
|
rclc package from rclc reporclc rclc_examples rclc_lifecycle rclc_parameter |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 4.0.2 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros2/rclc.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble |
| Last Updated | 2025-11-18 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Jan Staschulat
- Eugenio Collado
- Carlos Espinoza
Authors
- Jan Staschulat
- William Woodall
The rclc package
Table of contents
- Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
- Analysis of processing patterns
- rclc Executor
- Callback-group-level Executor
- Related Work
- References
Introduction
Predictable execution under given real-time constraints is a crucial requirement for many robotic applications. While the service-based paradigm of ROS allows a fast integration of many different functionalities, it does not provide sufficient control over the execution management. For example, there are no mechanisms to enforce a certain execution order of callbacks within a node. Also the execution order of multiple nodes is essential for control applications in mobile robotics. Cause-effect-chains comprising of sensor acquisition, evaluation of data and actuation control should be mapped to ROS nodes executed in this order, however there are no explicit mechanisms to enforce it. Furthermore, when data recordings collected in field tests as ROS-bags are re-played, then the results are often surprisingly different due to non-determinism of process scheduling.
Manually setting up a particular execution order of subscriptions and publishing topics as well as defining use-case specific priorities of the corresponding Linux processes is always possible. However, this approach is error-prone, difficult to extend and requires an in-depth knowledge of the deployed ROS 2 packages in the system.
Therefore the goal of the Executor in micro-ROS is to support roboticists with practical and easy-to-use real-time mechanisms which provide solutions for:
- Deterministic execution
- Real-time guarantees
- Integration of real-time and non real-time functionalities on one platform
- Specific support for RTOS and microcontrollers
In ROS 1 a network thread is responsible for receiving all messages and putting them into a FIFO queue (in roscpp). That is, all callbacks were called in a FIFO manner, without any execution management. With the introduction of DDS (data distribution service) in ROS 2, the messages are buffered in DDS. In ROS 2, an Executor concept was introduced to support execution management. At the rcl-layer, a wait-set is configured with handles to be received and in a second step, the handles are taken from the DDS-queue. A handle is a generic term defined in rcl-layer for timers, subscriptions, services, clients and guard conditions.
The standard implementation of the ROS 2 Executor for the C++ API (rclcpp) has, however, certain unusual features, like precedence of timers over all other DDS handles, non-preemptive round-robin scheduling for non-timer handles and considering only one input data for each handle (even if multiple could be available). These features have the consequence, that in certain situations the standard rclcpp Executor is not deterministic and it makes guaranteeing real-time requirements very hard [CB2019]. We have not looked at the ROS 2 Executor implementation for Python Frontend (rclpy) because we consider a micro-controllers platform, on which typically C or C++ appliations will run.
Given the goals for a Real-Time Executor and the limitations of the ROS 2 standard rclcpp Executor, the challenges are:
- to develop an adequate and well-defined scheduling mechanisms for the ROS 2 framework and the real-time operating system (RTOS)
- to define an easy-to-use interface for ROS developers
- to model requirements (like latencies, determinism in subsystems)
- mapping of ROS 2 framework and operating system schedulers (semi-automated and optimized mapping is desired as well as generic, well-understood framework mechanisms)
Our approach is to provide a real-time-capable Executor for the rcl+rclc layer (as described in section Introduction to Client Library.) in the C programming language .
As the first step, we propose the rclc Executor for the rcl-layer in C programming language with several new features to support real-time and deterministic execution: It supports 1.) user-defined static sequential execution, 2) conditional execution semantics, 3) multi-threaded execution with scheduling configuration, and 4) logical execution semantics (LET). Sequential execution refers to the runtime behavior, that all callbacks are executed in a pre-defined order independent of the arrival time of messages. Conditional execution is available with a trigger condition which enables typical processing patterns in robotics (which are analyzed in detail in section Analysis of processing patterns. Configuration of scheduling parameters for multi-threaded application accomplishes prioritized execution. The logical execution time concept (LET) provides data synchronization for fixed periodic task scheduling of embedded applications.
Beyond the advanced execution management mechanisms for micro-ROS, we also contributed to improving and extending the Executor concept in rclcpp for standard ROS 2: the callback group-level Executor. It is not a new Executor but rather a refinement of the ROS 2 Executor API allowing to prioritize a group of callbacks which is not possible with the ROS 2 default Executor in its current Galactic release.
Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
ROS 2 allows to bundle multiple nodes in one operating system process. To coordinate the execution of the callbacks of the nodes of a process, the Executor concept was introduced in rclcpp (and also in rclpy).
The ROS 2 design defines one Executor (instance of rclcpp::executor::Executor) per process, which is typically created either in a custom main function or by the launch system. The Executor coordinates the execution of all callbacks issued by these nodes by checking for available work (timers, services, messages, subscriptions, etc.) from the DDS queue and dispatching it to one or more threads, implemented in SingleThreadedExecutor and MultiThreadedExecutor, respectively.
The dispatching mechanism resembles the ROS 1 spin thread behavior: the Executor looks up the wait sets, which notifies it of any pending callback in the DDS queue. If there are multiple pending callbacks, the ROS 2 Executor executes them in an in the order as they were registered at the Executor.
Architecture
The following diagram depicts the relevant classes of the standard ROS 2 Executor implementation:
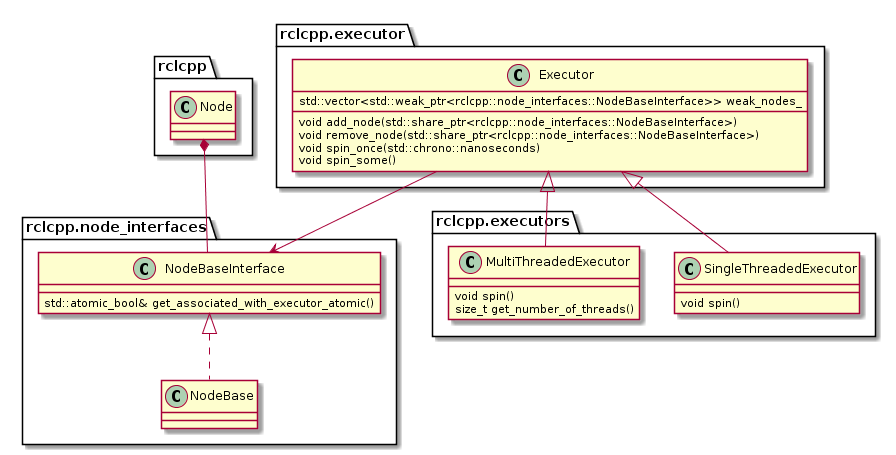
Note that an Executor instance maintains weak pointers to the NodeBaseInterfaces of the nodes only. Therefore, nodes can be destroyed safely, without notifying the Executor.
