Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.2.5 |
| License | BSD |
| Build type | CATKIN |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/locusrobotics/robot_navigation.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2020-07-03 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- David V. Lu!!
Authors
nav_core2
A replacement interface for nav_core that defines basic two dimensional planner interfaces.
There were a few key reasons for creating new interfaces rather than extending the old ones.
- Use
nav_2d_msgsto eliminate unused data fields - Use a new
Costmapinterface as a plugin rather that forcing all implementations of the interfaces to usecostmap_2d::Costmap2DROS. - Provide more data in the interfaces for easier testing.
- Use Exceptions rather than booleans to provide more information about the types of errors encountered.
Costmap
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS has been a vital part of the navigation stack for years, but it was not without its flaws.
- Initialization required a transform be available from the global frame to the base frame, which was later used to move rolling costmaps around (and a few other things). This made doing simple testing of any planner or other
Costmap2DROS-based behavior annoying, because transforms had to be set up, often outside of the immediate code that was being tested. - Initialization also started an update thread, which is also not always needed in testing.
- Using
Costmap2DROSlocked users into a layered costmap based approach, which made some tasks much easier, but didn’t give users the freedom to change the implementation.
The nav_core2::Costmap interface extends the nav_grid::NavGrid<unsigned char> for abstracting away the data storage and coordinate manipulation, and provides a few other key methods for costmap functioning such as
- a mutex
- a way to potentially track changes to the costmap
- a public
updatemethod that can be called in whatever thread you please
The Costmap can be loaded using pluginlib, allowing for arbitrary implementations of underlying update algorithms, include the layered costmap approach.
One basic implementation is provided in BasicCostmap. You can also use the nav_core_adapter::CostmapAdapter class which implements the Costmap interface while allowing you to still use Costmap2DROS.
Note: One could also imagine the Costmap interface being templatized itself like NavGrid instead of forcing use of unsigned char. While this may be possible, it was decided that it was a bit ambitious and the use of templates would force all of the implementation into headers, and would ultimately obfuscate the operation of algorithms.
Global Planner
Let us compare the old nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner to the new nav_core2/GlobalPlanner.
nav_core |
nav_core2 |
comments |
|---|---|---|
void initialize(std::string, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*) |
void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr) |
Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers, and provides a TFListener |
bool makePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&) |
nav_2d_msgs::Path2D makePlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&) |
Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual path. |
Local Planner
Now let’s compare the old nav_core::BaseLocalPlanner to the new nav_core2/LocalPlanner.
| nav_core | nav_core2 | comments |
|—|–|—|
|void initialize(std::string, tf::TransformListener*, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*)|void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr)|Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers|
|(no equivalent)|void setGoalPose(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&)|Explicitly set the new goal location, rather than using the last pose of the global plan
|bool setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&)|setPlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Path2D&)||
|bool computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist&)|nav_2d_msgs::Twist2DStamped computeVelocityCommands(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)|Explicitly provides the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual command.|
|bool isGoalReached() | bool isGoalReached(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)` | Explicitly provide the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. |
Exceptions
A hierarchical collection of exceptions is provided to allow for reacting to navigation failures in a more robust and contextual way.
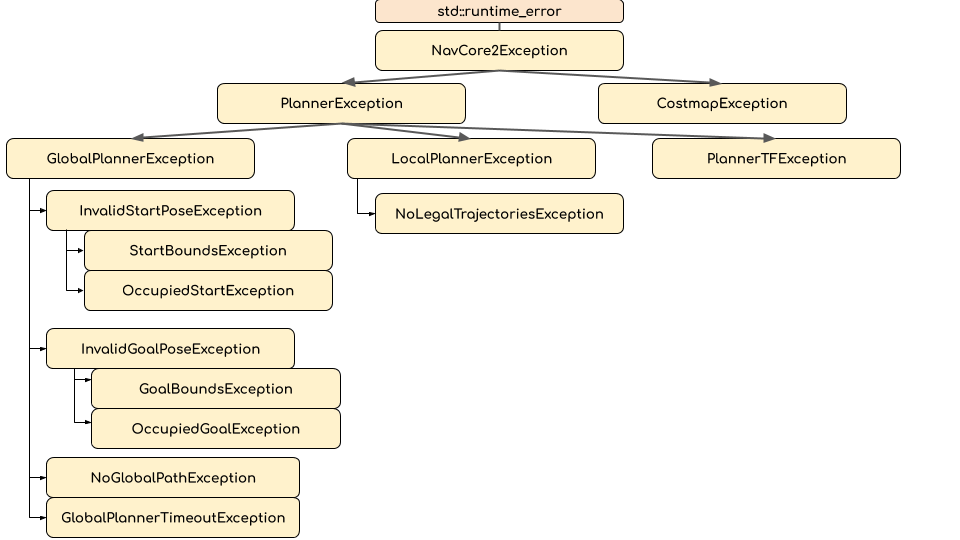 Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a
Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a StartBoundsException which has a corresponding result code of 6, it could also be seen as a InvalidStartPoseException, GlobalPlannerException, PlannerException or NavCore2Exception, all of which would also have the result code of 6.
Bounds
For use in tracking Costmap changes and more, this package also provides an implementation of bounding boxes. These are represented with the ranges [min_x, max_x] and [min_y, max_y] (inclusive).
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged nav_core2 at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.2.5 |
| License | BSD |
| Build type | CATKIN |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/locusrobotics/robot_navigation.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2020-07-03 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- David V. Lu!!
Authors
nav_core2
A replacement interface for nav_core that defines basic two dimensional planner interfaces.
There were a few key reasons for creating new interfaces rather than extending the old ones.
- Use
nav_2d_msgsto eliminate unused data fields - Use a new
Costmapinterface as a plugin rather that forcing all implementations of the interfaces to usecostmap_2d::Costmap2DROS. - Provide more data in the interfaces for easier testing.
- Use Exceptions rather than booleans to provide more information about the types of errors encountered.
Costmap
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS has been a vital part of the navigation stack for years, but it was not without its flaws.
- Initialization required a transform be available from the global frame to the base frame, which was later used to move rolling costmaps around (and a few other things). This made doing simple testing of any planner or other
Costmap2DROS-based behavior annoying, because transforms had to be set up, often outside of the immediate code that was being tested. - Initialization also started an update thread, which is also not always needed in testing.
- Using
Costmap2DROSlocked users into a layered costmap based approach, which made some tasks much easier, but didn’t give users the freedom to change the implementation.
The nav_core2::Costmap interface extends the nav_grid::NavGrid<unsigned char> for abstracting away the data storage and coordinate manipulation, and provides a few other key methods for costmap functioning such as
- a mutex
- a way to potentially track changes to the costmap
- a public
updatemethod that can be called in whatever thread you please
The Costmap can be loaded using pluginlib, allowing for arbitrary implementations of underlying update algorithms, include the layered costmap approach.
One basic implementation is provided in BasicCostmap. You can also use the nav_core_adapter::CostmapAdapter class which implements the Costmap interface while allowing you to still use Costmap2DROS.
Note: One could also imagine the Costmap interface being templatized itself like NavGrid instead of forcing use of unsigned char. While this may be possible, it was decided that it was a bit ambitious and the use of templates would force all of the implementation into headers, and would ultimately obfuscate the operation of algorithms.
Global Planner
Let us compare the old nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner to the new nav_core2/GlobalPlanner.
nav_core |
nav_core2 |
comments |
|---|---|---|
void initialize(std::string, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*) |
void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr) |
Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers, and provides a TFListener |
bool makePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&) |
nav_2d_msgs::Path2D makePlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&) |
Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual path. |
Local Planner
Now let’s compare the old nav_core::BaseLocalPlanner to the new nav_core2/LocalPlanner.
| nav_core | nav_core2 | comments |
|—|–|—|
|void initialize(std::string, tf::TransformListener*, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*)|void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr)|Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers|
|(no equivalent)|void setGoalPose(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&)|Explicitly set the new goal location, rather than using the last pose of the global plan
|bool setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&)|setPlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Path2D&)||
|bool computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist&)|nav_2d_msgs::Twist2DStamped computeVelocityCommands(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)|Explicitly provides the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual command.|
|bool isGoalReached() | bool isGoalReached(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)` | Explicitly provide the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. |
Exceptions
A hierarchical collection of exceptions is provided to allow for reacting to navigation failures in a more robust and contextual way.
 Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a
Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a StartBoundsException which has a corresponding result code of 6, it could also be seen as a InvalidStartPoseException, GlobalPlannerException, PlannerException or NavCore2Exception, all of which would also have the result code of 6.
Bounds
For use in tracking Costmap changes and more, this package also provides an implementation of bounding boxes. These are represented with the ranges [min_x, max_x] and [min_y, max_y] (inclusive).
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged nav_core2 at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.2.5 |
| License | BSD |
| Build type | CATKIN |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/locusrobotics/robot_navigation.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2020-07-03 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- David V. Lu!!
Authors
nav_core2
A replacement interface for nav_core that defines basic two dimensional planner interfaces.
There were a few key reasons for creating new interfaces rather than extending the old ones.
- Use
nav_2d_msgsto eliminate unused data fields - Use a new
Costmapinterface as a plugin rather that forcing all implementations of the interfaces to usecostmap_2d::Costmap2DROS. - Provide more data in the interfaces for easier testing.
