
|
raspimouse_ros2_examples package from raspimouse_ros2_examples reporaspimouse_ros2_examples |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 2.2.1 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble-devel |
| Last Updated | 2024-08-28 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- RT Corporation
Authors
- ShotaAk
- Daisuke Sato
- Shuhei Kozasa
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse.
ROS1 examples is here.
To run on Gazebo, click here.
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Supported ROS 2 distributions
- Foxy
- Humble (This branch)
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 22.04
- https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO-devel https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see LICENSE for details.
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
Launch nodes with the following command:
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
This picture shows the default key configuration.
To use Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710, set the input mode to D (DirectInput Mode).
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package raspimouse_ros2_examples
2.2.1 (2024-08-28)
- サービスクライアントでexecutorを使用しない (#59)
- SubscriberとService Clientに別々のcallback_groupを設定 (#58)
- Contributors: ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.2.0 (2024-03-05)
- READMEにSLAM&Navigationパッケージの案内を追加 (#53)
- Camera_FollowerクラスをCameraFollowerに変更 (#52)
- Update camera line follower: Set motor power with switch input. Add area_threthold param. (#51)
- Add velocity parameters for camera_line_follower (#50)
- カメラライントレースを修正 (#49)
- Change threthold of line detection
- Add usb_cam dependency (#48)
- RGBカメラによるライントレースの実装 (#47)
- リリースのためにCHANGELOG.rstとpackage.xmlを更新 (#45)
- Contributors: Shota Aoki, ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.1.0 (2023-11-07)
- READMEにGazeboでも実行できることを追記 (#44)
- object_trackingにおいて画像トピックをサブスクライブするように変更 (#43)
- Contributors: YusukeKato
2.0.0 (2023-08-03)
- Humble対応 (#41)
- Contributors: Shuhei Kozasa
1.0.0 (2022-07-28)
- Update map command (#38)
- Adds config file for DUALSHOCK4 (#36)
- Update README for foxy-devel (#34)
- Remove node_ prefix from launch files (#33)
- Use ament_export_targets instead of ament_export_interfaces. (#31)
- Remove dashing check from CI (#32)
- Update rviz config to show scan and graph topics (#29)
- Add descriptions to READMEs for use_pulse_counters param settings (#28)
- Use joy_linux instead of joy (#27)
- Update CI to support ROS Foxy (#26)
- Update package.xml (#25)
- Install raspimouse2 and imu packages via rosdep command (#22)
- Add rt_usb_9axisimu_driver dependency to package.xml (#21)
- Add direction control example (#18)
- Use images of rt-net/images repo. (#17)
- Add lidar example (#14)
- Turn on/off leds with joy inputs (#15)
- Update Gamepad F710 usage in README (#13)
- Use multi threads in the object tracking example to stabilize the tracking (#11)
- update video link (#12)
- Merge teleop_joy launch files into one file. (#10)
- Add line follower examples (#9)
- Add object tracking sample (#8)
- Rename launch files (#7)
- Refactoring (#6)
- Support remote control
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
| Name |
|---|
| libopencv-dev |
| v4l-utils |
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_slam |
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged raspimouse_ros2_examples at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
raspimouse_ros2_examples package from raspimouse_ros2_examples reporaspimouse_ros2_examples |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 3.0.0 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | jazzy |
| Last Updated | 2024-11-25 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- RT Corporation
Authors
- ShotaAk
- Daisuke Sato
- Shuhei Kozasa
- Yusuke Kato
- Kazushi Kurasawa
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse.
ROS1 examples is here.
To run on Gazebo, click here.
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Supported ROS 2 distributions
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 24.04
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see LICENSE for details.
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
Launch nodes with the following command:
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
This picture shows the default key configuration.
To use Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710, set the input mode to D (DirectInput Mode).
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package raspimouse_ros2_examples
3.0.0 (2024-11-25) -----------* Support ROS 2 Jazzy (#62) * Replaced "Twist" with "TwistStamped" * Contributors: Kazushi Kurasawa, YusukeKato
2.2.1 (2024-08-28)
- サービスクライアントでexecutorを使用しない (#59)
- SubscriberとService Clientに別々のcallback_groupを設定 (#58)
- Contributors: ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.2.0 (2024-03-05)
- READMEにSLAM&Navigationパッケージの案内を追加 (#53)
- Camera_FollowerクラスをCameraFollowerに変更 (#52)
- Update camera line follower: Set motor power with switch input. Add area_threthold param. (#51)
- Add velocity parameters for camera_line_follower (#50)
- カメラライントレースを修正 (#49)
- Change threthold of line detection
- Add usb_cam dependency (#48)
- RGBカメラによるライントレースの実装 (#47)
- リリースのためにCHANGELOG.rstとpackage.xmlを更新 (#45)
- Contributors: Shota Aoki, ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.1.0 (2023-11-07)
- READMEにGazeboでも実行できることを追記 (#44)
- object_trackingにおいて画像トピックをサブスクライブするように変更 (#43)
- Contributors: YusukeKato
2.0.0 (2023-08-03)
- Humble対応 (#41)
- Contributors: Shuhei Kozasa
1.0.0 (2022-07-28)
- Update map command (#38)
- Adds config file for DUALSHOCK4 (#36)
- Update README for foxy-devel (#34)
- Remove node_ prefix from launch files (#33)
- Use ament_export_targets instead of ament_export_interfaces. (#31)
- Remove dashing check from CI (#32)
- Update rviz config to show scan and graph topics (#29)
- Add descriptions to READMEs for use_pulse_counters param settings (#28)
- Use joy_linux instead of joy (#27)
- Update CI to support ROS Foxy (#26)
- Update package.xml (#25)
- Install raspimouse2 and imu packages via rosdep command (#22)
- Add rt_usb_9axisimu_driver dependency to package.xml (#21)
- Add direction control example (#18)
- Use images of rt-net/images repo. (#17)
- Add lidar example (#14)
- Turn on/off leds with joy inputs (#15)
- Update Gamepad F710 usage in README (#13)
- Use multi threads in the object tracking example to stabilize the tracking (#11)
- update video link (#12)
- Merge teleop_joy launch files into one file. (#10)
- Add line follower examples (#9)
- Add object tracking sample (#8)
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
| Name |
|---|
| libopencv-dev |
| v4l-utils |
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_slam |
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged raspimouse_ros2_examples at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
raspimouse_ros2_examples package from raspimouse_ros2_examples reporaspimouse_ros2_examples |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 2.2.1 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble-devel |
| Last Updated | 2024-08-28 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- RT Corporation
Authors
- ShotaAk
- Daisuke Sato
- Shuhei Kozasa
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse.
ROS1 examples is here.
To run on Gazebo, click here.
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Supported ROS 2 distributions
- Foxy
- Humble (This branch)
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 22.04
- https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO-devel https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see LICENSE for details.
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
Launch nodes with the following command:
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
This picture shows the default key configuration.
To use Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710, set the input mode to D (DirectInput Mode).