Also, the Executor does not maintain an explicit callback queue, but relies on the queue mechanism of the underlying DDS implementation as illustrated in the following sequence diagram:
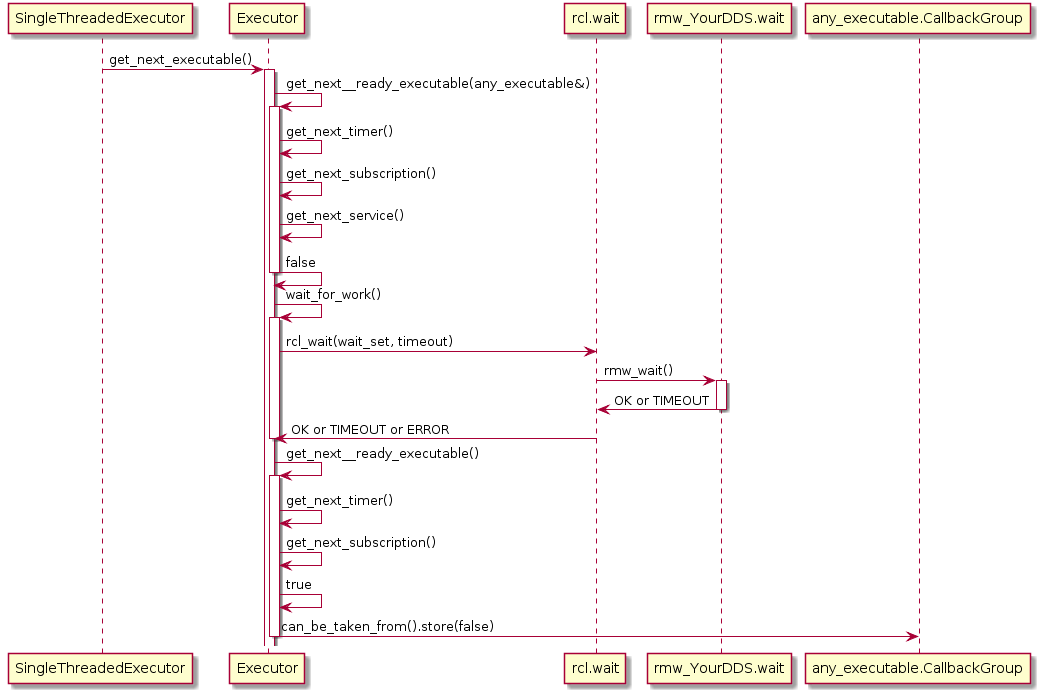
The Executor concept, however, does not provide means for prioritization or categorization of the incoming callback calls. Moreover, it does not leverage the real-time characteristics of the underlying operating-system scheduler to have finer control on the order of executions. The overall implication of this behavior is that time-critical callbacks could suffer possible deadline misses and a degraded performance since they are serviced later than non-critical callbacks. Additionally, due to the FIFO mechanism, it is difficult to determine usable bounds on the worst-case latency that each callback execution may incur.
Scheduling Semantics
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package rclc
4.0.2 (2023-03-22)
- Drop build dependency on std_msgs (backport #314) (#315)
- Updated <ros-tooling/setup-ros@0.4.2> and <ros-tooling/action-ros-ci@0.2.7> (#318) (#320)
- Removed build status for Galactic in README (EOL November 2022) (#321) (#322)
- Update documentation about number_of_handles (#326) (#327)
4.0.1 (2022-07-20)
- updated documentation bloom build status table (#291) (#292)
- updated os-version to ubuntu-22.04 (#295)
- [rolling] updated ros-tooling versions (backport #289) (#297)
- improved doxygen-generated API documentation (#301) (#302)
4.0.0 (2022-04-28)
- updated version for Humble release
3.0.8 (2022-04-14)
- Remove duplicate typedefs. (#249)
- Add rmw dependencies due to EventsExecutor PR in rcl (#255)
- Fix action client & server deallocation (#257)
- updated documentation: build status for Rolling (#266)
- Update action client goal callback signature (#282)
- Upgrade parameters (#274)
3.0.7 (2022-02-17)
- Fix enum naming for avoid collision (#242)
- Added dependency for package performance-test-fixture (#245)
3.0.6 (2022-01-25)
- executor ignore canceled timers (#220)
- uddated documentation README.md (#229)
- resolved error in unit test see issue #230 (#231)
- Add thread dependency to examples (Rolling) (#237) (resolves in this package only cpplint errors)
3.0.5 (2021-11-23)
- Fix data_available reset for timer (backport #215) (#217)
3.0.4 (2021-11-17)
- Ignoring unsuccessful SERVICE_TAKE (#175)
- Add rclc_parameter Quality Declaration (#144)
- use-ros2-testing (#185)
- Fix: printf in executor spin (#195)
- Fix init options handling (#202) (#205)
- Remove init options from support (#203)
- RCLC Actions Implementation (#170)
- Add rcl_action as build export dependency (#211)
3.0.3 (2021-07-28)
- Checking for valid ROS context in spin_some
- Refactoring executor (removing callback_type)
- Fixing codecov config
3.0.2 (2021-07-26)
- Updated codecov to ignore test folders
- Updated bloom release status table
3.0.1 (2021-07-17)
- Added rclc_parameter package
- Added quality of service entity creation API
- Added executor prepare API
- Added support for removing subscription from executor
- Added support for subscription with context
- Added quality declaration statement
- Updated compatability function for sleep
- Removed duplicate NOTICE files
2.0.0 (2021-04-23)
- Added codecov support
- New API of rcl_lifecycle in Rolling required major version bump
1.0.1 (2021-03-29)
- Windows port
- Compatibility sleep function (Windows, POSIX-OS)
- Fixed RCL lifecycle API change for Rolling
1.0.0 (2021-03-04)
- Service callbacks with context
- Fixed minor issues unit tests
- Upgraded setup_ros action (ci jobs)
- Removed Eloquent from ci jobs
0.1.7 (2021-01-20)
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged rclc at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
rclc package from rclc reporclc rclc_examples rclc_lifecycle rclc_parameter |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 6.2.0 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros2/rclc.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-18 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Jan Staschulat
- Eugenio Collado
- Carlos Espinoza
Authors
- Jan Staschulat
- William Woodall
The rclc package
Table of contents
- Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
- Analysis of processing patterns
- rclc Executor
- Callback-group-level Executor
- Related Work
- References
Introduction
Predictable execution under given real-time constraints is a crucial requirement for many robotic applications. While the service-based paradigm of ROS allows a fast integration of many different functionalities, it does not provide sufficient control over the execution management. For example, there are no mechanisms to enforce a certain execution order of callbacks within a node. Also the execution order of multiple nodes is essential for control applications in mobile robotics. Cause-effect-chains comprising of sensor acquisition, evaluation of data and actuation control should be mapped to ROS nodes executed in this order, however there are no explicit mechanisms to enforce it. Furthermore, when data recordings collected in field tests as ROS-bags are re-played, then the results are often surprisingly different due to non-determinism of process scheduling.