- Use Exceptions rather than booleans to provide more information about the types of errors encountered.
Costmap
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS has been a vital part of the navigation stack for years, but it was not without its flaws.
- Initialization required a transform be available from the global frame to the base frame, which was later used to move rolling costmaps around (and a few other things). This made doing simple testing of any planner or other
Costmap2DROS-based behavior annoying, because transforms had to be set up, often outside of the immediate code that was being tested. - Initialization also started an update thread, which is also not always needed in testing.
- Using
Costmap2DROSlocked users into a layered costmap based approach, which made some tasks much easier, but didn’t give users the freedom to change the implementation.
The nav_core2::Costmap interface extends the nav_grid::NavGrid<unsigned char> for abstracting away the data storage and coordinate manipulation, and provides a few other key methods for costmap functioning such as
- a mutex
- a way to potentially track changes to the costmap
- a public
updatemethod that can be called in whatever thread you please
The Costmap can be loaded using pluginlib, allowing for arbitrary implementations of underlying update algorithms, include the layered costmap approach.
One basic implementation is provided in BasicCostmap. You can also use the nav_core_adapter::CostmapAdapter class which implements the Costmap interface while allowing you to still use Costmap2DROS.
Note: One could also imagine the Costmap interface being templatized itself like NavGrid instead of forcing use of unsigned char. While this may be possible, it was decided that it was a bit ambitious and the use of templates would force all of the implementation into headers, and would ultimately obfuscate the operation of algorithms.
Global Planner
Let us compare the old nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner to the new nav_core2/GlobalPlanner.
nav_core |
nav_core2 |
comments |
|---|---|---|
void initialize(std::string, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*) |
void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr) |
Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers, and provides a TFListener |
bool makePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&) |
nav_2d_msgs::Path2D makePlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&) |
Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual path. |
Local Planner
Now let’s compare the old nav_core::BaseLocalPlanner to the new nav_core2/LocalPlanner.
| nav_core | nav_core2 | comments |
|—|–|—|
|void initialize(std::string, tf::TransformListener*, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*)|void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr)|Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers|
|(no equivalent)|void setGoalPose(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&)|Explicitly set the new goal location, rather than using the last pose of the global plan
|bool setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&)|setPlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Path2D&)||
|bool computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist&)|nav_2d_msgs::Twist2DStamped computeVelocityCommands(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)|Explicitly provides the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual command.|
|bool isGoalReached() | bool isGoalReached(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)` | Explicitly provide the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. |
Exceptions
A hierarchical collection of exceptions is provided to allow for reacting to navigation failures in a more robust and contextual way.
 Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a
Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a StartBoundsException which has a corresponding result code of 6, it could also be seen as a InvalidStartPoseException, GlobalPlannerException, PlannerException or NavCore2Exception, all of which would also have the result code of 6.
Bounds
For use in tracking Costmap changes and more, this package also provides an implementation of bounding boxes. These are represented with the ranges [min_x, max_x] and [min_y, max_y] (inclusive).
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged nav_core2 at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.2.5 |
| License | BSD |
| Build type | CATKIN |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/locusrobotics/robot_navigation.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2020-07-03 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- David V. Lu!!
Authors
nav_core2
A replacement interface for nav_core that defines basic two dimensional planner interfaces.
There were a few key reasons for creating new interfaces rather than extending the old ones.
- Use
nav_2d_msgsto eliminate unused data fields - Use a new
Costmapinterface as a plugin rather that forcing all implementations of the interfaces to usecostmap_2d::Costmap2DROS. - Provide more data in the interfaces for easier testing.
- Use Exceptions rather than booleans to provide more information about the types of errors encountered.
Costmap
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS has been a vital part of the navigation stack for years, but it was not without its flaws.
- Initialization required a transform be available from the global frame to the base frame, which was later used to move rolling costmaps around (and a few other things). This made doing simple testing of any planner or other
Costmap2DROS-based behavior annoying, because transforms had to be set up, often outside of the immediate code that was being tested. - Initialization also started an update thread, which is also not always needed in testing.
- Using
Costmap2DROSlocked users into a layered costmap based approach, which made some tasks much easier, but didn’t give users the freedom to change the implementation.
The nav_core2::Costmap interface extends the nav_grid::NavGrid<unsigned char> for abstracting away the data storage and coordinate manipulation, and provides a few other key methods for costmap functioning such as
- a mutex
- a way to potentially track changes to the costmap
- a public
updatemethod that can be called in whatever thread you please
The Costmap can be loaded using pluginlib, allowing for arbitrary implementations of underlying update algorithms, include the layered costmap approach.
One basic implementation is provided in BasicCostmap. You can also use the nav_core_adapter::CostmapAdapter class which implements the Costmap interface while allowing you to still use Costmap2DROS.
Note: One could also imagine the Costmap interface being templatized itself like NavGrid instead of forcing use of unsigned char. While this may be possible, it was decided that it was a bit ambitious and the use of templates would force all of the implementation into headers, and would ultimately obfuscate the operation of algorithms.
Global Planner
Let us compare the old nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner to the new nav_core2/GlobalPlanner.
nav_core |
nav_core2 |
comments |
|---|---|---|
void initialize(std::string, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*) |
void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr) |
Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers, and provides a TFListener |
bool makePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&) |
nav_2d_msgs::Path2D makePlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&) |
Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual path. |
Local Planner
Now let’s compare the old nav_core::BaseLocalPlanner to the new nav_core2/LocalPlanner.
| nav_core | nav_core2 | comments |
|—|–|—|
|void initialize(std::string, tf::TransformListener*, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*)|void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr)|Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers|
|(no equivalent)|void setGoalPose(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&)|Explicitly set the new goal location, rather than using the last pose of the global plan
|bool setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&)|setPlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Path2D&)||
|bool computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist&)|nav_2d_msgs::Twist2DStamped computeVelocityCommands(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)|Explicitly provides the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual command.|
|bool isGoalReached() | bool isGoalReached(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)` | Explicitly provide the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. |
Exceptions
A hierarchical collection of exceptions is provided to allow for reacting to navigation failures in a more robust and contextual way.
 Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a
Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a StartBoundsException which has a corresponding result code of 6, it could also be seen as a InvalidStartPoseException, GlobalPlannerException, PlannerException or NavCore2Exception, all of which would also have the result code of 6.
Bounds
For use in tracking Costmap changes and more, this package also provides an implementation of bounding boxes. These are represented with the ranges [min_x, max_x] and [min_y, max_y] (inclusive).
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged nav_core2 at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.2.5 |
| License | BSD |
| Build type | CATKIN |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/locusrobotics/robot_navigation.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2020-07-03 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- David V. Lu!!
Authors
nav_core2
A replacement interface for nav_core that defines basic two dimensional planner interfaces.
There were a few key reasons for creating new interfaces rather than extending the old ones.
- Use
nav_2d_msgsto eliminate unused data fields - Use a new
Costmapinterface as a plugin rather that forcing all implementations of the interfaces to usecostmap_2d::Costmap2DROS. - Provide more data in the interfaces for easier testing.
- Use Exceptions rather than booleans to provide more information about the types of errors encountered.
Costmap
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS has been a vital part of the navigation stack for years, but it was not without its flaws.
- Initialization required a transform be available from the global frame to the base frame, which was later used to move rolling costmaps around (and a few other things). This made doing simple testing of any planner or other
Costmap2DROS-based behavior annoying, because transforms had to be set up, often outside of the immediate code that was being tested. - Initialization also started an update thread, which is also not always needed in testing.
- Using
Costmap2DROSlocked users into a layered costmap based approach, which made some tasks much easier, but didn’t give users the freedom to change the implementation.
The nav_core2::Costmap interface extends the nav_grid::NavGrid<unsigned char> for abstracting away the data storage and coordinate manipulation, and provides a few other key methods for costmap functioning such as
- a mutex
- a way to potentially track changes to the costmap
- a public
updatemethod that can be called in whatever thread you please
The Costmap can be loaded using pluginlib, allowing for arbitrary implementations of underlying update algorithms, include the layered costmap approach.
One basic implementation is provided in BasicCostmap. You can also use the nav_core_adapter::CostmapAdapter class which implements the Costmap interface while allowing you to still use Costmap2DROS.
Note: One could also imagine the Costmap interface being templatized itself like NavGrid instead of forcing use of unsigned char. While this may be possible, it was decided that it was a bit ambitious and the use of templates would force all of the implementation into headers, and would ultimately obfuscate the operation of algorithms.
Global Planner
Let us compare the old nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner to the new nav_core2/GlobalPlanner.
nav_core |
nav_core2 |
comments |
|---|---|---|
void initialize(std::string, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*) |
void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr) |
Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers, and provides a TFListener |
bool makePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&) |
nav_2d_msgs::Path2D makePlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&) |
Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual path. |
Local Planner
Now let’s compare the old nav_core::BaseLocalPlanner to the new nav_core2/LocalPlanner.
| nav_core | nav_core2 | comments |
|—|–|—|
|void initialize(std::string, tf::TransformListener*, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*)|void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr)|Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers|
|(no equivalent)|void setGoalPose(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&)|Explicitly set the new goal location, rather than using the last pose of the global plan
|bool setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&)|setPlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Path2D&)||
|bool computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist&)|nav_2d_msgs::Twist2DStamped computeVelocityCommands(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)|Explicitly provides the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual command.|
|bool isGoalReached() | bool isGoalReached(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)` | Explicitly provide the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. |
Exceptions
A hierarchical collection of exceptions is provided to allow for reacting to navigation failures in a more robust and contextual way.
 Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a
Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a StartBoundsException which has a corresponding result code of 6, it could also be seen as a InvalidStartPoseException, GlobalPlannerException, PlannerException or NavCore2Exception, all of which would also have the result code of 6.
Bounds
For use in tracking Costmap changes and more, this package also provides an implementation of bounding boxes. These are represented with the ranges [min_x, max_x] and [min_y, max_y] (inclusive).
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged nav_core2 at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.2.5 |
| License | BSD |
| Build type | CATKIN |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/locusrobotics/robot_navigation.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2020-07-03 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- David V. Lu!!
Authors
nav_core2
A replacement interface for nav_core that defines basic two dimensional planner interfaces.
There were a few key reasons for creating new interfaces rather than extending the old ones.
- Use
nav_2d_msgsto eliminate unused data fields - Use a new
Costmapinterface as a plugin rather that forcing all implementations of the interfaces to usecostmap_2d::Costmap2DROS. - Provide more data in the interfaces for easier testing.
- Use Exceptions rather than booleans to provide more information about the types of errors encountered.
Costmap
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS has been a vital part of the navigation stack for years, but it was not without its flaws.
- Initialization required a transform be available from the global frame to the base frame, which was later used to move rolling costmaps around (and a few other things). This made doing simple testing of any planner or other
Costmap2DROS-based behavior annoying, because transforms had to be set up, often outside of the immediate code that was being tested. - Initialization also started an update thread, which is also not always needed in testing.
- Using
Costmap2DROSlocked users into a layered costmap based approach, which made some tasks much easier, but didn’t give users the freedom to change the implementation.
The nav_core2::Costmap interface extends the nav_grid::NavGrid<unsigned char> for abstracting away the data storage and coordinate manipulation, and provides a few other key methods for costmap functioning such as
- a mutex
- a way to potentially track changes to the costmap
- a public
updatemethod that can be called in whatever thread you please
The Costmap can be loaded using pluginlib, allowing for arbitrary implementations of underlying update algorithms, include the layered costmap approach.
One basic implementation is provided in BasicCostmap. You can also use the nav_core_adapter::CostmapAdapter class which implements the Costmap interface while allowing you to still use Costmap2DROS.
Note: One could also imagine the Costmap interface being templatized itself like NavGrid instead of forcing use of unsigned char. While this may be possible, it was decided that it was a bit ambitious and the use of templates would force all of the implementation into headers, and would ultimately obfuscate the operation of algorithms.
Global Planner
Let us compare the old nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner to the new nav_core2/GlobalPlanner.
nav_core |
nav_core2 |
comments |
|---|---|---|
void initialize(std::string, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*) |
void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr) |
Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers, and provides a TFListener |
bool makePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&) |
nav_2d_msgs::Path2D makePlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&) |
Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual path. |
Local Planner
Now let’s compare the old nav_core::BaseLocalPlanner to the new nav_core2/LocalPlanner.
| nav_core | nav_core2 | comments |
|—|–|—|
|void initialize(std::string, tf::TransformListener*, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*)|void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr)|Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers|
|(no equivalent)|void setGoalPose(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&)|Explicitly set the new goal location, rather than using the last pose of the global plan
|bool setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&)|setPlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Path2D&)||
|bool computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist&)|nav_2d_msgs::Twist2DStamped computeVelocityCommands(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)|Explicitly provides the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual command.|
|bool isGoalReached() | bool isGoalReached(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)` | Explicitly provide the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. |
Exceptions
A hierarchical collection of exceptions is provided to allow for reacting to navigation failures in a more robust and contextual way.
 Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a
Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a StartBoundsException which has a corresponding result code of 6, it could also be seen as a InvalidStartPoseException, GlobalPlannerException, PlannerException or NavCore2Exception, all of which would also have the result code of 6.
Bounds
For use in tracking Costmap changes and more, this package also provides an implementation of bounding boxes. These are represented with the ranges [min_x, max_x] and [min_y, max_y] (inclusive).
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged nav_core2 at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.2.5 |
| License | BSD |
| Build type | CATKIN |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/locusrobotics/robot_navigation.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2020-07-03 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- David V. Lu!!
Authors
nav_core2
A replacement interface for nav_core that defines basic two dimensional planner interfaces.
There were a few key reasons for creating new interfaces rather than extending the old ones.
- Use
nav_2d_msgsto eliminate unused data fields - Use a new
Costmapinterface as a plugin rather that forcing all implementations of the interfaces to usecostmap_2d::Costmap2DROS. - Provide more data in the interfaces for easier testing.
- Use Exceptions rather than booleans to provide more information about the types of errors encountered.
Costmap
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS has been a vital part of the navigation stack for years, but it was not without its flaws.
- Initialization required a transform be available from the global frame to the base frame, which was later used to move rolling costmaps around (and a few other things). This made doing simple testing of any planner or other
Costmap2DROS-based behavior annoying, because transforms had to be set up, often outside of the immediate code that was being tested. - Initialization also started an update thread, which is also not always needed in testing.
- Using
Costmap2DROSlocked users into a layered costmap based approach, which made some tasks much easier, but didn’t give users the freedom to change the implementation.
The nav_core2::Costmap interface extends the nav_grid::NavGrid<unsigned char> for abstracting away the data storage and coordinate manipulation, and provides a few other key methods for costmap functioning such as
- a mutex
- a way to potentially track changes to the costmap
- a public
updatemethod that can be called in whatever thread you please
The Costmap can be loaded using pluginlib, allowing for arbitrary implementations of underlying update algorithms, include the layered costmap approach.
One basic implementation is provided in BasicCostmap. You can also use the nav_core_adapter::CostmapAdapter class which implements the Costmap interface while allowing you to still use Costmap2DROS.
Note: One could also imagine the Costmap interface being templatized itself like NavGrid instead of forcing use of unsigned char. While this may be possible, it was decided that it was a bit ambitious and the use of templates would force all of the implementation into headers, and would ultimately obfuscate the operation of algorithms.
Global Planner
Let us compare the old nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner to the new nav_core2/GlobalPlanner.
nav_core |
nav_core2 |
comments |
|---|---|---|
void initialize(std::string, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*) |
void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr) |
Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers, and provides a TFListener |
bool makePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&) |
nav_2d_msgs::Path2D makePlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&) |
Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual path. |
Local Planner
Now let’s compare the old nav_core::BaseLocalPlanner to the new nav_core2/LocalPlanner.
| nav_core | nav_core2 | comments |
|—|–|—|
|void initialize(std::string, tf::TransformListener*, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*)|void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr)|Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers|
|(no equivalent)|void setGoalPose(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&)|Explicitly set the new goal location, rather than using the last pose of the global plan
|bool setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&)|setPlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Path2D&)||
|bool computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist&)|nav_2d_msgs::Twist2DStamped computeVelocityCommands(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)|Explicitly provides the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual command.|
|bool isGoalReached() | bool isGoalReached(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)` | Explicitly provide the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. |
Exceptions
A hierarchical collection of exceptions is provided to allow for reacting to navigation failures in a more robust and contextual way.
 Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a
Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a StartBoundsException which has a corresponding result code of 6, it could also be seen as a InvalidStartPoseException, GlobalPlannerException, PlannerException or NavCore2Exception, all of which would also have the result code of 6.
Bounds
For use in tracking Costmap changes and more, this package also provides an implementation of bounding boxes. These are represented with the ranges [min_x, max_x] and [min_y, max_y] (inclusive).
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged nav_core2 at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.2.5 |
| License | BSD |
| Build type | CATKIN |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/locusrobotics/robot_navigation.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2020-07-03 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- David V. Lu!!
Authors
nav_core2
A replacement interface for nav_core that defines basic two dimensional planner interfaces.
There were a few key reasons for creating new interfaces rather than extending the old ones.
- Use
nav_2d_msgsto eliminate unused data fields - Use a new
Costmapinterface as a plugin rather that forcing all implementations of the interfaces to usecostmap_2d::Costmap2DROS. - Provide more data in the interfaces for easier testing.
- Use Exceptions rather than booleans to provide more information about the types of errors encountered.
Costmap
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS has been a vital part of the navigation stack for years, but it was not without its flaws.
- Initialization required a transform be available from the global frame to the base frame, which was later used to move rolling costmaps around (and a few other things). This made doing simple testing of any planner or other
Costmap2DROS-based behavior annoying, because transforms had to be set up, often outside of the immediate code that was being tested. - Initialization also started an update thread, which is also not always needed in testing.
- Using
Costmap2DROSlocked users into a layered costmap based approach, which made some tasks much easier, but didn’t give users the freedom to change the implementation.
The nav_core2::Costmap interface extends the nav_grid::NavGrid<unsigned char> for abstracting away the data storage and coordinate manipulation, and provides a few other key methods for costmap functioning such as
- a mutex
- a way to potentially track changes to the costmap
- a public
updatemethod that can be called in whatever thread you please
The Costmap can be loaded using pluginlib, allowing for arbitrary implementations of underlying update algorithms, include the layered costmap approach.