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package raspimouse_ros2_examples
2.2.1 (2024-08-28)
- サービスクライアントでexecutorを使用しない (#59)
- SubscriberとService Clientに別々のcallback_groupを設定 (#58)
- Contributors: ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.2.0 (2024-03-05)
- READMEにSLAM&Navigationパッケージの案内を追加 (#53)
- Camera_FollowerクラスをCameraFollowerに変更 (#52)
- Update camera line follower: Set motor power with switch input. Add area_threthold param. (#51)
- Add velocity parameters for camera_line_follower (#50)
- カメラライントレースを修正 (#49)
- Change threthold of line detection
- Add usb_cam dependency (#48)
- RGBカメラによるライントレースの実装 (#47)
- リリースのためにCHANGELOG.rstとpackage.xmlを更新 (#45)
- Contributors: Shota Aoki, ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.1.0 (2023-11-07)
- READMEにGazeboでも実行できることを追記 (#44)
- object_trackingにおいて画像トピックをサブスクライブするように変更 (#43)
- Contributors: YusukeKato
2.0.0 (2023-08-03)
- Humble対応 (#41)
- Contributors: Shuhei Kozasa
1.0.0 (2022-07-28)
- Update map command (#38)
- Adds config file for DUALSHOCK4 (#36)
- Update README for foxy-devel (#34)
- Remove node_ prefix from launch files (#33)
- Use ament_export_targets instead of ament_export_interfaces. (#31)
- Remove dashing check from CI (#32)
- Update rviz config to show scan and graph topics (#29)
- Add descriptions to READMEs for use_pulse_counters param settings (#28)
- Use joy_linux instead of joy (#27)
- Update CI to support ROS Foxy (#26)
- Update package.xml (#25)
- Install raspimouse2 and imu packages via rosdep command (#22)
- Add rt_usb_9axisimu_driver dependency to package.xml (#21)
- Add direction control example (#18)
- Use images of rt-net/images repo. (#17)
- Add lidar example (#14)
- Turn on/off leds with joy inputs (#15)
- Update Gamepad F710 usage in README (#13)
- Use multi threads in the object tracking example to stabilize the tracking (#11)
- update video link (#12)
- Merge teleop_joy launch files into one file. (#10)
- Add line follower examples (#9)
- Add object tracking sample (#8)
- Rename launch files (#7)
- Refactoring (#6)
- Support remote control
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
| Name |
|---|
| libopencv-dev |
| v4l-utils |
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_slam |
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged raspimouse_ros2_examples at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
raspimouse_ros2_examples package from raspimouse_ros2_examples reporaspimouse_ros2_examples |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 2.2.1 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble-devel |
| Last Updated | 2024-08-28 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- RT Corporation
Authors
- ShotaAk
- Daisuke Sato
- Shuhei Kozasa
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse.
ROS1 examples is here.
To run on Gazebo, click here.
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Supported ROS 2 distributions
- Foxy
- Humble (This branch)
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 22.04
- https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO-devel https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see LICENSE for details.
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
Launch nodes with the following command:
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
This picture shows the default key configuration.
To use Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710, set the input mode to D (DirectInput Mode).
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package raspimouse_ros2_examples
2.2.1 (2024-08-28)
- サービスクライアントでexecutorを使用しない (#59)
- SubscriberとService Clientに別々のcallback_groupを設定 (#58)
- Contributors: ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.2.0 (2024-03-05)
- READMEにSLAM&Navigationパッケージの案内を追加 (#53)
- Camera_FollowerクラスをCameraFollowerに変更 (#52)
- Update camera line follower: Set motor power with switch input. Add area_threthold param. (#51)
- Add velocity parameters for camera_line_follower (#50)
- カメラライントレースを修正 (#49)
- Change threthold of line detection
- Add usb_cam dependency (#48)
- RGBカメラによるライントレースの実装 (#47)
- リリースのためにCHANGELOG.rstとpackage.xmlを更新 (#45)
- Contributors: Shota Aoki, ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.1.0 (2023-11-07)
- READMEにGazeboでも実行できることを追記 (#44)
- object_trackingにおいて画像トピックをサブスクライブするように変更 (#43)
- Contributors: YusukeKato
2.0.0 (2023-08-03)
- Humble対応 (#41)
- Contributors: Shuhei Kozasa
1.0.0 (2022-07-28)
- Update map command (#38)
- Adds config file for DUALSHOCK4 (#36)
- Update README for foxy-devel (#34)
- Remove node_ prefix from launch files (#33)
- Use ament_export_targets instead of ament_export_interfaces. (#31)
- Remove dashing check from CI (#32)
- Update rviz config to show scan and graph topics (#29)
- Add descriptions to READMEs for use_pulse_counters param settings (#28)
- Use joy_linux instead of joy (#27)
- Update CI to support ROS Foxy (#26)
- Update package.xml (#25)
- Install raspimouse2 and imu packages via rosdep command (#22)
- Add rt_usb_9axisimu_driver dependency to package.xml (#21)
- Add direction control example (#18)
- Use images of rt-net/images repo. (#17)
- Add lidar example (#14)
- Turn on/off leds with joy inputs (#15)
- Update Gamepad F710 usage in README (#13)
- Use multi threads in the object tracking example to stabilize the tracking (#11)
- update video link (#12)
- Merge teleop_joy launch files into one file. (#10)
- Add line follower examples (#9)
- Add object tracking sample (#8)
- Rename launch files (#7)
- Refactoring (#6)
- Support remote control
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
| Name |
|---|
| libopencv-dev |
| v4l-utils |
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_slam |
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged raspimouse_ros2_examples at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
raspimouse_ros2_examples package from raspimouse_ros2_examples reporaspimouse_ros2_examples |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 2.2.1 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble-devel |
| Last Updated | 2024-08-28 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- RT Corporation
Authors
- ShotaAk
- Daisuke Sato
- Shuhei Kozasa
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse.
ROS1 examples is here.
To run on Gazebo, click here.
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Supported ROS 2 distributions
- Foxy
- Humble (This branch)
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 22.04
- https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO-devel https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see LICENSE for details.
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
Launch nodes with the following command:
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
This picture shows the default key configuration.
To use Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710, set the input mode to D (DirectInput Mode).
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package raspimouse_ros2_examples
2.2.1 (2024-08-28)
- サービスクライアントでexecutorを使用しない (#59)
- SubscriberとService Clientに別々のcallback_groupを設定 (#58)
- Contributors: ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.2.0 (2024-03-05)
- READMEにSLAM&Navigationパッケージの案内を追加 (#53)
- Camera_FollowerクラスをCameraFollowerに変更 (#52)
- Update camera line follower: Set motor power with switch input. Add area_threthold param. (#51)
- Add velocity parameters for camera_line_follower (#50)
- カメラライントレースを修正 (#49)
- Change threthold of line detection
- Add usb_cam dependency (#48)
- RGBカメラによるライントレースの実装 (#47)
- リリースのためにCHANGELOG.rstとpackage.xmlを更新 (#45)
- Contributors: Shota Aoki, ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.1.0 (2023-11-07)
- READMEにGazeboでも実行できることを追記 (#44)
- object_trackingにおいて画像トピックをサブスクライブするように変更 (#43)
- Contributors: YusukeKato
2.0.0 (2023-08-03)
- Humble対応 (#41)
- Contributors: Shuhei Kozasa
1.0.0 (2022-07-28)
- Update map command (#38)
- Adds config file for DUALSHOCK4 (#36)
- Update README for foxy-devel (#34)
- Remove node_ prefix from launch files (#33)
- Use ament_export_targets instead of ament_export_interfaces. (#31)
- Remove dashing check from CI (#32)
- Update rviz config to show scan and graph topics (#29)
- Add descriptions to READMEs for use_pulse_counters param settings (#28)
- Use joy_linux instead of joy (#27)
- Update CI to support ROS Foxy (#26)
- Update package.xml (#25)
- Install raspimouse2 and imu packages via rosdep command (#22)
- Add rt_usb_9axisimu_driver dependency to package.xml (#21)
- Add direction control example (#18)
- Use images of rt-net/images repo. (#17)
- Add lidar example (#14)
- Turn on/off leds with joy inputs (#15)
- Update Gamepad F710 usage in README (#13)
- Use multi threads in the object tracking example to stabilize the tracking (#11)
- update video link (#12)
- Merge teleop_joy launch files into one file. (#10)
- Add line follower examples (#9)
- Add object tracking sample (#8)
- Rename launch files (#7)
- Refactoring (#6)
- Support remote control
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
| Name |
|---|
| libopencv-dev |
| v4l-utils |
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_slam |
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged raspimouse_ros2_examples at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
raspimouse_ros2_examples package from raspimouse_ros2_examples reporaspimouse_ros2_examples |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 2.2.1 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble-devel |
| Last Updated | 2024-08-28 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- RT Corporation
Authors
- ShotaAk
- Daisuke Sato
- Shuhei Kozasa
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse.