Manually setting up a particular execution order of subscriptions and publishing topics as well as defining use-case specific priorities of the corresponding Linux processes is always possible. However, this approach is error-prone, difficult to extend and requires an in-depth knowledge of the deployed ROS 2 packages in the system.
Therefore the goal of the Executor in micro-ROS is to support roboticists with practical and easy-to-use real-time mechanisms which provide solutions for:
- Deterministic execution
- Real-time guarantees
- Integration of real-time and non real-time functionalities on one platform
- Specific support for RTOS and microcontrollers
In ROS 1 a network thread is responsible for receiving all messages and putting them into a FIFO queue (in roscpp). That is, all callbacks were called in a FIFO manner, without any execution management. With the introduction of DDS (data distribution service) in ROS 2, the messages are buffered in DDS. In ROS 2, an Executor concept was introduced to support execution management. At the rcl-layer, a wait-set is configured with handles to be received and in a second step, the handles are taken from the DDS-queue. A handle is a generic term defined in rcl-layer for timers, subscriptions, services, clients and guard conditions.
The standard implementation of the ROS 2 Executor for the C++ API (rclcpp) has, however, certain unusual features, like precedence of timers over all other DDS handles, non-preemptive round-robin scheduling for non-timer handles and considering only one input data for each handle (even if multiple could be available). These features have the consequence, that in certain situations the standard rclcpp Executor is not deterministic and it makes guaranteeing real-time requirements very hard [CB2019]. We have not looked at the ROS 2 Executor implementation for Python Frontend (rclpy) because we consider a micro-controllers platform, on which typically C or C++ appliations will run.
Given the goals for a Real-Time Executor and the limitations of the ROS 2 standard rclcpp Executor, the challenges are:
- to develop an adequate and well-defined scheduling mechanisms for the ROS 2 framework and the real-time operating system (RTOS)
- to define an easy-to-use interface for ROS developers
- to model requirements (like latencies, determinism in subsystems)
- mapping of ROS 2 framework and operating system schedulers (semi-automated and optimized mapping is desired as well as generic, well-understood framework mechanisms)
Our approach is to provide a real-time-capable Executor for the rcl+rclc layer (as described in section Introduction to Client Library.) in the C programming language .
As the first step, we propose the rclc Executor for the rcl-layer in C programming language with several new features to support real-time and deterministic execution: It supports 1.) user-defined static sequential execution, 2) conditional execution semantics, 3) multi-threaded execution with scheduling configuration, and 4) logical execution semantics (LET). Sequential execution refers to the runtime behavior, that all callbacks are executed in a pre-defined order independent of the arrival time of messages. Conditional execution is available with a trigger condition which enables typical processing patterns in robotics (which are analyzed in detail in section Analysis of processing patterns. Configuration of scheduling parameters for multi-threaded application accomplishes prioritized execution. The logical execution time concept (LET) provides data synchronization for fixed periodic task scheduling of embedded applications.
Beyond the advanced execution management mechanisms for micro-ROS, we also contributed to improving and extending the Executor concept in rclcpp for standard ROS 2: the callback group-level Executor. It is not a new Executor but rather a refinement of the ROS 2 Executor API allowing to prioritize a group of callbacks which is not possible with the ROS 2 default Executor in its current Galactic release.
Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
ROS 2 allows to bundle multiple nodes in one operating system process. To coordinate the execution of the callbacks of the nodes of a process, the Executor concept was introduced in rclcpp (and also in rclpy).
The ROS 2 design defines one Executor (instance of rclcpp::executor::Executor) per process, which is typically created either in a custom main function or by the launch system. The Executor coordinates the execution of all callbacks issued by these nodes by checking for available work (timers, services, messages, subscriptions, etc.) from the DDS queue and dispatching it to one or more threads, implemented in SingleThreadedExecutor and MultiThreadedExecutor, respectively.
The dispatching mechanism resembles the ROS 1 spin thread behavior: the Executor looks up the wait sets, which notifies it of any pending callback in the DDS queue. If there are multiple pending callbacks, the ROS 2 Executor executes them in an in the order as they were registered at the Executor.
Architecture
The following diagram depicts the relevant classes of the standard ROS 2 Executor implementation:
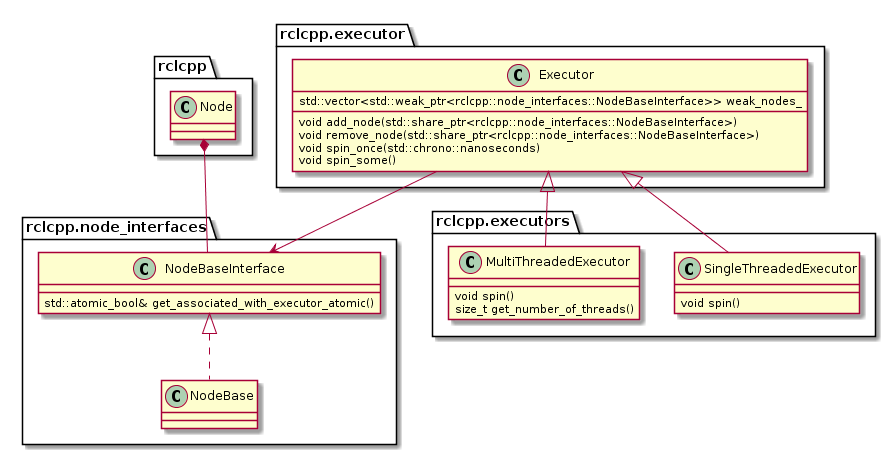
Note that an Executor instance maintains weak pointers to the NodeBaseInterfaces of the nodes only. Therefore, nodes can be destroyed safely, without notifying the Executor.