One basic implementation is provided in BasicCostmap. You can also use the nav_core_adapter::CostmapAdapter class which implements the Costmap interface while allowing you to still use Costmap2DROS.
Note: One could also imagine the Costmap interface being templatized itself like NavGrid instead of forcing use of unsigned char. While this may be possible, it was decided that it was a bit ambitious and the use of templates would force all of the implementation into headers, and would ultimately obfuscate the operation of algorithms.
Global Planner
Let us compare the old nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner to the new nav_core2/GlobalPlanner.
nav_core |
nav_core2 |
comments |
|---|---|---|
void initialize(std::string, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*) |
void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr) |
Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers, and provides a TFListener |
bool makePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&) |
nav_2d_msgs::Path2D makePlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&) |
Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual path. |
Local Planner
Now let’s compare the old nav_core::BaseLocalPlanner to the new nav_core2/LocalPlanner.
| nav_core | nav_core2 | comments |
|—|–|—|
|void initialize(std::string, tf::TransformListener*, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*)|void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr)|Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers|
|(no equivalent)|void setGoalPose(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&)|Explicitly set the new goal location, rather than using the last pose of the global plan
|bool setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&)|setPlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Path2D&)||
|bool computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist&)|nav_2d_msgs::Twist2DStamped computeVelocityCommands(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)|Explicitly provides the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual command.|
|bool isGoalReached() | bool isGoalReached(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)` | Explicitly provide the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. |
Exceptions
A hierarchical collection of exceptions is provided to allow for reacting to navigation failures in a more robust and contextual way.
 Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a
Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a StartBoundsException which has a corresponding result code of 6, it could also be seen as a InvalidStartPoseException, GlobalPlannerException, PlannerException or NavCore2Exception, all of which would also have the result code of 6.
Bounds
For use in tracking Costmap changes and more, this package also provides an implementation of bounding boxes. These are represented with the ranges [min_x, max_x] and [min_y, max_y] (inclusive).
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged nav_core2 at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.2.5 |
| License | BSD |
| Build type | CATKIN |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/locusrobotics/robot_navigation.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2020-07-03 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- David V. Lu!!
Authors
nav_core2
A replacement interface for nav_core that defines basic two dimensional planner interfaces.
There were a few key reasons for creating new interfaces rather than extending the old ones.
- Use
nav_2d_msgsto eliminate unused data fields - Use a new
Costmapinterface as a plugin rather that forcing all implementations of the interfaces to usecostmap_2d::Costmap2DROS. - Provide more data in the interfaces for easier testing.
- Use Exceptions rather than booleans to provide more information about the types of errors encountered.
Costmap
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS has been a vital part of the navigation stack for years, but it was not without its flaws.
- Initialization required a transform be available from the global frame to the base frame, which was later used to move rolling costmaps around (and a few other things). This made doing simple testing of any planner or other
Costmap2DROS-based behavior annoying, because transforms had to be set up, often outside of the immediate code that was being tested. - Initialization also started an update thread, which is also not always needed in testing.
- Using
Costmap2DROSlocked users into a layered costmap based approach, which made some tasks much easier, but didn’t give users the freedom to change the implementation.
The nav_core2::Costmap interface extends the nav_grid::NavGrid<unsigned char> for abstracting away the data storage and coordinate manipulation, and provides a few other key methods for costmap functioning such as
- a mutex
- a way to potentially track changes to the costmap
- a public
updatemethod that can be called in whatever thread you please
The Costmap can be loaded using pluginlib, allowing for arbitrary implementations of underlying update algorithms, include the layered costmap approach.
One basic implementation is provided in BasicCostmap. You can also use the nav_core_adapter::CostmapAdapter class which implements the Costmap interface while allowing you to still use Costmap2DROS.
Note: One could also imagine the Costmap interface being templatized itself like NavGrid instead of forcing use of unsigned char. While this may be possible, it was decided that it was a bit ambitious and the use of templates would force all of the implementation into headers, and would ultimately obfuscate the operation of algorithms.
Global Planner
Let us compare the old nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner to the new nav_core2/GlobalPlanner.
nav_core |
nav_core2 |
comments |
|---|---|---|
void initialize(std::string, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*) |
void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr) |
Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers, and provides a TFListener |
bool makePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&) |
nav_2d_msgs::Path2D makePlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&) |
Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual path. |
Local Planner
Now let’s compare the old nav_core::BaseLocalPlanner to the new nav_core2/LocalPlanner.
| nav_core | nav_core2 | comments |
|—|–|—|
|void initialize(std::string, tf::TransformListener*, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*)|void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr)|Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers|
|(no equivalent)|void setGoalPose(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&)|Explicitly set the new goal location, rather than using the last pose of the global plan
|bool setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&)|setPlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Path2D&)||
|bool computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist&)|nav_2d_msgs::Twist2DStamped computeVelocityCommands(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)|Explicitly provides the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual command.|
|bool isGoalReached() | bool isGoalReached(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)` | Explicitly provide the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. |
Exceptions
A hierarchical collection of exceptions is provided to allow for reacting to navigation failures in a more robust and contextual way.
 Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a
Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a StartBoundsException which has a corresponding result code of 6, it could also be seen as a InvalidStartPoseException, GlobalPlannerException, PlannerException or NavCore2Exception, all of which would also have the result code of 6.
Bounds
For use in tracking Costmap changes and more, this package also provides an implementation of bounding boxes. These are represented with the ranges [min_x, max_x] and [min_y, max_y] (inclusive).
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged nav_core2 at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.2.5 |
| License | BSD |
| Build type | CATKIN |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/locusrobotics/robot_navigation.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2020-07-03 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- David V. Lu!!
Authors
nav_core2
A replacement interface for nav_core that defines basic two dimensional planner interfaces.
There were a few key reasons for creating new interfaces rather than extending the old ones.
- Use
nav_2d_msgsto eliminate unused data fields - Use a new
Costmapinterface as a plugin rather that forcing all implementations of the interfaces to usecostmap_2d::Costmap2DROS. - Provide more data in the interfaces for easier testing.
- Use Exceptions rather than booleans to provide more information about the types of errors encountered.
Costmap
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS has been a vital part of the navigation stack for years, but it was not without its flaws.
- Initialization required a transform be available from the global frame to the base frame, which was later used to move rolling costmaps around (and a few other things). This made doing simple testing of any planner or other
Costmap2DROS-based behavior annoying, because transforms had to be set up, often outside of the immediate code that was being tested. - Initialization also started an update thread, which is also not always needed in testing.
- Using
Costmap2DROSlocked users into a layered costmap based approach, which made some tasks much easier, but didn’t give users the freedom to change the implementation.
The nav_core2::Costmap interface extends the nav_grid::NavGrid<unsigned char> for abstracting away the data storage and coordinate manipulation, and provides a few other key methods for costmap functioning such as
- a mutex
- a way to potentially track changes to the costmap
- a public
updatemethod that can be called in whatever thread you please
The Costmap can be loaded using pluginlib, allowing for arbitrary implementations of underlying update algorithms, include the layered costmap approach.
One basic implementation is provided in BasicCostmap. You can also use the nav_core_adapter::CostmapAdapter class which implements the Costmap interface while allowing you to still use Costmap2DROS.
Note: One could also imagine the Costmap interface being templatized itself like NavGrid instead of forcing use of unsigned char. While this may be possible, it was decided that it was a bit ambitious and the use of templates would force all of the implementation into headers, and would ultimately obfuscate the operation of algorithms.
Global Planner
Let us compare the old nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner to the new nav_core2/GlobalPlanner.
nav_core |
nav_core2 |
comments |
|---|---|---|
void initialize(std::string, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*) |
void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr) |
Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers, and provides a TFListener |
bool makePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&) |
nav_2d_msgs::Path2D makePlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&) |
Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual path. |
Local Planner
Now let’s compare the old nav_core::BaseLocalPlanner to the new nav_core2/LocalPlanner.
| nav_core | nav_core2 | comments |
|—|–|—|
|void initialize(std::string, tf::TransformListener*, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*)|void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr)|Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers|
|(no equivalent)|void setGoalPose(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&)|Explicitly set the new goal location, rather than using the last pose of the global plan
|bool setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&)|setPlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Path2D&)||
|bool computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist&)|nav_2d_msgs::Twist2DStamped computeVelocityCommands(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)|Explicitly provides the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual command.|
|bool isGoalReached() | bool isGoalReached(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)` | Explicitly provide the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. |
Exceptions
A hierarchical collection of exceptions is provided to allow for reacting to navigation failures in a more robust and contextual way.
 Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a
Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a StartBoundsException which has a corresponding result code of 6, it could also be seen as a InvalidStartPoseException, GlobalPlannerException, PlannerException or NavCore2Exception, all of which would also have the result code of 6.
Bounds
For use in tracking Costmap changes and more, this package also provides an implementation of bounding boxes. These are represented with the ranges [min_x, max_x] and [min_y, max_y] (inclusive).
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged nav_core2 at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.2.5 |
| License | BSD |
| Build type | CATKIN |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/locusrobotics/robot_navigation.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2020-07-03 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- David V. Lu!!
Authors
nav_core2
A replacement interface for nav_core that defines basic two dimensional planner interfaces.
There were a few key reasons for creating new interfaces rather than extending the old ones.