ROS1 examples is here.
To run on Gazebo, click here.
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Supported ROS 2 distributions
- Foxy
- Humble (This branch)
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 22.04
- https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO-devel https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see LICENSE for details.
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
Launch nodes with the following command:
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
This picture shows the default key configuration.
To use Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710, set the input mode to D (DirectInput Mode).
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package raspimouse_ros2_examples
2.2.1 (2024-08-28)
- サービスクライアントでexecutorを使用しない (#59)
- SubscriberとService Clientに別々のcallback_groupを設定 (#58)
- Contributors: ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.2.0 (2024-03-05)
- READMEにSLAM&Navigationパッケージの案内を追加 (#53)
- Camera_FollowerクラスをCameraFollowerに変更 (#52)
- Update camera line follower: Set motor power with switch input. Add area_threthold param. (#51)
- Add velocity parameters for camera_line_follower (#50)
- カメラライントレースを修正 (#49)
- Change threthold of line detection
- Add usb_cam dependency (#48)
- RGBカメラによるライントレースの実装 (#47)
- リリースのためにCHANGELOG.rstとpackage.xmlを更新 (#45)
- Contributors: Shota Aoki, ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.1.0 (2023-11-07)
- READMEにGazeboでも実行できることを追記 (#44)
- object_trackingにおいて画像トピックをサブスクライブするように変更 (#43)
- Contributors: YusukeKato
2.0.0 (2023-08-03)
- Humble対応 (#41)
- Contributors: Shuhei Kozasa
1.0.0 (2022-07-28)
- Update map command (#38)
- Adds config file for DUALSHOCK4 (#36)
- Update README for foxy-devel (#34)
- Remove node_ prefix from launch files (#33)
- Use ament_export_targets instead of ament_export_interfaces. (#31)
- Remove dashing check from CI (#32)
- Update rviz config to show scan and graph topics (#29)
- Add descriptions to READMEs for use_pulse_counters param settings (#28)
- Use joy_linux instead of joy (#27)
- Update CI to support ROS Foxy (#26)
- Update package.xml (#25)
- Install raspimouse2 and imu packages via rosdep command (#22)
- Add rt_usb_9axisimu_driver dependency to package.xml (#21)
- Add direction control example (#18)
- Use images of rt-net/images repo. (#17)
- Add lidar example (#14)
- Turn on/off leds with joy inputs (#15)
- Update Gamepad F710 usage in README (#13)
- Use multi threads in the object tracking example to stabilize the tracking (#11)
- update video link (#12)
- Merge teleop_joy launch files into one file. (#10)
- Add line follower examples (#9)
- Add object tracking sample (#8)
- Rename launch files (#7)
- Refactoring (#6)
- Support remote control
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
| Name |
|---|
| libopencv-dev |
| v4l-utils |
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_slam |
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged raspimouse_ros2_examples at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
raspimouse_ros2_examples package from raspimouse_ros2_examples reporaspimouse_ros2_examples |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 2.2.1 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble-devel |
| Last Updated | 2024-08-28 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- RT Corporation
Authors
- ShotaAk
- Daisuke Sato
- Shuhei Kozasa
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse.
ROS1 examples is here.
To run on Gazebo, click here.
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Supported ROS 2 distributions
- Foxy
- Humble (This branch)
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 22.04
- https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO-devel https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see LICENSE for details.
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
Launch nodes with the following command:
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
This picture shows the default key configuration.
To use Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710, set the input mode to D (DirectInput Mode).
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package raspimouse_ros2_examples
2.2.1 (2024-08-28)
- サービスクライアントでexecutorを使用しない (#59)
- SubscriberとService Clientに別々のcallback_groupを設定 (#58)
- Contributors: ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.2.0 (2024-03-05)
- READMEにSLAM&Navigationパッケージの案内を追加 (#53)
- Camera_FollowerクラスをCameraFollowerに変更 (#52)
- Update camera line follower: Set motor power with switch input. Add area_threthold param. (#51)
- Add velocity parameters for camera_line_follower (#50)
- カメラライントレースを修正 (#49)
- Change threthold of line detection
- Add usb_cam dependency (#48)
- RGBカメラによるライントレースの実装 (#47)
- リリースのためにCHANGELOG.rstとpackage.xmlを更新 (#45)
- Contributors: Shota Aoki, ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.1.0 (2023-11-07)
- READMEにGazeboでも実行できることを追記 (#44)
- object_trackingにおいて画像トピックをサブスクライブするように変更 (#43)
- Contributors: YusukeKato
2.0.0 (2023-08-03)
- Humble対応 (#41)
- Contributors: Shuhei Kozasa
1.0.0 (2022-07-28)
- Update map command (#38)
- Adds config file for DUALSHOCK4 (#36)
- Update README for foxy-devel (#34)
- Remove node_ prefix from launch files (#33)
- Use ament_export_targets instead of ament_export_interfaces. (#31)
- Remove dashing check from CI (#32)
- Update rviz config to show scan and graph topics (#29)
- Add descriptions to READMEs for use_pulse_counters param settings (#28)
- Use joy_linux instead of joy (#27)
- Update CI to support ROS Foxy (#26)
- Update package.xml (#25)
- Install raspimouse2 and imu packages via rosdep command (#22)
- Add rt_usb_9axisimu_driver dependency to package.xml (#21)
- Add direction control example (#18)
- Use images of rt-net/images repo. (#17)
- Add lidar example (#14)
- Turn on/off leds with joy inputs (#15)
- Update Gamepad F710 usage in README (#13)
- Use multi threads in the object tracking example to stabilize the tracking (#11)
- update video link (#12)
- Merge teleop_joy launch files into one file. (#10)
- Add line follower examples (#9)
- Add object tracking sample (#8)
- Rename launch files (#7)
- Refactoring (#6)
- Support remote control
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
| Name |
|---|
| libopencv-dev |
| v4l-utils |
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_slam |
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged raspimouse_ros2_examples at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
raspimouse_ros2_examples package from raspimouse_ros2_examples reporaspimouse_ros2_examples |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 2.2.1 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble-devel |
| Last Updated | 2024-08-28 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- RT Corporation
Authors
- ShotaAk
- Daisuke Sato
- Shuhei Kozasa
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse.
ROS1 examples is here.
To run on Gazebo, click here.
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Supported ROS 2 distributions
- Foxy
- Humble (This branch)
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 22.04
- https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO-devel https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see LICENSE for details.
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
Launch nodes with the following command:
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
This picture shows the default key configuration.
To use Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710, set the input mode to D (DirectInput Mode).