Also, the Executor does not maintain an explicit callback queue, but relies on the queue mechanism of the underlying DDS implementation as illustrated in the following sequence diagram:
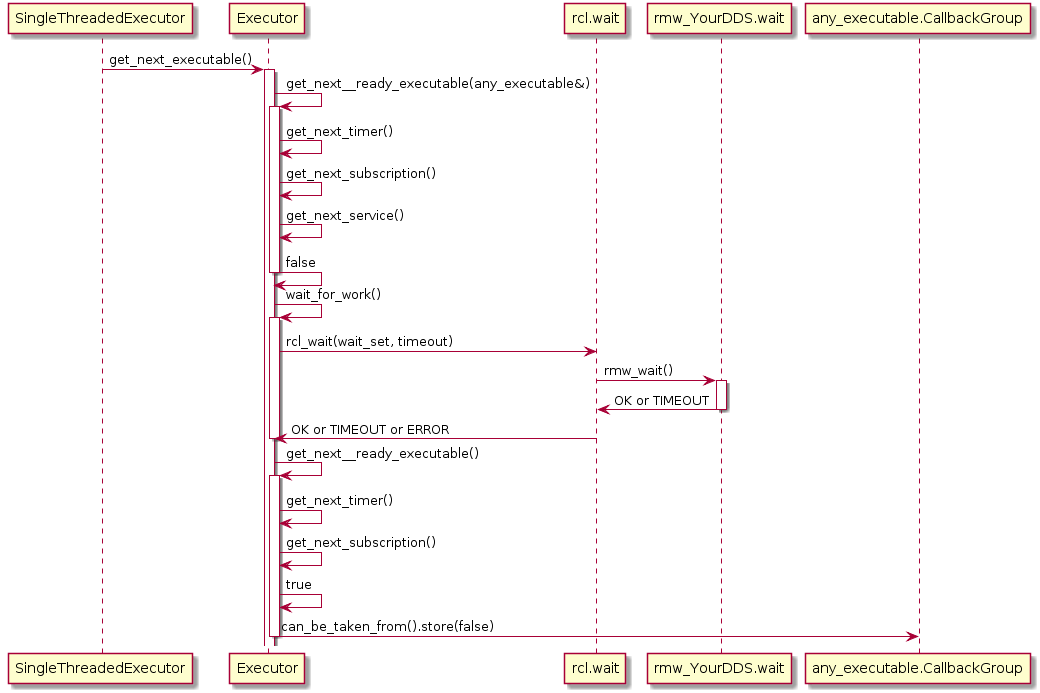
The Executor concept, however, does not provide means for prioritization or categorization of the incoming callback calls. Moreover, it does not leverage the real-time characteristics of the underlying operating-system scheduler to have finer control on the order of executions. The overall implication of this behavior is that time-critical callbacks could suffer possible deadline misses and a degraded performance since they are serviced later than non-critical callbacks. Additionally, due to the FIFO mechanism, it is difficult to determine usable bounds on the worst-case latency that each callback execution may incur.
Scheduling Semantics
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package rclc
6.2.0 (2024-10-15)
- added CI status for iron builds (#377)
- rclc_executor: improve enum type names (#379)
- fix rclc_example: memory leaking in msg.data allocation (backport #386) (#387)
- updated ci versions (#396)
- updated ros-tooling versions (#407)
6.1.0 (2023-06-15)
- Data structures interfaces for multi-threaded executor (#355)
- update ros-tooling versions (#361)
- updated actions/checkout version (#367)
- updated branch names to rolling (#370)
3.0.9 (2023-03-22)
- Added build status of bloom-releases for Humble distribution (#291)
- [rolling] updated ros-tooling versions (#289)
- github action: updated os-version to ubuntu-22.04 (backport #295) (#296)
- Added documentation (#301)
- Drop build dependency on std_msgs (#314)
- Updated <ros-tooling/setup-ros@0.4.2> and <ros-tooling/action-ros-ci@0.2.7> (#318)
- Removed build status for Galactic in README (EOL November 2022) (#321)
- Update documentation about number_of_handles (#326)
- executor.h: Fix a few docs typos (#338)
3.0.8 (2022-04-14)
- Remove duplicate typedefs. (#249)
- Add rmw dependencies due to EventsExecutor PR in rcl (#255)
- Fix action client & server deallocation (#257)
- updated documentation: build status for Rolling (#266)
- Update action client goal callback signature (#282)
- Upgrade parameters (#274)
3.0.7 (2022-02-17)
- Fix enum naming for avoid collision (#242)
- Added dependency for package performance-test-fixture (#245)
3.0.6 (2022-01-25)
- executor ignore canceled timers (#220)
- uddated documentation README.md (#229)
- resolved error in unit test see issue #230 (#231)
- Add thread dependency to examples (Rolling) (#237) (resolves in this package only cpplint errors)
3.0.5 (2021-11-23)
- Fix data_available reset for timer (backport #215) (#217)
3.0.4 (2021-11-17)
- Ignoring unsuccessful SERVICE_TAKE (#175)
- Add rclc_parameter Quality Declaration (#144)
- use-ros2-testing (#185)
- Fix: printf in executor spin (#195)
- Fix init options handling (#202) (#205)
- Remove init options from support (#203)
- RCLC Actions Implementation (#170)
- Add rcl_action as build export dependency (#211)
3.0.3 (2021-07-28)
- Checking for valid ROS context in spin_some
- Refactoring executor (removing callback_type)
- Fixing codecov config
3.0.2 (2021-07-26)
- Updated codecov to ignore test folders
- Updated bloom release status table
3.0.1 (2021-07-17)
- Added rclc_parameter package
- Added quality of service entity creation API
- Added executor prepare API
- Added support for removing subscription from executor
- Added support for subscription with context
- Added quality declaration statement
- Updated compatability function for sleep
- Removed duplicate NOTICE files
2.0.0 (2021-04-23)
- Added codecov support
- New API of rcl_lifecycle in Rolling required major version bump
1.0.1 (2021-03-29)
- Windows port
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged rclc at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
rclc package from rclc reporclc rclc_examples rclc_lifecycle rclc_parameter |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 6.2.0 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros2/rclc.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-18 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Jan Staschulat
- Eugenio Collado
- Carlos Espinoza
Authors
- Jan Staschulat
- William Woodall
The rclc package
Table of contents
- Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
- Analysis of processing patterns
- rclc Executor
- Callback-group-level Executor
- Related Work
- References
Introduction
Predictable execution under given real-time constraints is a crucial requirement for many robotic applications. While the service-based paradigm of ROS allows a fast integration of many different functionalities, it does not provide sufficient control over the execution management. For example, there are no mechanisms to enforce a certain execution order of callbacks within a node. Also the execution order of multiple nodes is essential for control applications in mobile robotics. Cause-effect-chains comprising of sensor acquisition, evaluation of data and actuation control should be mapped to ROS nodes executed in this order, however there are no explicit mechanisms to enforce it. Furthermore, when data recordings collected in field tests as ROS-bags are re-played, then the results are often surprisingly different due to non-determinism of process scheduling.
Manually setting up a particular execution order of subscriptions and publishing topics as well as defining use-case specific priorities of the corresponding Linux processes is always possible. However, this approach is error-prone, difficult to extend and requires an in-depth knowledge of the deployed ROS 2 packages in the system.
