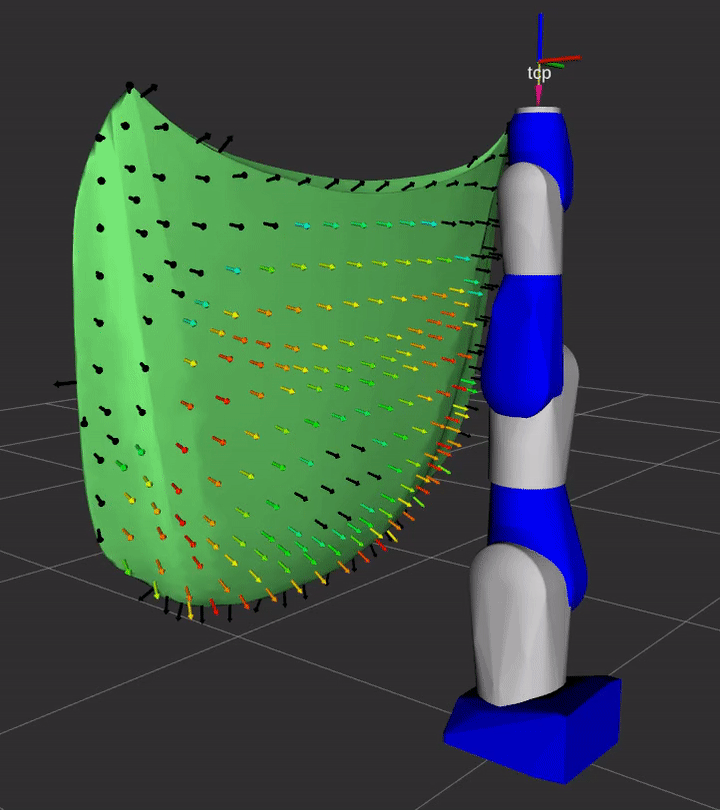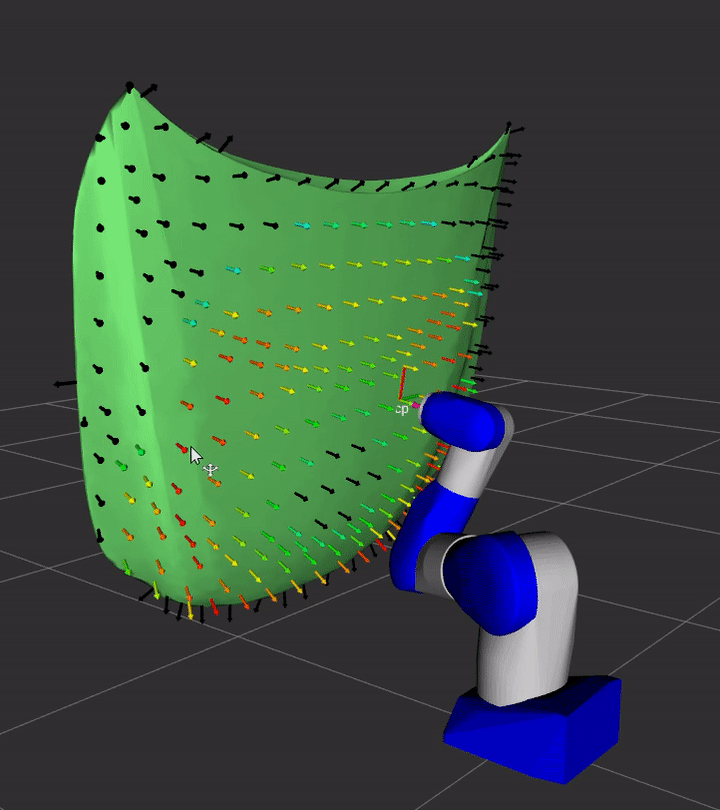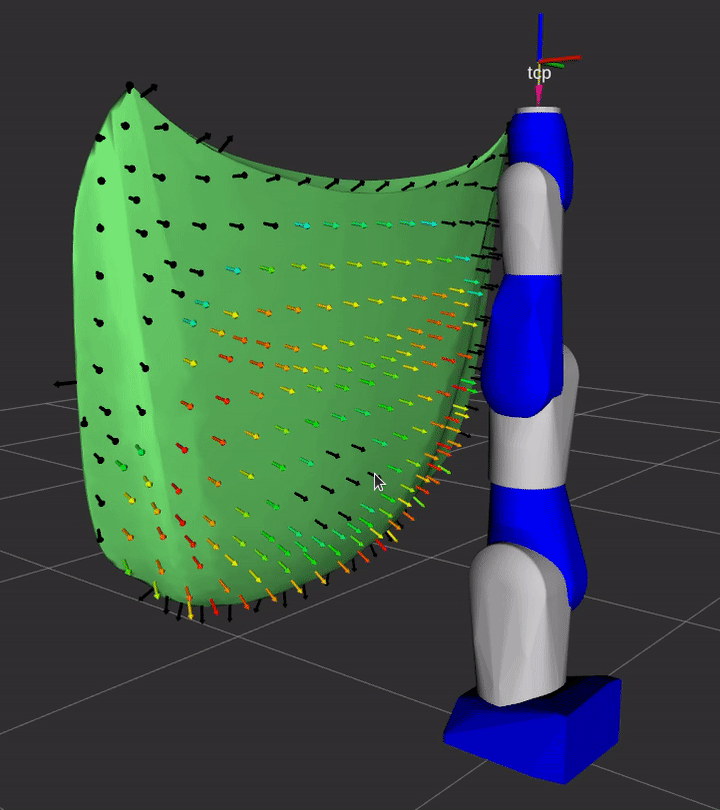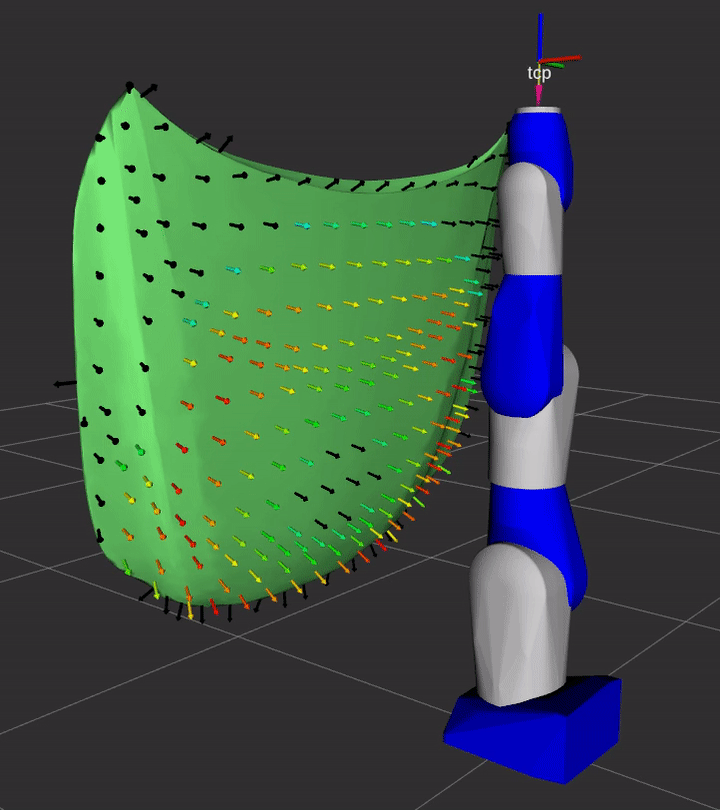
Installation
First, clone the repository into a catkin workspace
cd ~/reach_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/reach_ros.git
cd ..
Install the dependencies
vcs import src < src/reach_ros/dependencies.repos
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Build the repository
catkin build
Demo
A simple demonstration of the capability of this repository is provided in the demo sub-directory.
See the instructions for details on how to run the demo.
Usage
Use the following steps to run a reach study with a robot using the ROS1 infrastructure and plugins.