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package raspimouse_ros2_examples
2.2.1 (2024-08-28)
- サービスクライアントでexecutorを使用しない (#59)
- SubscriberとService Clientに別々のcallback_groupを設定 (#58)
- Contributors: ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.2.0 (2024-03-05)
- READMEにSLAM&Navigationパッケージの案内を追加 (#53)
- Camera_FollowerクラスをCameraFollowerに変更 (#52)
- Update camera line follower: Set motor power with switch input. Add area_threthold param. (#51)
- Add velocity parameters for camera_line_follower (#50)
- カメラライントレースを修正 (#49)
- Change threthold of line detection
- Add usb_cam dependency (#48)
- RGBカメラによるライントレースの実装 (#47)
- リリースのためにCHANGELOG.rstとpackage.xmlを更新 (#45)
- Contributors: Shota Aoki, ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.1.0 (2023-11-07)
- READMEにGazeboでも実行できることを追記 (#44)
- object_trackingにおいて画像トピックをサブスクライブするように変更 (#43)
- Contributors: YusukeKato
2.0.0 (2023-08-03)
- Humble対応 (#41)
- Contributors: Shuhei Kozasa
1.0.0 (2022-07-28)
- Update map command (#38)
- Adds config file for DUALSHOCK4 (#36)
- Update README for foxy-devel (#34)
- Remove node_ prefix from launch files (#33)
- Use ament_export_targets instead of ament_export_interfaces. (#31)
- Remove dashing check from CI (#32)
- Update rviz config to show scan and graph topics (#29)
- Add descriptions to READMEs for use_pulse_counters param settings (#28)
- Use joy_linux instead of joy (#27)
- Update CI to support ROS Foxy (#26)
- Update package.xml (#25)
- Install raspimouse2 and imu packages via rosdep command (#22)
- Add rt_usb_9axisimu_driver dependency to package.xml (#21)
- Add direction control example (#18)
- Use images of rt-net/images repo. (#17)
- Add lidar example (#14)
- Turn on/off leds with joy inputs (#15)
- Update Gamepad F710 usage in README (#13)
- Use multi threads in the object tracking example to stabilize the tracking (#11)
- update video link (#12)
- Merge teleop_joy launch files into one file. (#10)
- Add line follower examples (#9)
- Add object tracking sample (#8)
- Rename launch files (#7)
- Refactoring (#6)
- Support remote control
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
| Name |
|---|
| libopencv-dev |
| v4l-utils |
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_slam |
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged raspimouse_ros2_examples at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
raspimouse_ros2_examples package from raspimouse_ros2_examples reporaspimouse_ros2_examples |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 2.2.1 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble-devel |
| Last Updated | 2024-08-28 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- RT Corporation
Authors
- ShotaAk
- Daisuke Sato
- Shuhei Kozasa
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse.
ROS1 examples is here.
To run on Gazebo, click here.
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Supported ROS 2 distributions
- Foxy
- Humble (This branch)
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 22.04
- https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO-devel https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see LICENSE for details.
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
Launch nodes with the following command:
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
This picture shows the default key configuration.
To use Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710, set the input mode to D (DirectInput Mode).
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package raspimouse_ros2_examples
2.2.1 (2024-08-28)
- サービスクライアントでexecutorを使用しない (#59)
- SubscriberとService Clientに別々のcallback_groupを設定 (#58)
- Contributors: ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.2.0 (2024-03-05)
- READMEにSLAM&Navigationパッケージの案内を追加 (#53)
- Camera_FollowerクラスをCameraFollowerに変更 (#52)
- Update camera line follower: Set motor power with switch input. Add area_threthold param. (#51)
- Add velocity parameters for camera_line_follower (#50)
- カメラライントレースを修正 (#49)
- Change threthold of line detection
- Add usb_cam dependency (#48)
- RGBカメラによるライントレースの実装 (#47)
- リリースのためにCHANGELOG.rstとpackage.xmlを更新 (#45)
- Contributors: Shota Aoki, ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.1.0 (2023-11-07)
- READMEにGazeboでも実行できることを追記 (#44)
- object_trackingにおいて画像トピックをサブスクライブするように変更 (#43)
- Contributors: YusukeKato
2.0.0 (2023-08-03)
- Humble対応 (#41)
- Contributors: Shuhei Kozasa
1.0.0 (2022-07-28)
- Update map command (#38)
- Adds config file for DUALSHOCK4 (#36)
- Update README for foxy-devel (#34)
- Remove node_ prefix from launch files (#33)
- Use ament_export_targets instead of ament_export_interfaces. (#31)
- Remove dashing check from CI (#32)
- Update rviz config to show scan and graph topics (#29)
- Add descriptions to READMEs for use_pulse_counters param settings (#28)
- Use joy_linux instead of joy (#27)
- Update CI to support ROS Foxy (#26)
- Update package.xml (#25)
- Install raspimouse2 and imu packages via rosdep command (#22)
- Add rt_usb_9axisimu_driver dependency to package.xml (#21)
- Add direction control example (#18)
- Use images of rt-net/images repo. (#17)
- Add lidar example (#14)
- Turn on/off leds with joy inputs (#15)
- Update Gamepad F710 usage in README (#13)
- Use multi threads in the object tracking example to stabilize the tracking (#11)
- update video link (#12)
- Merge teleop_joy launch files into one file. (#10)
- Add line follower examples (#9)
- Add object tracking sample (#8)
- Rename launch files (#7)
- Refactoring (#6)
- Support remote control
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
| Name |
|---|
| libopencv-dev |
| v4l-utils |
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_slam |
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged raspimouse_ros2_examples at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
raspimouse_ros2_examples package from raspimouse_ros2_examples reporaspimouse_ros2_examples |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 2.2.1 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble-devel |
| Last Updated | 2024-08-28 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- RT Corporation
Authors
- ShotaAk
- Daisuke Sato
- Shuhei Kozasa
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse.
ROS1 examples is here.
To run on Gazebo, click here.
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Supported ROS 2 distributions
- Foxy
- Humble (This branch)
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 22.04
- https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO-devel https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see LICENSE for details.
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
Launch nodes with the following command:
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
This picture shows the default key configuration.
To use Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710, set the input mode to D (DirectInput Mode).