Therefore the goal of the Executor in micro-ROS is to support roboticists with practical and easy-to-use real-time mechanisms which provide solutions for:
- Deterministic execution
- Real-time guarantees
- Integration of real-time and non real-time functionalities on one platform
- Specific support for RTOS and microcontrollers
In ROS 1 a network thread is responsible for receiving all messages and putting them into a FIFO queue (in roscpp). That is, all callbacks were called in a FIFO manner, without any execution management. With the introduction of DDS (data distribution service) in ROS 2, the messages are buffered in DDS. In ROS 2, an Executor concept was introduced to support execution management. At the rcl-layer, a wait-set is configured with handles to be received and in a second step, the handles are taken from the DDS-queue. A handle is a generic term defined in rcl-layer for timers, subscriptions, services, clients and guard conditions.
The standard implementation of the ROS 2 Executor for the C++ API (rclcpp) has, however, certain unusual features, like precedence of timers over all other DDS handles, non-preemptive round-robin scheduling for non-timer handles and considering only one input data for each handle (even if multiple could be available). These features have the consequence, that in certain situations the standard rclcpp Executor is not deterministic and it makes guaranteeing real-time requirements very hard [CB2019]. We have not looked at the ROS 2 Executor implementation for Python Frontend (rclpy) because we consider a micro-controllers platform, on which typically C or C++ appliations will run.
Given the goals for a Real-Time Executor and the limitations of the ROS 2 standard rclcpp Executor, the challenges are:
- to develop an adequate and well-defined scheduling mechanisms for the ROS 2 framework and the real-time operating system (RTOS)
- to define an easy-to-use interface for ROS developers
- to model requirements (like latencies, determinism in subsystems)
- mapping of ROS 2 framework and operating system schedulers (semi-automated and optimized mapping is desired as well as generic, well-understood framework mechanisms)
Our approach is to provide a real-time-capable Executor for the rcl+rclc layer (as described in section Introduction to Client Library.) in the C programming language .
As the first step, we propose the rclc Executor for the rcl-layer in C programming language with several new features to support real-time and deterministic execution: It supports 1.) user-defined static sequential execution, 2) conditional execution semantics, 3) multi-threaded execution with scheduling configuration, and 4) logical execution semantics (LET). Sequential execution refers to the runtime behavior, that all callbacks are executed in a pre-defined order independent of the arrival time of messages. Conditional execution is available with a trigger condition which enables typical processing patterns in robotics (which are analyzed in detail in section Analysis of processing patterns. Configuration of scheduling parameters for multi-threaded application accomplishes prioritized execution. The logical execution time concept (LET) provides data synchronization for fixed periodic task scheduling of embedded applications.
Beyond the advanced execution management mechanisms for micro-ROS, we also contributed to improving and extending the Executor concept in rclcpp for standard ROS 2: the callback group-level Executor. It is not a new Executor but rather a refinement of the ROS 2 Executor API allowing to prioritize a group of callbacks which is not possible with the ROS 2 default Executor in its current Galactic release.
Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
ROS 2 allows to bundle multiple nodes in one operating system process. To coordinate the execution of the callbacks of the nodes of a process, the Executor concept was introduced in rclcpp (and also in rclpy).
The ROS 2 design defines one Executor (instance of rclcpp::executor::Executor) per process, which is typically created either in a custom main function or by the launch system. The Executor coordinates the execution of all callbacks issued by these nodes by checking for available work (timers, services, messages, subscriptions, etc.) from the DDS queue and dispatching it to one or more threads, implemented in SingleThreadedExecutor and MultiThreadedExecutor, respectively.
The dispatching mechanism resembles the ROS 1 spin thread behavior: the Executor looks up the wait sets, which notifies it of any pending callback in the DDS queue. If there are multiple pending callbacks, the ROS 2 Executor executes them in an in the order as they were registered at the Executor.
Architecture
The following diagram depicts the relevant classes of the standard ROS 2 Executor implementation:

Note that an Executor instance maintains weak pointers to the NodeBaseInterfaces of the nodes only. Therefore, nodes can be destroyed safely, without notifying the Executor.
Also, the Executor does not maintain an explicit callback queue, but relies on the queue mechanism of the underlying DDS implementation as illustrated in the following sequence diagram:

The Executor concept, however, does not provide means for prioritization or categorization of the incoming callback calls. Moreover, it does not leverage the real-time characteristics of the underlying operating-system scheduler to have finer control on the order of executions. The overall implication of this behavior is that time-critical callbacks could suffer possible deadline misses and a degraded performance since they are serviced later than non-critical callbacks. Additionally, due to the FIFO mechanism, it is difficult to determine usable bounds on the worst-case latency that each callback execution may incur.