- Create a URDF of your robot system
- Create a launch file to load the URDF, SRDF, and other required parameters (e.g. related to kinematics, joint, limits) to the parameter server (see this demo example file)
- Create a mesh model of the workpiece
Note: the origin of this model should align with the kinematic base frame of the robot
- Create a point cloud of the target points on the workpiece
- This point cloud can be generated using a command line tool from PCL 1.8:
pcl_mesh_sampling <workpiece_mesh>.ply <output_cloud>.pcd -n_samples <number of samples> -leaf_size <leaf_size> -write_normals true
- Create a configuration YAML file defining the parameters of the reach study and the configuration of the interface plugins (see this demo example)
- Run the setup launch file
roslaunch reach_ros setup.launch robot:=<load_robot_parameters>.launch
- Run the reach study analysis
roslaunch reach_ros start.launch config_file:=<config_file.yaml> config_name:=<arbitrary_config>
Evaluation Plugins
Manipulability
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose. Higher manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
Manipulability Scaled
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose divided by the characteristic length of the motion group. The characteristic length is computed by walking from the base link to the tip link of the motion group and summing the distances between adjacent links. Higher scaled manipulability results in a higher pose score. Range: [0, inf)
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
-
excluded_links(optional)- The names of links contained in the motion group that should not contribute to the characteristic length
Manipulability Ratio
This plugin uses MoveIt! to calculate the manipulability of a robot pose and evaluate a score. The score is calculated as the ratio of the smallest manipulability value to the largest manipulability value. The larger this ratio, the more uniform the dexterity and the higher the score. Range [0, 1]
Parameters:
-
planning_group- The name of the planning group with which to evaluate the manipulability of a given robot pose
-
jacobian_row_subset(optional)- The indices of the rows of the Jacobian to use when evaluating the manipulability. The row indices should be on [0, 6) and correspond to the output space [x, y, z, rx, ry, rz]
- Ex.
jacobian_row_subset: [0, 1, 2] # position manipulability only
Distance Penalty
This plugin uses the MoveIt! collision environment to calculate the distance to closest collision for a robot pose. That distance value is then used to score the robot pose. Larger distance to closest collision
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package reach_ros
1.1.4 (2024-06-15)
- Merge pull request #20 from marip8/fix/visualization-speed Fixed speed of loading interactive markers
- Fixed speed of loading interactive markers
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.1.3 (2024-06-10)
- Take self collisions into account in distance_penalty
- Run format jobs on 20.04
- Check that IK solver has been loaded for move group
- Replace deprecated function
- Migrate utility function to reach
- Contributors: Iñigo Moreno, Michael Ripperger
1.1.2 (2023-09-22)
- Merge pull request #15 from ros-industrial/update/demo-yaml Use YAML anchors in reach study config files to simplify
- Merge pull request #14 from ros-industrial/update/ci Updated CI to run on tag push and workflow dispatch
- Updated CI to run on tag push and workflow dispatch
- Use YAML anchors in reach study config files to simplify
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.1.1 (2023-09-07)
- Merge pull request #10 from ros-industrial/updates Minor Updates
- Use RICB in CMakeLists
- Update function to pass by reference
- Export reach_ros library target
- Merge pull request #9 from ros-industrial/fix/plugin Fixed typo in plugin export
- Fixed typo in plugin export
- Contributors: Michael Ripperger
1.1.0 (2023-06-13)
- Merge pull request #8 from marip8/update/reach Updated to REACH 1.3.0
- Updated to REACH 1.3.0
- Merge pull request #7 from marip8/update/collision-distance-eval Collision distance evaluator update
- Regenerated demo results
- Clipped collision distance penalty cost on [0, 1]
- Updated collision distance penalty to optionally include collision mesh; updated README
- Merge pull request #6 from marip8/update/README README updates
- Added installation instructions
- Added documentation for the collision_mesh_frame parameter
- Merge pull request #5 from marip8/updates Updates
- Updated to reach 1.2.0
- Updated the README
- Added transformed point cloud target pose generator
- Exposed plugins in separate library
- Fixed collision mesh frame key
- Merge pull request #4 from marip8/updates Updates
- Set environment variable so plugin loader can find reach_ros plugins
- Fixed tf2 issue
- Merge pull request #3 from marip8/update/deps Updated to reach 0.1.1
- Updated to reach 1.1.0
- Merge pull request #2 from marip8/update/changelog Cleared changelog
- Cleared changelog
- Merge pull request #1 from marip8/update Replace eigen_conversions dependency with tf2
- Replace eigen_conversions dependency with tf2
- Removed the Python tests
- Added reach to the dependencies.repos
- Install the demo files
- Updated README to include documentation about demo and usage
- Added GIF to README
- Flattened reach_ros directory
- Removed docs directory
- Removed reach directory
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
- demo/config/robot.launch
- launch/setup.launch
-
- rviz [default: true] — Launch Rviz
- robot — Launch file that loads URDF, SRDF, and other kinematics-related parameters
- launch/start.launch
-
- config_file — YAML configuration file for the reach study
- config_name [default: reach_study] — Arbitrary configuration name for the reach study
- results_dir [default: /tmp] — Location in which reach study results will be saved