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package raspimouse_ros2_examples
2.2.1 (2024-08-28)
- サービスクライアントでexecutorを使用しない (#59)
- SubscriberとService Clientに別々のcallback_groupを設定 (#58)
- Contributors: ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.2.0 (2024-03-05)
- READMEにSLAM&Navigationパッケージの案内を追加 (#53)
- Camera_FollowerクラスをCameraFollowerに変更 (#52)
- Update camera line follower: Set motor power with switch input. Add area_threthold param. (#51)
- Add velocity parameters for camera_line_follower (#50)
- カメラライントレースを修正 (#49)
- Change threthold of line detection
- Add usb_cam dependency (#48)
- RGBカメラによるライントレースの実装 (#47)
- リリースのためにCHANGELOG.rstとpackage.xmlを更新 (#45)
- Contributors: Shota Aoki, ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.1.0 (2023-11-07)
- READMEにGazeboでも実行できることを追記 (#44)
- object_trackingにおいて画像トピックをサブスクライブするように変更 (#43)
- Contributors: YusukeKato
2.0.0 (2023-08-03)
- Humble対応 (#41)
- Contributors: Shuhei Kozasa
1.0.0 (2022-07-28)
- Update map command (#38)
- Adds config file for DUALSHOCK4 (#36)
- Update README for foxy-devel (#34)
- Remove node_ prefix from launch files (#33)
- Use ament_export_targets instead of ament_export_interfaces. (#31)
- Remove dashing check from CI (#32)
- Update rviz config to show scan and graph topics (#29)
- Add descriptions to READMEs for use_pulse_counters param settings (#28)
- Use joy_linux instead of joy (#27)
- Update CI to support ROS Foxy (#26)
- Update package.xml (#25)
- Install raspimouse2 and imu packages via rosdep command (#22)
- Add rt_usb_9axisimu_driver dependency to package.xml (#21)
- Add direction control example (#18)
- Use images of rt-net/images repo. (#17)
- Add lidar example (#14)
- Turn on/off leds with joy inputs (#15)
- Update Gamepad F710 usage in README (#13)
- Use multi threads in the object tracking example to stabilize the tracking (#11)
- update video link (#12)
- Merge teleop_joy launch files into one file. (#10)
- Add line follower examples (#9)
- Add object tracking sample (#8)
- Rename launch files (#7)
- Refactoring (#6)
- Support remote control
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
| Name |
|---|
| libopencv-dev |
| v4l-utils |
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_slam |
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged raspimouse_ros2_examples at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
raspimouse_ros2_examples package from raspimouse_ros2_examples reporaspimouse_ros2_examples |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 1.0.0 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | foxy-devel |
| Last Updated | 2022-07-29 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- RT Corporation
Authors
- ShotaAk
- Daisuke Sato
- Shuhei Kozasa
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse.
ROS1 examples is here.
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 20.04
- https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO-devel https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see LICENSE for details.
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
Launch nodes with the following command:
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
This picture shows the default key configuration.
To use Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710, set the input mode to D (DirectInput Mode).
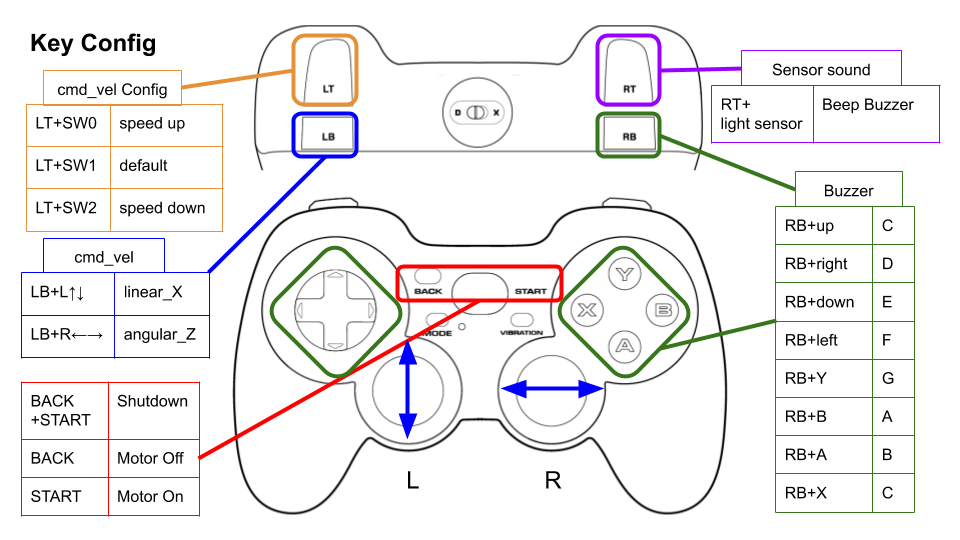
Configure
Key assignments can be edited with key numbers in ./config/joy_f710.yml or ./config/joy_dualshock3.yml.
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package raspimouse_ros2_examples
1.0.0 (2022-07-28)
- Update map command (#38)
- Adds config file for DUALSHOCK4 (#36)
- Update README for foxy-devel (#34)
- Remove node_ prefix from launch files (#33)
- Use ament_export_targets instead of ament_export_interfaces. (#31)
- Remove dashing check from CI (#32)
- Update rviz config to show scan and graph topics (#29)
- Add descriptions to READMEs for use_pulse_counters param settings (#28)
- Use joy_linux instead of joy (#27)
- Update CI to support ROS Foxy (#26)
- Update package.xml (#25)
- Install raspimouse2 and imu packages via rosdep command (#22)
- Add rt_usb_9axisimu_driver dependency to package.xml (#21)
- Add direction control example (#18)
- Use images of rt-net/images repo. (#17)
- Add lidar example (#14)
- Turn on/off leds with joy inputs (#15)
- Update Gamepad F710 usage in README (#13)
- Use multi threads in the object tracking example to stabilize the tracking (#11)
- update video link (#12)
- Merge teleop_joy launch files into one file. (#10)
- Add line follower examples (#9)
- Add object tracking sample (#8)
- Rename launch files (#7)
- Refactoring (#6)
- Support remote control (#5)
- Add Joystic example (#4)
- Add industrial_ci test settings (#3)
- Fix teleop.launch for flake8 check (#2)
- Add github workflow (#1)
- Contributors: Daisuke Sato, Shota Aoki, Shuhei Kozasa
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
| Name |
|---|
| libopencv-dev |
| v4l-utils |
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_slam |
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged raspimouse_ros2_examples at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
raspimouse_ros2_examples package from raspimouse_ros2_examples reporaspimouse_ros2_examples |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 2.2.1 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble-devel |
| Last Updated | 2024-08-28 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- RT Corporation
Authors
- ShotaAk
- Daisuke Sato
- Shuhei Kozasa
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse.
ROS1 examples is here.
To run on Gazebo, click here.
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Supported ROS 2 distributions
- Foxy
- Humble (This branch)
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 22.04
- https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO-devel https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see LICENSE for details.
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
Launch nodes with the following command:
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
This picture shows the default key configuration.
To use Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710, set the input mode to D (DirectInput Mode).
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package raspimouse_ros2_examples
2.2.1 (2024-08-28)
- サービスクライアントでexecutorを使用しない (#59)
- SubscriberとService Clientに別々のcallback_groupを設定 (#58)
- Contributors: ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.2.0 (2024-03-05)
- READMEにSLAM&Navigationパッケージの案内を追加 (#53)
- Camera_FollowerクラスをCameraFollowerに変更 (#52)
- Update camera line follower: Set motor power with switch input. Add area_threthold param. (#51)
- Add velocity parameters for camera_line_follower (#50)
- カメラライントレースを修正 (#49)
- Change threthold of line detection
- Add usb_cam dependency (#48)
- RGBカメラによるライントレースの実装 (#47)
- リリースのためにCHANGELOG.rstとpackage.xmlを更新 (#45)
- Contributors: Shota Aoki, ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.1.0 (2023-11-07)
- READMEにGazeboでも実行できることを追記 (#44)
- object_trackingにおいて画像トピックをサブスクライブするように変更 (#43)
- Contributors: YusukeKato
2.0.0 (2023-08-03)
- Humble対応 (#41)
- Contributors: Shuhei Kozasa
1.0.0 (2022-07-28)
- Update map command (#38)
- Adds config file for DUALSHOCK4 (#36)
- Update README for foxy-devel (#34)
- Remove node_ prefix from launch files (#33)
- Use ament_export_targets instead of ament_export_interfaces. (#31)
- Remove dashing check from CI (#32)
- Update rviz config to show scan and graph topics (#29)
- Add descriptions to READMEs for use_pulse_counters param settings (#28)
- Use joy_linux instead of joy (#27)
- Update CI to support ROS Foxy (#26)
- Update package.xml (#25)
- Install raspimouse2 and imu packages via rosdep command (#22)
- Add rt_usb_9axisimu_driver dependency to package.xml (#21)
- Add direction control example (#18)
- Use images of rt-net/images repo. (#17)
- Add lidar example (#14)
- Turn on/off leds with joy inputs (#15)
- Update Gamepad F710 usage in README (#13)
- Use multi threads in the object tracking example to stabilize the tracking (#11)
- update video link (#12)
- Merge teleop_joy launch files into one file. (#10)
- Add line follower examples (#9)
- Add object tracking sample (#8)
- Rename launch files (#7)
- Refactoring (#6)
- Support remote control
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
| Name |
|---|
| libopencv-dev |
| v4l-utils |
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_slam |
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged raspimouse_ros2_examples at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
raspimouse_ros2_examples package from raspimouse_ros2_examples reporaspimouse_ros2_examples |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 2.2.1 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble-devel |
| Last Updated | 2024-08-28 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- RT Corporation
Authors
- ShotaAk
- Daisuke Sato
- Shuhei Kozasa
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse.