Scheduling Semantics
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package rclc
6.2.0 (2024-10-15)
- added CI status for iron builds (#377)
- rclc_executor: improve enum type names (#379)
- fix rclc_example: memory leaking in msg.data allocation (backport #386) (#387)
- updated ci versions (#396)
- updated ros-tooling versions (#407)
6.1.0 (2023-06-15)
- Data structures interfaces for multi-threaded executor (#355)
- update ros-tooling versions (#361)
- updated actions/checkout version (#367)
- updated branch names to rolling (#370)
3.0.9 (2023-03-22)
- Added build status of bloom-releases for Humble distribution (#291)
- [rolling] updated ros-tooling versions (#289)
- github action: updated os-version to ubuntu-22.04 (backport #295) (#296)
- Added documentation (#301)
- Drop build dependency on std_msgs (#314)
- Updated <ros-tooling/setup-ros@0.4.2> and <ros-tooling/action-ros-ci@0.2.7> (#318)
- Removed build status for Galactic in README (EOL November 2022) (#321)
- Update documentation about number_of_handles (#326)
- executor.h: Fix a few docs typos (#338)
3.0.8 (2022-04-14)
- Remove duplicate typedefs. (#249)
- Add rmw dependencies due to EventsExecutor PR in rcl (#255)
- Fix action client & server deallocation (#257)
- updated documentation: build status for Rolling (#266)
- Update action client goal callback signature (#282)
- Upgrade parameters (#274)
3.0.7 (2022-02-17)
- Fix enum naming for avoid collision (#242)
- Added dependency for package performance-test-fixture (#245)
3.0.6 (2022-01-25)
- executor ignore canceled timers (#220)
- uddated documentation README.md (#229)
- resolved error in unit test see issue #230 (#231)
- Add thread dependency to examples (Rolling) (#237) (resolves in this package only cpplint errors)
3.0.5 (2021-11-23)
- Fix data_available reset for timer (backport #215) (#217)
3.0.4 (2021-11-17)
- Ignoring unsuccessful SERVICE_TAKE (#175)
- Add rclc_parameter Quality Declaration (#144)
- use-ros2-testing (#185)
- Fix: printf in executor spin (#195)
- Fix init options handling (#202) (#205)
- Remove init options from support (#203)
- RCLC Actions Implementation (#170)
- Add rcl_action as build export dependency (#211)
3.0.3 (2021-07-28)
- Checking for valid ROS context in spin_some
- Refactoring executor (removing callback_type)
- Fixing codecov config
3.0.2 (2021-07-26)
- Updated codecov to ignore test folders
- Updated bloom release status table
3.0.1 (2021-07-17)
- Added rclc_parameter package
- Added quality of service entity creation API
- Added executor prepare API
- Added support for removing subscription from executor
- Added support for subscription with context
- Added quality declaration statement
- Updated compatability function for sleep
- Removed duplicate NOTICE files
2.0.0 (2021-04-23)
- Added codecov support
- New API of rcl_lifecycle in Rolling required major version bump
1.0.1 (2021-03-29)
- Windows port
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged rclc at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
rclc package from rclc reporclc rclc_examples rclc_lifecycle rclc_parameter |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 6.2.0 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros2/rclc.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-18 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Jan Staschulat
- Eugenio Collado
- Carlos Espinoza
Authors
- Jan Staschulat
- William Woodall
The rclc package
Table of contents
- Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
- Analysis of processing patterns
- rclc Executor
- Callback-group-level Executor
- Related Work
- References
Introduction
Predictable execution under given real-time constraints is a crucial requirement for many robotic applications. While the service-based paradigm of ROS allows a fast integration of many different functionalities, it does not provide sufficient control over the execution management. For example, there are no mechanisms to enforce a certain execution order of callbacks within a node. Also the execution order of multiple nodes is essential for control applications in mobile robotics. Cause-effect-chains comprising of sensor acquisition, evaluation of data and actuation control should be mapped to ROS nodes executed in this order, however there are no explicit mechanisms to enforce it. Furthermore, when data recordings collected in field tests as ROS-bags are re-played, then the results are often surprisingly different due to non-determinism of process scheduling.
Manually setting up a particular execution order of subscriptions and publishing topics as well as defining use-case specific priorities of the corresponding Linux processes is always possible. However, this approach is error-prone, difficult to extend and requires an in-depth knowledge of the deployed ROS 2 packages in the system.
Therefore the goal of the Executor in micro-ROS is to support roboticists with practical and easy-to-use real-time mechanisms which provide solutions for:
- Deterministic execution
- Real-time guarantees
- Integration of real-time and non real-time functionalities on one platform
- Specific support for RTOS and microcontrollers
In ROS 1 a network thread is responsible for receiving all messages and putting them into a FIFO queue (in roscpp). That is, all callbacks were called in a FIFO manner, without any execution management. With the introduction of DDS (data distribution service) in ROS 2, the messages are buffered in DDS. In ROS 2, an Executor concept was introduced to support execution management. At the rcl-layer, a wait-set is configured with handles to be received and in a second step, the handles are taken from the DDS-queue. A handle is a generic term defined in rcl-layer for timers, subscriptions, services, clients and guard conditions.
The standard implementation of the ROS 2 Executor for the C++ API (rclcpp) has, however, certain unusual features, like precedence of timers over all other DDS handles, non-preemptive round-robin scheduling for non-timer handles and considering only one input data for each handle (even if multiple could be available). These features have the consequence, that in certain situations the standard rclcpp Executor is not deterministic and it makes guaranteeing real-time requirements very hard [CB2019]. We have not looked at the ROS 2 Executor implementation for Python Frontend (rclpy) because we consider a micro-controllers platform, on which typically C or C++ appliations will run.
Given the goals for a Real-Time Executor and the limitations of the ROS 2 standard rclcpp Executor, the challenges are:
- to develop an adequate and well-defined scheduling mechanisms for the ROS 2 framework and the real-time operating system (RTOS)
- to define an easy-to-use interface for ROS developers
- to model requirements (like latencies, determinism in subsystems)
- mapping of ROS 2 framework and operating system schedulers (semi-automated and optimized mapping is desired as well as generic, well-understood framework mechanisms)
Our approach is to provide a real-time-capable Executor for the rcl+rclc layer (as described in section Introduction to Client Library.) in the C programming language .
As the first step, we propose the rclc Executor for the rcl-layer in C programming language with several new features to support real-time and deterministic execution: It supports 1.) user-defined static sequential execution, 2) conditional execution semantics, 3) multi-threaded execution with scheduling configuration, and 4) logical execution semantics (LET). Sequential execution refers to the runtime behavior, that all callbacks are executed in a pre-defined order independent of the arrival time of messages. Conditional execution is available with a trigger condition which enables typical processing patterns in robotics (which are analyzed in detail in section Analysis of processing patterns. Configuration of scheduling parameters for multi-threaded application accomplishes prioritized execution. The logical execution time concept (LET) provides data synchronization for fixed periodic task scheduling of embedded applications.
Beyond the advanced execution management mechanisms for micro-ROS, we also contributed to improving and extending the Executor concept in rclcpp for standard ROS 2: the callback group-level Executor. It is not a new Executor but rather a refinement of the ROS 2 Executor API allowing to prioritize a group of callbacks which is not possible with the ROS 2 default Executor in its current Galactic release.
Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
ROS 2 allows to bundle multiple nodes in one operating system process. To coordinate the execution of the callbacks of the nodes of a process, the Executor concept was introduced in rclcpp (and also in rclpy).
The ROS 2 design defines one Executor (instance of rclcpp::executor::Executor) per process, which is typically created either in a custom main function or by the launch system. The Executor coordinates the execution of all callbacks issued by these nodes by checking for available work (timers, services, messages, subscriptions, etc.) from the DDS queue and dispatching it to one or more threads, implemented in SingleThreadedExecutor and MultiThreadedExecutor, respectively.
The dispatching mechanism resembles the ROS 1 spin thread behavior: the Executor looks up the wait sets, which notifies it of any pending callback in the DDS queue. If there are multiple pending callbacks, the ROS 2 Executor executes them in an in the order as they were registered at the Executor.
Architecture
The following diagram depicts the relevant classes of the standard ROS 2 Executor implementation:

Note that an Executor instance maintains weak pointers to the NodeBaseInterfaces of the nodes only. Therefore, nodes can be destroyed safely, without notifying the Executor.