- Use
nav_2d_msgsto eliminate unused data fields - Use a new
Costmapinterface as a plugin rather that forcing all implementations of the interfaces to usecostmap_2d::Costmap2DROS. - Provide more data in the interfaces for easier testing.
- Use Exceptions rather than booleans to provide more information about the types of errors encountered.
Costmap
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS has been a vital part of the navigation stack for years, but it was not without its flaws.
- Initialization required a transform be available from the global frame to the base frame, which was later used to move rolling costmaps around (and a few other things). This made doing simple testing of any planner or other
Costmap2DROS-based behavior annoying, because transforms had to be set up, often outside of the immediate code that was being tested. - Initialization also started an update thread, which is also not always needed in testing.
- Using
Costmap2DROSlocked users into a layered costmap based approach, which made some tasks much easier, but didn’t give users the freedom to change the implementation.
The nav_core2::Costmap interface extends the nav_grid::NavGrid<unsigned char> for abstracting away the data storage and coordinate manipulation, and provides a few other key methods for costmap functioning such as
- a mutex
- a way to potentially track changes to the costmap
- a public
updatemethod that can be called in whatever thread you please
The Costmap can be loaded using pluginlib, allowing for arbitrary implementations of underlying update algorithms, include the layered costmap approach.
One basic implementation is provided in BasicCostmap. You can also use the nav_core_adapter::CostmapAdapter class which implements the Costmap interface while allowing you to still use Costmap2DROS.
Note: One could also imagine the Costmap interface being templatized itself like NavGrid instead of forcing use of unsigned char. While this may be possible, it was decided that it was a bit ambitious and the use of templates would force all of the implementation into headers, and would ultimately obfuscate the operation of algorithms.
Global Planner
Let us compare the old nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner to the new nav_core2/GlobalPlanner.
nav_core |
nav_core2 |
comments |
|---|---|---|
void initialize(std::string, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*) |
void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr) |
Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers, and provides a TFListener |
bool makePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&) |
nav_2d_msgs::Path2D makePlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&) |
Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual path. |
Local Planner
Now let’s compare the old nav_core::BaseLocalPlanner to the new nav_core2/LocalPlanner.
| nav_core | nav_core2 | comments |
|—|–|—|
|void initialize(std::string, tf::TransformListener*, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*)|void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr)|Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers|
|(no equivalent)|void setGoalPose(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&)|Explicitly set the new goal location, rather than using the last pose of the global plan
|bool setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&)|setPlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Path2D&)||
|bool computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist&)|nav_2d_msgs::Twist2DStamped computeVelocityCommands(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)|Explicitly provides the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual command.|
|bool isGoalReached() | bool isGoalReached(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)` | Explicitly provide the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. |
Exceptions
A hierarchical collection of exceptions is provided to allow for reacting to navigation failures in a more robust and contextual way.
 Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a
Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a StartBoundsException which has a corresponding result code of 6, it could also be seen as a InvalidStartPoseException, GlobalPlannerException, PlannerException or NavCore2Exception, all of which would also have the result code of 6.
Bounds
For use in tracking Costmap changes and more, this package also provides an implementation of bounding boxes. These are represented with the ranges [min_x, max_x] and [min_y, max_y] (inclusive).
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged nav_core2 at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.2.5 |
| License | BSD |
| Build type | CATKIN |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/locusrobotics/robot_navigation.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2020-07-03 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- David V. Lu!!
Authors
nav_core2
A replacement interface for nav_core that defines basic two dimensional planner interfaces.
There were a few key reasons for creating new interfaces rather than extending the old ones.
- Use
nav_2d_msgsto eliminate unused data fields - Use a new
Costmapinterface as a plugin rather that forcing all implementations of the interfaces to usecostmap_2d::Costmap2DROS. - Provide more data in the interfaces for easier testing.
- Use Exceptions rather than booleans to provide more information about the types of errors encountered.
Costmap
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS has been a vital part of the navigation stack for years, but it was not without its flaws.
- Initialization required a transform be available from the global frame to the base frame, which was later used to move rolling costmaps around (and a few other things). This made doing simple testing of any planner or other
Costmap2DROS-based behavior annoying, because transforms had to be set up, often outside of the immediate code that was being tested. - Initialization also started an update thread, which is also not always needed in testing.
- Using
Costmap2DROSlocked users into a layered costmap based approach, which made some tasks much easier, but didn’t give users the freedom to change the implementation.
The nav_core2::Costmap interface extends the nav_grid::NavGrid<unsigned char> for abstracting away the data storage and coordinate manipulation, and provides a few other key methods for costmap functioning such as
- a mutex
- a way to potentially track changes to the costmap
- a public
updatemethod that can be called in whatever thread you please
The Costmap can be loaded using pluginlib, allowing for arbitrary implementations of underlying update algorithms, include the layered costmap approach.
One basic implementation is provided in BasicCostmap. You can also use the nav_core_adapter::CostmapAdapter class which implements the Costmap interface while allowing you to still use Costmap2DROS.
Note: One could also imagine the Costmap interface being templatized itself like NavGrid instead of forcing use of unsigned char. While this may be possible, it was decided that it was a bit ambitious and the use of templates would force all of the implementation into headers, and would ultimately obfuscate the operation of algorithms.
Global Planner
Let us compare the old nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner to the new nav_core2/GlobalPlanner.
nav_core |
nav_core2 |
comments |
|---|---|---|
void initialize(std::string, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*) |
void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr) |
Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers, and provides a TFListener |
bool makePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&) |
nav_2d_msgs::Path2D makePlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&) |
Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual path. |
Local Planner
Now let’s compare the old nav_core::BaseLocalPlanner to the new nav_core2/LocalPlanner.
| nav_core | nav_core2 | comments |
|—|–|—|
|void initialize(std::string, tf::TransformListener*, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*)|void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr)|Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers|
|(no equivalent)|void setGoalPose(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&)|Explicitly set the new goal location, rather than using the last pose of the global plan
|bool setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&)|setPlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Path2D&)||
|bool computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist&)|nav_2d_msgs::Twist2DStamped computeVelocityCommands(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)|Explicitly provides the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual command.|
|bool isGoalReached() | bool isGoalReached(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)` | Explicitly provide the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. |
Exceptions
A hierarchical collection of exceptions is provided to allow for reacting to navigation failures in a more robust and contextual way.
 Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a
Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a StartBoundsException which has a corresponding result code of 6, it could also be seen as a InvalidStartPoseException, GlobalPlannerException, PlannerException or NavCore2Exception, all of which would also have the result code of 6.
Bounds
For use in tracking Costmap changes and more, this package also provides an implementation of bounding boxes. These are represented with the ranges [min_x, max_x] and [min_y, max_y] (inclusive).
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged nav_core2 at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.2.5 |
| License | BSD |
| Build type | CATKIN |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/locusrobotics/robot_navigation.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2020-07-03 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- David V. Lu!!
Authors
nav_core2
A replacement interface for nav_core that defines basic two dimensional planner interfaces.
There were a few key reasons for creating new interfaces rather than extending the old ones.
- Use
nav_2d_msgsto eliminate unused data fields - Use a new
Costmapinterface as a plugin rather that forcing all implementations of the interfaces to usecostmap_2d::Costmap2DROS. - Provide more data in the interfaces for easier testing.
- Use Exceptions rather than booleans to provide more information about the types of errors encountered.
Costmap
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS has been a vital part of the navigation stack for years, but it was not without its flaws.
- Initialization required a transform be available from the global frame to the base frame, which was later used to move rolling costmaps around (and a few other things). This made doing simple testing of any planner or other
Costmap2DROS-based behavior annoying, because transforms had to be set up, often outside of the immediate code that was being tested. - Initialization also started an update thread, which is also not always needed in testing.
- Using
Costmap2DROSlocked users into a layered costmap based approach, which made some tasks much easier, but didn’t give users the freedom to change the implementation.
The nav_core2::Costmap interface extends the nav_grid::NavGrid<unsigned char> for abstracting away the data storage and coordinate manipulation, and provides a few other key methods for costmap functioning such as
- a mutex
- a way to potentially track changes to the costmap
- a public
updatemethod that can be called in whatever thread you please
The Costmap can be loaded using pluginlib, allowing for arbitrary implementations of underlying update algorithms, include the layered costmap approach.
One basic implementation is provided in BasicCostmap. You can also use the nav_core_adapter::CostmapAdapter class which implements the Costmap interface while allowing you to still use Costmap2DROS.
Note: One could also imagine the Costmap interface being templatized itself like NavGrid instead of forcing use of unsigned char. While this may be possible, it was decided that it was a bit ambitious and the use of templates would force all of the implementation into headers, and would ultimately obfuscate the operation of algorithms.
Global Planner
Let us compare the old nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner to the new nav_core2/GlobalPlanner.
nav_core |
nav_core2 |
comments |
|---|---|---|
void initialize(std::string, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*) |
void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr) |
Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers, and provides a TFListener |
bool makePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&) |
nav_2d_msgs::Path2D makePlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&) |
Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual path. |
Local Planner
Now let’s compare the old nav_core::BaseLocalPlanner to the new nav_core2/LocalPlanner.
| nav_core | nav_core2 | comments |
|—|–|—|
|void initialize(std::string, tf::TransformListener*, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*)|void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr)|Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers|
|(no equivalent)|void setGoalPose(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&)|Explicitly set the new goal location, rather than using the last pose of the global plan
|bool setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&)|setPlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Path2D&)||
|bool computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist&)|nav_2d_msgs::Twist2DStamped computeVelocityCommands(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)|Explicitly provides the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual command.|
|bool isGoalReached() | bool isGoalReached(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)` | Explicitly provide the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. |
Exceptions
A hierarchical collection of exceptions is provided to allow for reacting to navigation failures in a more robust and contextual way.
 Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a
Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a StartBoundsException which has a corresponding result code of 6, it could also be seen as a InvalidStartPoseException, GlobalPlannerException, PlannerException or NavCore2Exception, all of which would also have the result code of 6.
Bounds
For use in tracking Costmap changes and more, this package also provides an implementation of bounding boxes. These are represented with the ranges [min_x, max_x] and [min_y, max_y] (inclusive).
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged nav_core2 at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.2.5 |
| License | BSD |
| Build type | CATKIN |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/locusrobotics/robot_navigation.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2020-07-03 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- David V. Lu!!
Authors
nav_core2
A replacement interface for nav_core that defines basic two dimensional planner interfaces.
There were a few key reasons for creating new interfaces rather than extending the old ones.
- Use
nav_2d_msgsto eliminate unused data fields - Use a new
Costmapinterface as a plugin rather that forcing all implementations of the interfaces to usecostmap_2d::Costmap2DROS. - Provide more data in the interfaces for easier testing.
- Use Exceptions rather than booleans to provide more information about the types of errors encountered.
Costmap
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS has been a vital part of the navigation stack for years, but it was not without its flaws.
- Initialization required a transform be available from the global frame to the base frame, which was later used to move rolling costmaps around (and a few other things). This made doing simple testing of any planner or other
Costmap2DROS-based behavior annoying, because transforms had to be set up, often outside of the immediate code that was being tested. - Initialization also started an update thread, which is also not always needed in testing.
- Using
Costmap2DROSlocked users into a layered costmap based approach, which made some tasks much easier, but didn’t give users the freedom to change the implementation.
The nav_core2::Costmap interface extends the nav_grid::NavGrid<unsigned char> for abstracting away the data storage and coordinate manipulation, and provides a few other key methods for costmap functioning such as
- a mutex
- a way to potentially track changes to the costmap
- a public
updatemethod that can be called in whatever thread you please
The Costmap can be loaded using pluginlib, allowing for arbitrary implementations of underlying update algorithms, include the layered costmap approach.
One basic implementation is provided in BasicCostmap. You can also use the nav_core_adapter::CostmapAdapter class which implements the Costmap interface while allowing you to still use Costmap2DROS.
Note: One could also imagine the Costmap interface being templatized itself like NavGrid instead of forcing use of unsigned char. While this may be possible, it was decided that it was a bit ambitious and the use of templates would force all of the implementation into headers, and would ultimately obfuscate the operation of algorithms.
Global Planner
Let us compare the old nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner to the new nav_core2/GlobalPlanner.
nav_core |
nav_core2 |
comments |
|---|---|---|
void initialize(std::string, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*) |
void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr) |
Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers, and provides a TFListener |
bool makePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&) |
nav_2d_msgs::Path2D makePlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&) |
Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual path. |
Local Planner
Now let’s compare the old nav_core::BaseLocalPlanner to the new nav_core2/LocalPlanner.
| nav_core | nav_core2 | comments |
|—|–|—|
|void initialize(std::string, tf::TransformListener*, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*)|void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr)|Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers|
|(no equivalent)|void setGoalPose(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&)|Explicitly set the new goal location, rather than using the last pose of the global plan
|bool setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&)|setPlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Path2D&)||
|bool computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist&)|nav_2d_msgs::Twist2DStamped computeVelocityCommands(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)|Explicitly provides the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual command.|
|bool isGoalReached() | bool isGoalReached(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)` | Explicitly provide the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. |
Exceptions
A hierarchical collection of exceptions is provided to allow for reacting to navigation failures in a more robust and contextual way.
 Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a
Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a StartBoundsException which has a corresponding result code of 6, it could also be seen as a InvalidStartPoseException, GlobalPlannerException, PlannerException or NavCore2Exception, all of which would also have the result code of 6.
Bounds
For use in tracking Costmap changes and more, this package also provides an implementation of bounding boxes. These are represented with the ranges [min_x, max_x] and [min_y, max_y] (inclusive).
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged nav_core2 at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.2.5 |
| License | BSD |
| Build type | CATKIN |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/locusrobotics/robot_navigation.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2020-07-03 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- David V. Lu!!
Authors
nav_core2
A replacement interface for nav_core that defines basic two dimensional planner interfaces.
There were a few key reasons for creating new interfaces rather than extending the old ones.
- Use
nav_2d_msgsto eliminate unused data fields - Use a new
Costmapinterface as a plugin rather that forcing all implementations of the interfaces to usecostmap_2d::Costmap2DROS. - Provide more data in the interfaces for easier testing.
- Use Exceptions rather than booleans to provide more information about the types of errors encountered.
Costmap
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS has been a vital part of the navigation stack for years, but it was not without its flaws.
- Initialization required a transform be available from the global frame to the base frame, which was later used to move rolling costmaps around (and a few other things). This made doing simple testing of any planner or other
Costmap2DROS-based behavior annoying, because transforms had to be set up, often outside of the immediate code that was being tested. - Initialization also started an update thread, which is also not always needed in testing.
- Using
Costmap2DROSlocked users into a layered costmap based approach, which made some tasks much easier, but didn’t give users the freedom to change the implementation.
The nav_core2::Costmap interface extends the nav_grid::NavGrid<unsigned char> for abstracting away the data storage and coordinate manipulation, and provides a few other key methods for costmap functioning such as
- a mutex
- a way to potentially track changes to the costmap
- a public
updatemethod that can be called in whatever thread you please
The Costmap can be loaded using pluginlib, allowing for arbitrary implementations of underlying update algorithms, include the layered costmap approach.
One basic implementation is provided in BasicCostmap. You can also use the nav_core_adapter::CostmapAdapter class which implements the Costmap interface while allowing you to still use Costmap2DROS.
Note: One could also imagine the Costmap interface being templatized itself like NavGrid instead of forcing use of unsigned char. While this may be possible, it was decided that it was a bit ambitious and the use of templates would force all of the implementation into headers, and would ultimately obfuscate the operation of algorithms.
Global Planner
Let us compare the old nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner to the new nav_core2/GlobalPlanner.
nav_core |
nav_core2 |
comments |
|---|---|---|
void initialize(std::string, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*) |
void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr) |
Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers, and provides a TFListener |
bool makePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&) |
nav_2d_msgs::Path2D makePlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&) |
Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual path. |
Local Planner
Now let’s compare the old nav_core::BaseLocalPlanner to the new nav_core2/LocalPlanner.
| nav_core | nav_core2 | comments |
|—|–|—|
|void initialize(std::string, tf::TransformListener*, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*)|void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr)|Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers|
|(no equivalent)|void setGoalPose(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&)|Explicitly set the new goal location, rather than using the last pose of the global plan
|bool setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&)|setPlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Path2D&)||
|bool computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist&)|nav_2d_msgs::Twist2DStamped computeVelocityCommands(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)|Explicitly provides the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual command.|
|bool isGoalReached() | bool isGoalReached(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)` | Explicitly provide the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. |
Exceptions
A hierarchical collection of exceptions is provided to allow for reacting to navigation failures in a more robust and contextual way.
 Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a
Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a StartBoundsException which has a corresponding result code of 6, it could also be seen as a InvalidStartPoseException, GlobalPlannerException, PlannerException or NavCore2Exception, all of which would also have the result code of 6.
Bounds
For use in tracking Costmap changes and more, this package also provides an implementation of bounding boxes. These are represented with the ranges [min_x, max_x] and [min_y, max_y] (inclusive).
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged nav_core2 at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.2.5 |
| License | BSD |
| Build type | CATKIN |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/locusrobotics/robot_navigation.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2020-07-03 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- David V. Lu!!
Authors
nav_core2
A replacement interface for nav_core that defines basic two dimensional planner interfaces.
There were a few key reasons for creating new interfaces rather than extending the old ones.
- Use
nav_2d_msgsto eliminate unused data fields - Use a new
Costmapinterface as a plugin rather that forcing all implementations of the interfaces to usecostmap_2d::Costmap2DROS. - Provide more data in the interfaces for easier testing.
- Use Exceptions rather than booleans to provide more information about the types of errors encountered.
Costmap
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS has been a vital part of the navigation stack for years, but it was not without its flaws.
- Initialization required a transform be available from the global frame to the base frame, which was later used to move rolling costmaps around (and a few other things). This made doing simple testing of any planner or other
Costmap2DROS-based behavior annoying, because transforms had to be set up, often outside of the immediate code that was being tested. - Initialization also started an update thread, which is also not always needed in testing.
- Using
Costmap2DROSlocked users into a layered costmap based approach, which made some tasks much easier, but didn’t give users the freedom to change the implementation.
The nav_core2::Costmap interface extends the nav_grid::NavGrid<unsigned char> for abstracting away the data storage and coordinate manipulation, and provides a few other key methods for costmap functioning such as
- a mutex
- a way to potentially track changes to the costmap
- a public
updatemethod that can be called in whatever thread you please
The Costmap can be loaded using pluginlib, allowing for arbitrary implementations of underlying update algorithms, include the layered costmap approach.