ROS1 examples is here.
To run on Gazebo, click here.
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Supported ROS 2 distributions
- Foxy
- Humble (This branch)
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 22.04
- https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO-devel https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see LICENSE for details.
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
Launch nodes with the following command:
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
This picture shows the default key configuration.
To use Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710, set the input mode to D (DirectInput Mode).
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package raspimouse_ros2_examples
2.2.1 (2024-08-28)
- サービスクライアントでexecutorを使用しない (#59)
- SubscriberとService Clientに別々のcallback_groupを設定 (#58)
- Contributors: ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.2.0 (2024-03-05)
- READMEにSLAM&Navigationパッケージの案内を追加 (#53)
- Camera_FollowerクラスをCameraFollowerに変更 (#52)
- Update camera line follower: Set motor power with switch input. Add area_threthold param. (#51)
- Add velocity parameters for camera_line_follower (#50)
- カメラライントレースを修正 (#49)
- Change threthold of line detection
- Add usb_cam dependency (#48)
- RGBカメラによるライントレースの実装 (#47)
- リリースのためにCHANGELOG.rstとpackage.xmlを更新 (#45)
- Contributors: Shota Aoki, ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.1.0 (2023-11-07)
- READMEにGazeboでも実行できることを追記 (#44)
- object_trackingにおいて画像トピックをサブスクライブするように変更 (#43)
- Contributors: YusukeKato
2.0.0 (2023-08-03)
- Humble対応 (#41)
- Contributors: Shuhei Kozasa
1.0.0 (2022-07-28)
- Update map command (#38)
- Adds config file for DUALSHOCK4 (#36)
- Update README for foxy-devel (#34)
- Remove node_ prefix from launch files (#33)
- Use ament_export_targets instead of ament_export_interfaces. (#31)
- Remove dashing check from CI (#32)
- Update rviz config to show scan and graph topics (#29)
- Add descriptions to READMEs for use_pulse_counters param settings (#28)
- Use joy_linux instead of joy (#27)
- Update CI to support ROS Foxy (#26)
- Update package.xml (#25)
- Install raspimouse2 and imu packages via rosdep command (#22)
- Add rt_usb_9axisimu_driver dependency to package.xml (#21)
- Add direction control example (#18)
- Use images of rt-net/images repo. (#17)
- Add lidar example (#14)
- Turn on/off leds with joy inputs (#15)
- Update Gamepad F710 usage in README (#13)
- Use multi threads in the object tracking example to stabilize the tracking (#11)
- update video link (#12)
- Merge teleop_joy launch files into one file. (#10)
- Add line follower examples (#9)
- Add object tracking sample (#8)
- Rename launch files (#7)
- Refactoring (#6)
- Support remote control
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
| Name |
|---|
| libopencv-dev |
| v4l-utils |
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_slam |
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged raspimouse_ros2_examples at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
raspimouse_ros2_examples package from raspimouse_ros2_examples reporaspimouse_ros2_examples |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 2.2.1 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble-devel |
| Last Updated | 2024-08-28 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- RT Corporation
Authors
- ShotaAk
- Daisuke Sato
- Shuhei Kozasa
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse.
ROS1 examples is here.
To run on Gazebo, click here.
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Supported ROS 2 distributions
- Foxy
- Humble (This branch)
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 22.04
- https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO-devel https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see LICENSE for details.
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
Launch nodes with the following command:
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
This picture shows the default key configuration.
To use Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710, set the input mode to D (DirectInput Mode).
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package raspimouse_ros2_examples
2.2.1 (2024-08-28)
- サービスクライアントでexecutorを使用しない (#59)
- SubscriberとService Clientに別々のcallback_groupを設定 (#58)
- Contributors: ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.2.0 (2024-03-05)
- READMEにSLAM&Navigationパッケージの案内を追加 (#53)
- Camera_FollowerクラスをCameraFollowerに変更 (#52)
- Update camera line follower: Set motor power with switch input. Add area_threthold param. (#51)
- Add velocity parameters for camera_line_follower (#50)
- カメラライントレースを修正 (#49)
- Change threthold of line detection
- Add usb_cam dependency (#48)
- RGBカメラによるライントレースの実装 (#47)
- リリースのためにCHANGELOG.rstとpackage.xmlを更新 (#45)
- Contributors: Shota Aoki, ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.1.0 (2023-11-07)
- READMEにGazeboでも実行できることを追記 (#44)
- object_trackingにおいて画像トピックをサブスクライブするように変更 (#43)
- Contributors: YusukeKato
2.0.0 (2023-08-03)
- Humble対応 (#41)
- Contributors: Shuhei Kozasa
1.0.0 (2022-07-28)
- Update map command (#38)
- Adds config file for DUALSHOCK4 (#36)
- Update README for foxy-devel (#34)
- Remove node_ prefix from launch files (#33)
- Use ament_export_targets instead of ament_export_interfaces. (#31)
- Remove dashing check from CI (#32)
- Update rviz config to show scan and graph topics (#29)
- Add descriptions to READMEs for use_pulse_counters param settings (#28)
- Use joy_linux instead of joy (#27)
- Update CI to support ROS Foxy (#26)
- Update package.xml (#25)
- Install raspimouse2 and imu packages via rosdep command (#22)
- Add rt_usb_9axisimu_driver dependency to package.xml (#21)
- Add direction control example (#18)
- Use images of rt-net/images repo. (#17)
- Add lidar example (#14)
- Turn on/off leds with joy inputs (#15)
- Update Gamepad F710 usage in README (#13)
- Use multi threads in the object tracking example to stabilize the tracking (#11)
- update video link (#12)
- Merge teleop_joy launch files into one file. (#10)
- Add line follower examples (#9)
- Add object tracking sample (#8)
- Rename launch files (#7)
- Refactoring (#6)
- Support remote control
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
| Name |
|---|
| libopencv-dev |
| v4l-utils |
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_slam |
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged raspimouse_ros2_examples at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
raspimouse_ros2_examples package from raspimouse_ros2_examples reporaspimouse_ros2_examples |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 2.2.1 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble-devel |
| Last Updated | 2024-08-28 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- RT Corporation
Authors
- ShotaAk
- Daisuke Sato
- Shuhei Kozasa
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse.
ROS1 examples is here.
To run on Gazebo, click here.
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Supported ROS 2 distributions
- Foxy
- Humble (This branch)
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 22.04
- https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO-devel https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see LICENSE for details.