Also, the Executor does not maintain an explicit callback queue, but relies on the queue mechanism of the underlying DDS implementation as illustrated in the following sequence diagram:

The Executor concept, however, does not provide means for prioritization or categorization of the incoming callback calls. Moreover, it does not leverage the real-time characteristics of the underlying operating-system scheduler to have finer control on the order of executions. The overall implication of this behavior is that time-critical callbacks could suffer possible deadline misses and a degraded performance since they are serviced later than non-critical callbacks. Additionally, due to the FIFO mechanism, it is difficult to determine usable bounds on the worst-case latency that each callback execution may incur.
Scheduling Semantics
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package rclc
6.2.0 (2024-10-15)
- added CI status for iron builds (#377)
- rclc_executor: improve enum type names (#379)
- fix rclc_example: memory leaking in msg.data allocation (backport #386) (#387)
- updated ci versions (#396)
- updated ros-tooling versions (#407)
6.1.0 (2023-06-15)
- Data structures interfaces for multi-threaded executor (#355)
- update ros-tooling versions (#361)
- updated actions/checkout version (#367)
- updated branch names to rolling (#370)
3.0.9 (2023-03-22)
- Added build status of bloom-releases for Humble distribution (#291)
- [rolling] updated ros-tooling versions (#289)
- github action: updated os-version to ubuntu-22.04 (backport #295) (#296)
- Added documentation (#301)
- Drop build dependency on std_msgs (#314)
- Updated <ros-tooling/setup-ros@0.4.2> and <ros-tooling/action-ros-ci@0.2.7> (#318)
- Removed build status for Galactic in README (EOL November 2022) (#321)
- Update documentation about number_of_handles (#326)
- executor.h: Fix a few docs typos (#338)
3.0.8 (2022-04-14)
- Remove duplicate typedefs. (#249)
- Add rmw dependencies due to EventsExecutor PR in rcl (#255)
- Fix action client & server deallocation (#257)
- updated documentation: build status for Rolling (#266)
- Update action client goal callback signature (#282)
- Upgrade parameters (#274)
3.0.7 (2022-02-17)
- Fix enum naming for avoid collision (#242)
- Added dependency for package performance-test-fixture (#245)
3.0.6 (2022-01-25)
- executor ignore canceled timers (#220)
- uddated documentation README.md (#229)
- resolved error in unit test see issue #230 (#231)
- Add thread dependency to examples (Rolling) (#237) (resolves in this package only cpplint errors)
3.0.5 (2021-11-23)
- Fix data_available reset for timer (backport #215) (#217)
3.0.4 (2021-11-17)
- Ignoring unsuccessful SERVICE_TAKE (#175)
- Add rclc_parameter Quality Declaration (#144)
- use-ros2-testing (#185)
- Fix: printf in executor spin (#195)
- Fix init options handling (#202) (#205)
- Remove init options from support (#203)
- RCLC Actions Implementation (#170)
- Add rcl_action as build export dependency (#211)
3.0.3 (2021-07-28)
- Checking for valid ROS context in spin_some
- Refactoring executor (removing callback_type)
- Fixing codecov config
3.0.2 (2021-07-26)
- Updated codecov to ignore test folders
- Updated bloom release status table
3.0.1 (2021-07-17)
- Added rclc_parameter package
- Added quality of service entity creation API
- Added executor prepare API
- Added support for removing subscription from executor
- Added support for subscription with context
- Added quality declaration statement
- Updated compatability function for sleep
- Removed duplicate NOTICE files
2.0.0 (2021-04-23)
- Added codecov support
- New API of rcl_lifecycle in Rolling required major version bump
1.0.1 (2021-03-29)
- Windows port
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged rclc at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
rclc package from rclc reporclc rclc_examples rclc_lifecycle rclc_parameter |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 4.0.2 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros2/rclc.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble |
| Last Updated | 2025-11-18 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Jan Staschulat
- Eugenio Collado
- Carlos Espinoza
Authors
- Jan Staschulat
- William Woodall
The rclc package
Table of contents
- Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
- Analysis of processing patterns
- rclc Executor
- Callback-group-level Executor
- Related Work
- References
Introduction
Predictable execution under given real-time constraints is a crucial requirement for many robotic applications. While the service-based paradigm of ROS allows a fast integration of many different functionalities, it does not provide sufficient control over the execution management. For example, there are no mechanisms to enforce a certain execution order of callbacks within a node. Also the execution order of multiple nodes is essential for control applications in mobile robotics. Cause-effect-chains comprising of sensor acquisition, evaluation of data and actuation control should be mapped to ROS nodes executed in this order, however there are no explicit mechanisms to enforce it. Furthermore, when data recordings collected in field tests as ROS-bags are re-played, then the results are often surprisingly different due to non-determinism of process scheduling.
Manually setting up a particular execution order of subscriptions and publishing topics as well as defining use-case specific priorities of the corresponding Linux processes is always possible. However, this approach is error-prone, difficult to extend and requires an in-depth knowledge of the deployed ROS 2 packages in the system.
Therefore the goal of the Executor in micro-ROS is to support roboticists with practical and easy-to-use real-time mechanisms which provide solutions for:
- Deterministic execution
- Real-time guarantees
- Integration of real-time and non real-time functionalities on one platform
- Specific support for RTOS and microcontrollers
In ROS 1 a network thread is responsible for receiving all messages and putting them into a FIFO queue (in roscpp). That is, all callbacks were called in a FIFO manner, without any execution management. With the introduction of DDS (data distribution service) in ROS 2, the messages are buffered in DDS. In ROS 2, an Executor concept was introduced to support execution management. At the rcl-layer, a wait-set is configured with handles to be received and in a second step, the handles are taken from the DDS-queue. A handle is a generic term defined in rcl-layer for timers, subscriptions, services, clients and guard conditions.
The standard implementation of the ROS 2 Executor for the C++ API (rclcpp) has, however, certain unusual features, like precedence of timers over all other DDS handles, non-preemptive round-robin scheduling for non-timer handles and considering only one input data for each handle (even if multiple could be available). These features have the consequence, that in certain situations the standard rclcpp Executor is not deterministic and it makes guaranteeing real-time requirements very hard [CB2019]. We have not looked at the ROS 2 Executor implementation for Python Frontend (rclpy) because we consider a micro-controllers platform, on which typically C or C++ appliations will run.
Given the goals for a Real-Time Executor and the limitations of the ROS 2 standard rclcpp Executor, the challenges are:
- to develop an adequate and well-defined scheduling mechanisms for the ROS 2 framework and the real-time operating system (RTOS)
- to define an easy-to-use interface for ROS developers
- to model requirements (like latencies, determinism in subsystems)
- mapping of ROS 2 framework and operating system schedulers (semi-automated and optimized mapping is desired as well as generic, well-understood framework mechanisms)
Our approach is to provide a real-time-capable Executor for the rcl+rclc layer (as described in section Introduction to Client Library.) in the C programming language .