One basic implementation is provided in BasicCostmap. You can also use the nav_core_adapter::CostmapAdapter class which implements the Costmap interface while allowing you to still use Costmap2DROS.
Note: One could also imagine the Costmap interface being templatized itself like NavGrid instead of forcing use of unsigned char. While this may be possible, it was decided that it was a bit ambitious and the use of templates would force all of the implementation into headers, and would ultimately obfuscate the operation of algorithms.
Global Planner
Let us compare the old nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner to the new nav_core2/GlobalPlanner.
nav_core |
nav_core2 |
comments |
|---|---|---|
void initialize(std::string, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*) |
void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr) |
Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers, and provides a TFListener |
bool makePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&) |
nav_2d_msgs::Path2D makePlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&) |
Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual path. |
Local Planner
Now let’s compare the old nav_core::BaseLocalPlanner to the new nav_core2/LocalPlanner.
| nav_core | nav_core2 | comments |
|—|–|—|
|void initialize(std::string, tf::TransformListener*, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*)|void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr)|Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers|
|(no equivalent)|void setGoalPose(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&)|Explicitly set the new goal location, rather than using the last pose of the global plan
|bool setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&)|setPlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Path2D&)||
|bool computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist&)|nav_2d_msgs::Twist2DStamped computeVelocityCommands(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)|Explicitly provides the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual command.|
|bool isGoalReached() | bool isGoalReached(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)` | Explicitly provide the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. |
Exceptions
A hierarchical collection of exceptions is provided to allow for reacting to navigation failures in a more robust and contextual way.
 Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a
Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a StartBoundsException which has a corresponding result code of 6, it could also be seen as a InvalidStartPoseException, GlobalPlannerException, PlannerException or NavCore2Exception, all of which would also have the result code of 6.
Bounds
For use in tracking Costmap changes and more, this package also provides an implementation of bounding boxes. These are represented with the ranges [min_x, max_x] and [min_y, max_y] (inclusive).
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged nav_core2 at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.3.0 |
| License | BSD |
| Build type | CATKIN |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/locusrobotics/robot_navigation.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | kinetic |
| Last Updated | 2021-01-08 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- David V. Lu!!
Authors
nav_core2
A replacement interface for nav_core that defines basic two dimensional planner interfaces.
There were a few key reasons for creating new interfaces rather than extending the old ones.
- Use
nav_2d_msgsto eliminate unused data fields - Use a new
Costmapinterface as a plugin rather that forcing all implementations of the interfaces to usecostmap_2d::Costmap2DROS. - Provide more data in the interfaces for easier testing.
- Use Exceptions rather than booleans to provide more information about the types of errors encountered.
Costmap
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS has been a vital part of the navigation stack for years, but it was not without its flaws.
- Initialization required a transform be available from the global frame to the base frame, which was later used to move rolling costmaps around (and a few other things). This made doing simple testing of any planner or other
Costmap2DROS-based behavior annoying, because transforms had to be set up, often outside of the immediate code that was being tested. - Initialization also started an update thread, which is also not always needed in testing.
- Using
Costmap2DROSlocked users into a layered costmap based approach, which made some tasks much easier, but didn’t give users the freedom to change the implementation.
The nav_core2::Costmap interface extends the nav_grid::NavGrid<unsigned char> for abstracting away the data storage and coordinate manipulation, and provides a few other key methods for costmap functioning such as
- a mutex
- a way to potentially track changes to the costmap
- a public
updatemethod that can be called in whatever thread you please
The Costmap can be loaded using pluginlib, allowing for arbitrary implementations of underlying update algorithms, include the layered costmap approach.
One basic implementation is provided in BasicCostmap. You can also use the nav_core_adapter::CostmapAdapter class which implements the Costmap interface while allowing you to still use Costmap2DROS.
Note: One could also imagine the Costmap interface being templatized itself like NavGrid instead of forcing use of unsigned char. While this may be possible, it was decided that it was a bit ambitious and the use of templates would force all of the implementation into headers, and would ultimately obfuscate the operation of algorithms.
Global Planner
Let us compare the old nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner to the new nav_core2/GlobalPlanner.
nav_core |
nav_core2 |
comments |
|---|---|---|
void initialize(std::string, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*) |
void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr) |
Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers, and provides a TFListener |
bool makePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&) |
nav_2d_msgs::Path2D makePlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&) |
Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual path. |
Local Planner
Now let’s compare the old nav_core::BaseLocalPlanner to the new nav_core2/LocalPlanner.
| nav_core | nav_core2 | comments |
|—|–|—|
|void initialize(std::string, tf::TransformListener*, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*)|void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr)|Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers|
|(no equivalent)|void setGoalPose(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&)|Explicitly set the new goal location, rather than using the last pose of the global plan
|bool setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&)|setPlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Path2D&)||
|bool computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist&)|nav_2d_msgs::Twist2DStamped computeVelocityCommands(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)|Explicitly provides the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual command.|
|bool isGoalReached() | bool isGoalReached(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)` | Explicitly provide the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. |
Exceptions
A hierarchical collection of exceptions is provided to allow for reacting to navigation failures in a more robust and contextual way.
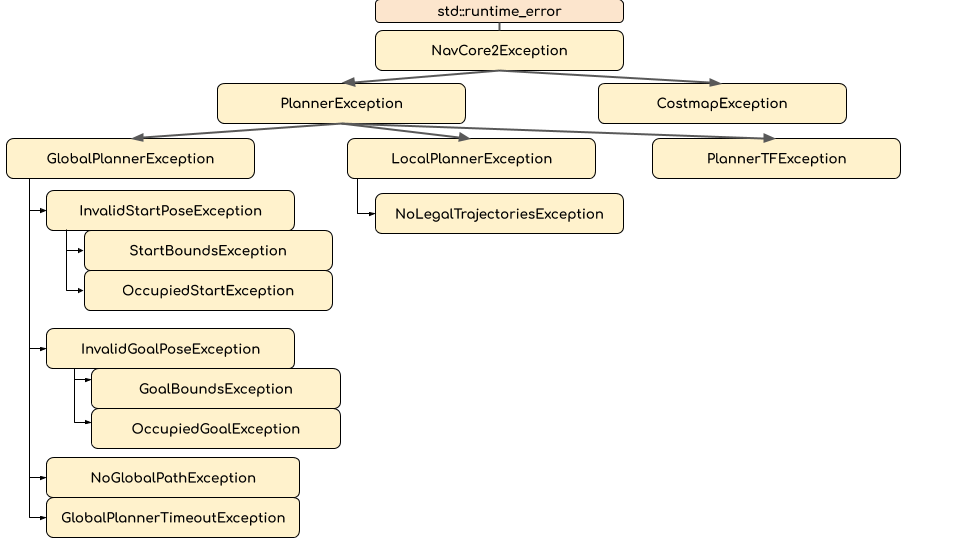 Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a
Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a StartBoundsException which has a corresponding result code of 6, it could also be seen as a InvalidStartPoseException, GlobalPlannerException, PlannerException or NavCore2Exception, all of which would also have the result code of 6.
Bounds
For use in tracking Costmap changes and more, this package also provides an implementation of bounding boxes. These are represented with the ranges [min_x, max_x] and [min_y, max_y] (inclusive).
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged nav_core2 at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.3.0 |
| License | BSD |
| Build type | CATKIN |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/locusrobotics/robot_navigation.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | melodic |
| Last Updated | 2021-07-30 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- David V. Lu!!
Authors
nav_core2
A replacement interface for nav_core that defines basic two dimensional planner interfaces.
There were a few key reasons for creating new interfaces rather than extending the old ones.
- Use
nav_2d_msgsto eliminate unused data fields - Use a new
Costmapinterface as a plugin rather that forcing all implementations of the interfaces to usecostmap_2d::Costmap2DROS. - Provide more data in the interfaces for easier testing.
- Use Exceptions rather than booleans to provide more information about the types of errors encountered.
Costmap
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS has been a vital part of the navigation stack for years, but it was not without its flaws.
- Initialization required a transform be available from the global frame to the base frame, which was later used to move rolling costmaps around (and a few other things). This made doing simple testing of any planner or other
Costmap2DROS-based behavior annoying, because transforms had to be set up, often outside of the immediate code that was being tested. - Initialization also started an update thread, which is also not always needed in testing.
- Using
Costmap2DROSlocked users into a layered costmap based approach, which made some tasks much easier, but didn’t give users the freedom to change the implementation.
The nav_core2::Costmap interface extends the nav_grid::NavGrid<unsigned char> for abstracting away the data storage and coordinate manipulation, and provides a few other key methods for costmap functioning such as
- a mutex
- a way to potentially track changes to the costmap
- a public
updatemethod that can be called in whatever thread you please
The Costmap can be loaded using pluginlib, allowing for arbitrary implementations of underlying update algorithms, include the layered costmap approach.
One basic implementation is provided in BasicCostmap. You can also use the nav_core_adapter::CostmapAdapter class which implements the Costmap interface while allowing you to still use Costmap2DROS.