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
Launch nodes with the following command:
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
This picture shows the default key configuration.
To use Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710, set the input mode to D (DirectInput Mode).
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package raspimouse_ros2_examples
2.2.1 (2024-08-28)
- サービスクライアントでexecutorを使用しない (#59)
- SubscriberとService Clientに別々のcallback_groupを設定 (#58)
- Contributors: ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.2.0 (2024-03-05)
- READMEにSLAM&Navigationパッケージの案内を追加 (#53)
- Camera_FollowerクラスをCameraFollowerに変更 (#52)
- Update camera line follower: Set motor power with switch input. Add area_threthold param. (#51)
- Add velocity parameters for camera_line_follower (#50)
- カメラライントレースを修正 (#49)
- Change threthold of line detection
- Add usb_cam dependency (#48)
- RGBカメラによるライントレースの実装 (#47)
- リリースのためにCHANGELOG.rstとpackage.xmlを更新 (#45)
- Contributors: Shota Aoki, ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.1.0 (2023-11-07)
- READMEにGazeboでも実行できることを追記 (#44)
- object_trackingにおいて画像トピックをサブスクライブするように変更 (#43)
- Contributors: YusukeKato
2.0.0 (2023-08-03)
- Humble対応 (#41)
- Contributors: Shuhei Kozasa
1.0.0 (2022-07-28)
- Update map command (#38)
- Adds config file for DUALSHOCK4 (#36)
- Update README for foxy-devel (#34)
- Remove node_ prefix from launch files (#33)
- Use ament_export_targets instead of ament_export_interfaces. (#31)
- Remove dashing check from CI (#32)
- Update rviz config to show scan and graph topics (#29)
- Add descriptions to READMEs for use_pulse_counters param settings (#28)
- Use joy_linux instead of joy (#27)
- Update CI to support ROS Foxy (#26)
- Update package.xml (#25)
- Install raspimouse2 and imu packages via rosdep command (#22)
- Add rt_usb_9axisimu_driver dependency to package.xml (#21)
- Add direction control example (#18)
- Use images of rt-net/images repo. (#17)
- Add lidar example (#14)
- Turn on/off leds with joy inputs (#15)
- Update Gamepad F710 usage in README (#13)
- Use multi threads in the object tracking example to stabilize the tracking (#11)
- update video link (#12)
- Merge teleop_joy launch files into one file. (#10)
- Add line follower examples (#9)
- Add object tracking sample (#8)
- Rename launch files (#7)
- Refactoring (#6)
- Support remote control
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
| Name |
|---|
| libopencv-dev |
| v4l-utils |
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_slam |
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged raspimouse_ros2_examples at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
raspimouse_ros2_examples package from raspimouse_ros2_examples reporaspimouse_ros2_examples |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 2.2.1 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble-devel |
| Last Updated | 2024-08-28 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- RT Corporation
Authors
- ShotaAk
- Daisuke Sato
- Shuhei Kozasa
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse.
ROS1 examples is here.
To run on Gazebo, click here.
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Supported ROS 2 distributions
- Foxy
- Humble (This branch)
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 22.04
- https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO-devel https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see LICENSE for details.
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
Launch nodes with the following command:
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
This picture shows the default key configuration.
To use Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710, set the input mode to D (DirectInput Mode).
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package raspimouse_ros2_examples
2.2.1 (2024-08-28)
- サービスクライアントでexecutorを使用しない (#59)
- SubscriberとService Clientに別々のcallback_groupを設定 (#58)
- Contributors: ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.2.0 (2024-03-05)
- READMEにSLAM&Navigationパッケージの案内を追加 (#53)
- Camera_FollowerクラスをCameraFollowerに変更 (#52)
- Update camera line follower: Set motor power with switch input. Add area_threthold param. (#51)
- Add velocity parameters for camera_line_follower (#50)
- カメラライントレースを修正 (#49)
- Change threthold of line detection
- Add usb_cam dependency (#48)
- RGBカメラによるライントレースの実装 (#47)
- リリースのためにCHANGELOG.rstとpackage.xmlを更新 (#45)
- Contributors: Shota Aoki, ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.1.0 (2023-11-07)
- READMEにGazeboでも実行できることを追記 (#44)
- object_trackingにおいて画像トピックをサブスクライブするように変更 (#43)
- Contributors: YusukeKato
2.0.0 (2023-08-03)
- Humble対応 (#41)
- Contributors: Shuhei Kozasa
1.0.0 (2022-07-28)
- Update map command (#38)
- Adds config file for DUALSHOCK4 (#36)
- Update README for foxy-devel (#34)
- Remove node_ prefix from launch files (#33)
- Use ament_export_targets instead of ament_export_interfaces. (#31)
- Remove dashing check from CI (#32)
- Update rviz config to show scan and graph topics (#29)
- Add descriptions to READMEs for use_pulse_counters param settings (#28)
- Use joy_linux instead of joy (#27)
- Update CI to support ROS Foxy (#26)
- Update package.xml (#25)
- Install raspimouse2 and imu packages via rosdep command (#22)
- Add rt_usb_9axisimu_driver dependency to package.xml (#21)
- Add direction control example (#18)
- Use images of rt-net/images repo. (#17)
- Add lidar example (#14)
- Turn on/off leds with joy inputs (#15)
- Update Gamepad F710 usage in README (#13)
- Use multi threads in the object tracking example to stabilize the tracking (#11)
- update video link (#12)
- Merge teleop_joy launch files into one file. (#10)
- Add line follower examples (#9)
- Add object tracking sample (#8)
- Rename launch files (#7)
- Refactoring (#6)
- Support remote control
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
| Name |
|---|
| libopencv-dev |
| v4l-utils |
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_slam |
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged raspimouse_ros2_examples at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
raspimouse_ros2_examples package from raspimouse_ros2_examples reporaspimouse_ros2_examples |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 2.2.1 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble-devel |
| Last Updated | 2024-08-28 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- RT Corporation
Authors
- ShotaAk
- Daisuke Sato
- Shuhei Kozasa
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse.
ROS1 examples is here.
To run on Gazebo, click here.
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Supported ROS 2 distributions
- Foxy
- Humble (This branch)
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 22.04
- https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO-devel https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see LICENSE for details.
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
Launch nodes with the following command:
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
This picture shows the default key configuration.
To use Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710, set the input mode to D (DirectInput Mode).
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package raspimouse_ros2_examples
2.2.1 (2024-08-28)
- サービスクライアントでexecutorを使用しない (#59)
- SubscriberとService Clientに別々のcallback_groupを設定 (#58)
- Contributors: ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.2.0 (2024-03-05)
- READMEにSLAM&Navigationパッケージの案内を追加 (#53)
- Camera_FollowerクラスをCameraFollowerに変更 (#52)
- Update camera line follower: Set motor power with switch input. Add area_threthold param. (#51)
- Add velocity parameters for camera_line_follower (#50)
- カメラライントレースを修正 (#49)
- Change threthold of line detection
- Add usb_cam dependency (#48)
- RGBカメラによるライントレースの実装 (#47)
- リリースのためにCHANGELOG.rstとpackage.xmlを更新 (#45)
- Contributors: Shota Aoki, ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.1.0 (2023-11-07)
- READMEにGazeboでも実行できることを追記 (#44)
- object_trackingにおいて画像トピックをサブスクライブするように変更 (#43)
- Contributors: YusukeKato
2.0.0 (2023-08-03)
- Humble対応 (#41)
- Contributors: Shuhei Kozasa
1.0.0 (2022-07-28)
- Update map command (#38)
- Adds config file for DUALSHOCK4 (#36)
- Update README for foxy-devel (#34)
- Remove node_ prefix from launch files (#33)
- Use ament_export_targets instead of ament_export_interfaces. (#31)
- Remove dashing check from CI (#32)
- Update rviz config to show scan and graph topics (#29)
- Add descriptions to READMEs for use_pulse_counters param settings (#28)
- Use joy_linux instead of joy (#27)
- Update CI to support ROS Foxy (#26)
- Update package.xml (#25)
- Install raspimouse2 and imu packages via rosdep command (#22)
- Add rt_usb_9axisimu_driver dependency to package.xml (#21)
- Add direction control example (#18)
- Use images of rt-net/images repo. (#17)
- Add lidar example (#14)
- Turn on/off leds with joy inputs (#15)
- Update Gamepad F710 usage in README (#13)
- Use multi threads in the object tracking example to stabilize the tracking (#11)
- update video link (#12)
- Merge teleop_joy launch files into one file. (#10)
- Add line follower examples (#9)
- Add object tracking sample (#8)
- Rename launch files (#7)
- Refactoring (#6)
- Support remote control
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
| Name |
|---|
| libopencv-dev |
| v4l-utils |
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_slam |
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged raspimouse_ros2_examples at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
raspimouse_ros2_examples package from raspimouse_ros2_examples reporaspimouse_ros2_examples |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 2.2.1 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble-devel |
| Last Updated | 2024-08-28 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- RT Corporation
Authors
- ShotaAk
- Daisuke Sato
- Shuhei Kozasa
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse.
ROS1 examples is here.
To run on Gazebo, click here.
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Supported ROS 2 distributions
- Foxy
- Humble (This branch)
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 22.04
- https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO-devel https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see LICENSE for details.
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
Launch nodes with the following command:
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
This picture shows the default key configuration.
To use Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710, set the input mode to D (DirectInput Mode).
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package raspimouse_ros2_examples
2.2.1 (2024-08-28)
- サービスクライアントでexecutorを使用しない (#59)
- SubscriberとService Clientに別々のcallback_groupを設定 (#58)
- Contributors: ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.2.0 (2024-03-05)
- READMEにSLAM&Navigationパッケージの案内を追加 (#53)
- Camera_FollowerクラスをCameraFollowerに変更 (#52)
- Update camera line follower: Set motor power with switch input. Add area_threthold param. (#51)
- Add velocity parameters for camera_line_follower (#50)
- カメラライントレースを修正 (#49)
- Change threthold of line detection
- Add usb_cam dependency (#48)
- RGBカメラによるライントレースの実装 (#47)
- リリースのためにCHANGELOG.rstとpackage.xmlを更新 (#45)
- Contributors: Shota Aoki, ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.1.0 (2023-11-07)
- READMEにGazeboでも実行できることを追記 (#44)
- object_trackingにおいて画像トピックをサブスクライブするように変更 (#43)
- Contributors: YusukeKato
2.0.0 (2023-08-03)
- Humble対応 (#41)
- Contributors: Shuhei Kozasa
1.0.0 (2022-07-28)
- Update map command (#38)
- Adds config file for DUALSHOCK4 (#36)
- Update README for foxy-devel (#34)
- Remove node_ prefix from launch files (#33)
- Use ament_export_targets instead of ament_export_interfaces. (#31)
- Remove dashing check from CI (#32)
- Update rviz config to show scan and graph topics (#29)
- Add descriptions to READMEs for use_pulse_counters param settings (#28)
- Use joy_linux instead of joy (#27)
- Update CI to support ROS Foxy (#26)
- Update package.xml (#25)
- Install raspimouse2 and imu packages via rosdep command (#22)
- Add rt_usb_9axisimu_driver dependency to package.xml (#21)
- Add direction control example (#18)
- Use images of rt-net/images repo. (#17)
- Add lidar example (#14)
- Turn on/off leds with joy inputs (#15)
- Update Gamepad F710 usage in README (#13)
- Use multi threads in the object tracking example to stabilize the tracking (#11)
- update video link (#12)
- Merge teleop_joy launch files into one file. (#10)
- Add line follower examples (#9)
- Add object tracking sample (#8)
- Rename launch files (#7)
- Refactoring (#6)
- Support remote control
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
| Name |
|---|
| libopencv-dev |
| v4l-utils |
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_slam |
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged raspimouse_ros2_examples at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
raspimouse_ros2_examples package from raspimouse_ros2_examples reporaspimouse_ros2_examples |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 2.2.1 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble-devel |
| Last Updated | 2024-08-28 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- RT Corporation
Authors
- ShotaAk
- Daisuke Sato
- Shuhei Kozasa
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse.
ROS1 examples is here.
To run on Gazebo, click here.
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Supported ROS 2 distributions
- Foxy
- Humble (This branch)
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 22.04
- https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO-devel https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see LICENSE for details.
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
Launch nodes with the following command:
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
This picture shows the default key configuration.
To use Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710, set the input mode to D (DirectInput Mode).
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package raspimouse_ros2_examples
2.2.1 (2024-08-28)
- サービスクライアントでexecutorを使用しない (#59)
- SubscriberとService Clientに別々のcallback_groupを設定 (#58)
- Contributors: ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.2.0 (2024-03-05)
- READMEにSLAM&Navigationパッケージの案内を追加 (#53)
- Camera_FollowerクラスをCameraFollowerに変更 (#52)
- Update camera line follower: Set motor power with switch input. Add area_threthold param. (#51)
- Add velocity parameters for camera_line_follower (#50)
- カメラライントレースを修正 (#49)
- Change threthold of line detection
- Add usb_cam dependency (#48)
- RGBカメラによるライントレースの実装 (#47)
- リリースのためにCHANGELOG.rstとpackage.xmlを更新 (#45)
- Contributors: Shota Aoki, ShotaAk, YusukeKato
2.1.0 (2023-11-07)
- READMEにGazeboでも実行できることを追記 (#44)
- object_trackingにおいて画像トピックをサブスクライブするように変更 (#43)
- Contributors: YusukeKato
2.0.0 (2023-08-03)
- Humble対応 (#41)
- Contributors: Shuhei Kozasa
1.0.0 (2022-07-28)
- Update map command (#38)
- Adds config file for DUALSHOCK4 (#36)
- Update README for foxy-devel (#34)
- Remove node_ prefix from launch files (#33)
- Use ament_export_targets instead of ament_export_interfaces. (#31)
- Remove dashing check from CI (#32)
- Update rviz config to show scan and graph topics (#29)
- Add descriptions to READMEs for use_pulse_counters param settings (#28)
- Use joy_linux instead of joy (#27)
- Update CI to support ROS Foxy (#26)
- Update package.xml (#25)
- Install raspimouse2 and imu packages via rosdep command (#22)
- Add rt_usb_9axisimu_driver dependency to package.xml (#21)
- Add direction control example (#18)
- Use images of rt-net/images repo. (#17)
- Add lidar example (#14)
- Turn on/off leds with joy inputs (#15)
- Update Gamepad F710 usage in README (#13)
- Use multi threads in the object tracking example to stabilize the tracking (#11)
- update video link (#12)
- Merge teleop_joy launch files into one file. (#10)
- Add line follower examples (#9)
- Add object tracking sample (#8)
- Rename launch files (#7)
- Refactoring (#6)
- Support remote control
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
| Name |
|---|
| libopencv-dev |
| v4l-utils |
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_slam |