Note: One could also imagine the Costmap interface being templatized itself like NavGrid instead of forcing use of unsigned char. While this may be possible, it was decided that it was a bit ambitious and the use of templates would force all of the implementation into headers, and would ultimately obfuscate the operation of algorithms.
Global Planner
Let us compare the old nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner to the new nav_core2/GlobalPlanner.
nav_core |
nav_core2 |
comments |
|---|---|---|
void initialize(std::string, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*) |
void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr) |
Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers, and provides a TFListener |
bool makePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&) |
nav_2d_msgs::Path2D makePlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&) |
Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual path. |
Local Planner
Now let’s compare the old nav_core::BaseLocalPlanner to the new nav_core2/LocalPlanner.
| nav_core | nav_core2 | comments |
|—|–|—|
|void initialize(std::string, tf::TransformListener*, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*)|void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr)|Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers|
|(no equivalent)|void setGoalPose(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&)|Explicitly set the new goal location, rather than using the last pose of the global plan
|bool setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&)|setPlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Path2D&)||
|bool computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist&)|nav_2d_msgs::Twist2DStamped computeVelocityCommands(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)|Explicitly provides the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual command.|
|bool isGoalReached() | bool isGoalReached(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)` | Explicitly provide the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. |
Exceptions
A hierarchical collection of exceptions is provided to allow for reacting to navigation failures in a more robust and contextual way.
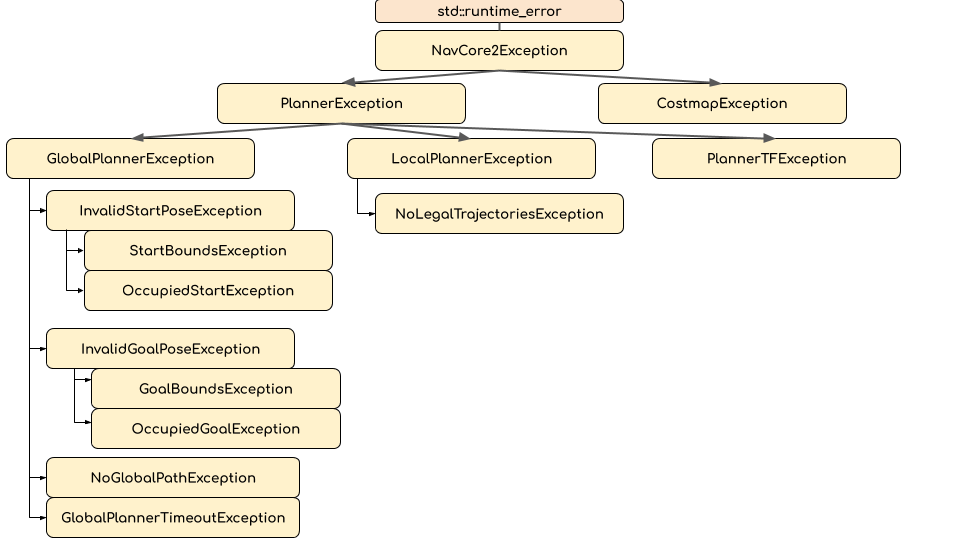 Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a
Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a StartBoundsException which has a corresponding result code of 6, it could also be seen as a InvalidStartPoseException, GlobalPlannerException, PlannerException or NavCore2Exception, all of which would also have the result code of 6.
Bounds
For use in tracking Costmap changes and more, this package also provides an implementation of bounding boxes. These are represented with the ranges [min_x, max_x] and [min_y, max_y] (inclusive).
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged nav_core2 at Robotics Stack Exchange
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.3.1 |
| License | BSD |
| Build type | CATKIN |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/locusrobotics/robot_navigation.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | noetic |
| Last Updated | 2025-05-16 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- David V. Lu!!
Authors
nav_core2
A replacement interface for nav_core that defines basic two dimensional planner interfaces.
There were a few key reasons for creating new interfaces rather than extending the old ones.
- Use
nav_2d_msgsto eliminate unused data fields - Use a new
Costmapinterface as a plugin rather that forcing all implementations of the interfaces to usecostmap_2d::Costmap2DROS. - Provide more data in the interfaces for easier testing.
- Use Exceptions rather than booleans to provide more information about the types of errors encountered.
Costmap
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS has been a vital part of the navigation stack for years, but it was not without its flaws.
- Initialization required a transform be available from the global frame to the base frame, which was later used to move rolling costmaps around (and a few other things). This made doing simple testing of any planner or other
Costmap2DROS-based behavior annoying, because transforms had to be set up, often outside of the immediate code that was being tested. - Initialization also started an update thread, which is also not always needed in testing.
- Using
Costmap2DROSlocked users into a layered costmap based approach, which made some tasks much easier, but didn’t give users the freedom to change the implementation.
The nav_core2::Costmap interface extends the nav_grid::NavGrid<unsigned char> for abstracting away the data storage and coordinate manipulation, and provides a few other key methods for costmap functioning such as
- a mutex
- a way to potentially track changes to the costmap
- a public
updatemethod that can be called in whatever thread you please
The Costmap can be loaded using pluginlib, allowing for arbitrary implementations of underlying update algorithms, include the layered costmap approach.
One basic implementation is provided in BasicCostmap. You can also use the nav_core_adapter::CostmapAdapter class which implements the Costmap interface while allowing you to still use Costmap2DROS.
Note: One could also imagine the Costmap interface being templatized itself like NavGrid instead of forcing use of unsigned char. While this may be possible, it was decided that it was a bit ambitious and the use of templates would force all of the implementation into headers, and would ultimately obfuscate the operation of algorithms.
Global Planner
Let us compare the old nav_core::BaseGlobalPlanner to the new nav_core2/GlobalPlanner.
nav_core |
nav_core2 |
comments |
|---|---|---|
void initialize(std::string, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*) |
void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr) |
Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers, and provides a TFListener |
bool makePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped&, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&) |
nav_2d_msgs::Path2D makePlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&) |
Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual path. |
Local Planner
Now let’s compare the old nav_core::BaseLocalPlanner to the new nav_core2/LocalPlanner.
| nav_core | nav_core2 | comments |
|—|–|—|
|void initialize(std::string, tf::TransformListener*, costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS*)|void initialize(const ros::NodeHandle& parent, const std::string&, TFListenerPtr, Costmap::Ptr)|Uses modern pointers instead of raw pointers|
|(no equivalent)|void setGoalPose(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&)|Explicitly set the new goal location, rather than using the last pose of the global plan
|bool setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>&)|setPlan(const nav_2d_msgs::Path2D&)||
|bool computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist&)|nav_2d_msgs::Twist2DStamped computeVelocityCommands(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)|Explicitly provides the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. Uses exceptions for errors instead of returning a bool, which frees up the return for the actual command.|
|bool isGoalReached() | bool isGoalReached(const nav_2d_msgs::Pose2DStamped&, const nav_2d_msgs::Twist2D&)` | Explicitly provide the current pose and velocity for more explicit data control and easier testing. |
Exceptions
A hierarchical collection of exceptions is provided to allow for reacting to navigation failures in a more robust and contextual way.
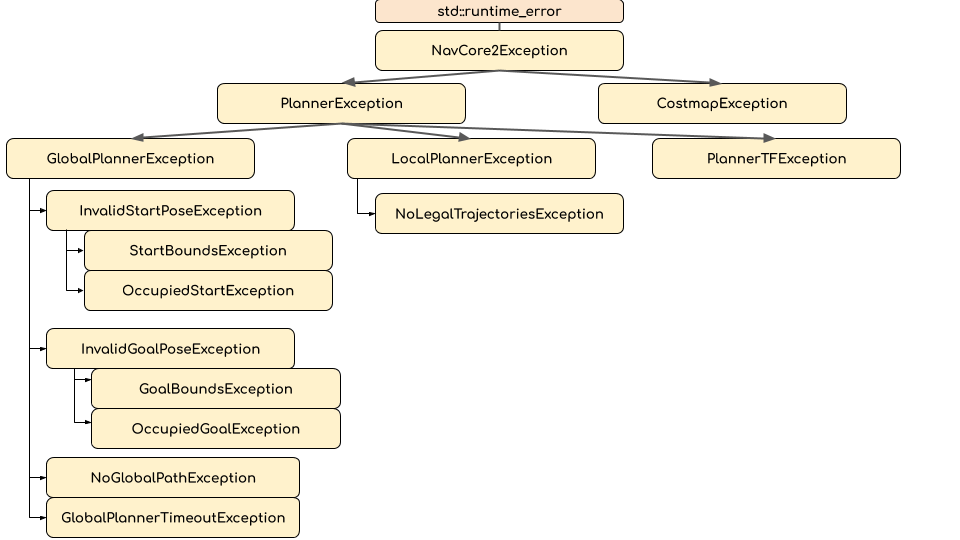 Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a
Each exception has a corresponding integer “result code” that can be used in ROS interfaces where passing the C++ object is infeasible. Note that due to the hierarchy, the result_code will be for the child-most exception. For example, if you throw a StartBoundsException which has a corresponding result code of 6, it could also be seen as a InvalidStartPoseException, GlobalPlannerException, PlannerException or NavCore2Exception, all of which would also have the result code of 6.
Bounds
For use in tracking Costmap changes and more, this package also provides an implementation of bounding boxes. These are represented with the ranges [min_x, max_x] and [min_y, max_y] (inclusive).