As the first step, we propose the rclc Executor for the rcl-layer in C programming language with several new features to support real-time and deterministic execution: It supports 1.) user-defined static sequential execution, 2) conditional execution semantics, 3) multi-threaded execution with scheduling configuration, and 4) logical execution semantics (LET). Sequential execution refers to the runtime behavior, that all callbacks are executed in a pre-defined order independent of the arrival time of messages. Conditional execution is available with a trigger condition which enables typical processing patterns in robotics (which are analyzed in detail in section Analysis of processing patterns. Configuration of scheduling parameters for multi-threaded application accomplishes prioritized execution. The logical execution time concept (LET) provides data synchronization for fixed periodic task scheduling of embedded applications.
Beyond the advanced execution management mechanisms for micro-ROS, we also contributed to improving and extending the Executor concept in rclcpp for standard ROS 2: the callback group-level Executor. It is not a new Executor but rather a refinement of the ROS 2 Executor API allowing to prioritize a group of callbacks which is not possible with the ROS 2 default Executor in its current Galactic release.
Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
ROS 2 allows to bundle multiple nodes in one operating system process. To coordinate the execution of the callbacks of the nodes of a process, the Executor concept was introduced in rclcpp (and also in rclpy).
The ROS 2 design defines one Executor (instance of rclcpp::executor::Executor) per process, which is typically created either in a custom main function or by the launch system. The Executor coordinates the execution of all callbacks issued by these nodes by checking for available work (timers, services, messages, subscriptions, etc.) from the DDS queue and dispatching it to one or more threads, implemented in SingleThreadedExecutor and MultiThreadedExecutor, respectively.
The dispatching mechanism resembles the ROS 1 spin thread behavior: the Executor looks up the wait sets, which notifies it of any pending callback in the DDS queue. If there are multiple pending callbacks, the ROS 2 Executor executes them in an in the order as they were registered at the Executor.
Architecture
The following diagram depicts the relevant classes of the standard ROS 2 Executor implementation:

Note that an Executor instance maintains weak pointers to the NodeBaseInterfaces of the nodes only. Therefore, nodes can be destroyed safely, without notifying the Executor.
Also, the Executor does not maintain an explicit callback queue, but relies on the queue mechanism of the underlying DDS implementation as illustrated in the following sequence diagram:

The Executor concept, however, does not provide means for prioritization or categorization of the incoming callback calls. Moreover, it does not leverage the real-time characteristics of the underlying operating-system scheduler to have finer control on the order of executions. The overall implication of this behavior is that time-critical callbacks could suffer possible deadline misses and a degraded performance since they are serviced later than non-critical callbacks. Additionally, due to the FIFO mechanism, it is difficult to determine usable bounds on the worst-case latency that each callback execution may incur.
Scheduling Semantics
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package rclc
4.0.2 (2023-03-22)
- Drop build dependency on std_msgs (backport #314) (#315)
- Updated <ros-tooling/setup-ros@0.4.2> and <ros-tooling/action-ros-ci@0.2.7> (#318) (#320)
- Removed build status for Galactic in README (EOL November 2022) (#321) (#322)
- Update documentation about number_of_handles (#326) (#327)
4.0.1 (2022-07-20)
- updated documentation bloom build status table (#291) (#292)
- updated os-version to ubuntu-22.04 (#295)
- [rolling] updated ros-tooling versions (backport #289) (#297)
- improved doxygen-generated API documentation (#301) (#302)
4.0.0 (2022-04-28)
- updated version for Humble release
3.0.8 (2022-04-14)
- Remove duplicate typedefs. (#249)
- Add rmw dependencies due to EventsExecutor PR in rcl (#255)
- Fix action client & server deallocation (#257)
- updated documentation: build status for Rolling (#266)
- Update action client goal callback signature (#282)
- Upgrade parameters (#274)
3.0.7 (2022-02-17)
- Fix enum naming for avoid collision (#242)
- Added dependency for package performance-test-fixture (#245)
3.0.6 (2022-01-25)
- executor ignore canceled timers (#220)
- uddated documentation README.md (#229)
- resolved error in unit test see issue #230 (#231)
- Add thread dependency to examples (Rolling) (#237) (resolves in this package only cpplint errors)
3.0.5 (2021-11-23)
- Fix data_available reset for timer (backport #215) (#217)
3.0.4 (2021-11-17)
- Ignoring unsuccessful SERVICE_TAKE (#175)
- Add rclc_parameter Quality Declaration (#144)
- use-ros2-testing (#185)
- Fix: printf in executor spin (#195)
- Fix init options handling (#202) (#205)
- Remove init options from support (#203)
- RCLC Actions Implementation (#170)
- Add rcl_action as build export dependency (#211)
3.0.3 (2021-07-28)
- Checking for valid ROS context in spin_some
- Refactoring executor (removing callback_type)
- Fixing codecov config
3.0.2 (2021-07-26)
- Updated codecov to ignore test folders
- Updated bloom release status table
3.0.1 (2021-07-17)
- Added rclc_parameter package
- Added quality of service entity creation API
- Added executor prepare API
- Added support for removing subscription from executor
- Added support for subscription with context
- Added quality declaration statement
- Updated compatability function for sleep
- Removed duplicate NOTICE files
2.0.0 (2021-04-23)
- Added codecov support
- New API of rcl_lifecycle in Rolling required major version bump
1.0.1 (2021-03-29)
- Windows port
- Compatibility sleep function (Windows, POSIX-OS)
- Fixed RCL lifecycle API change for Rolling
1.0.0 (2021-03-04)
- Service callbacks with context
- Fixed minor issues unit tests
- Upgraded setup_ros action (ci jobs)
- Removed Eloquent from ci jobs
0.1.7 (2021-01-20)
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged rclc at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
rclc package from rclc reporclc rclc_examples rclc_lifecycle rclc_parameter |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 4.0.2 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros2/rclc.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble |
| Last Updated | 2025-11-18 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Jan Staschulat
- Eugenio Collado
- Carlos Espinoza
Authors
- Jan Staschulat
- William Woodall
The rclc package
Table of contents
- Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
- Analysis of processing patterns
- rclc Executor
- Callback-group-level Executor
- Related Work
- References
Introduction
Predictable execution under given real-time constraints is a crucial requirement for many robotic applications. While the service-based paradigm of ROS allows a fast integration of many different functionalities, it does not provide sufficient control over the execution management. For example, there are no mechanisms to enforce a certain execution order of callbacks within a node. Also the execution order of multiple nodes is essential for control applications in mobile robotics. Cause-effect-chains comprising of sensor acquisition, evaluation of data and actuation control should be mapped to ROS nodes executed in this order, however there are no explicit mechanisms to enforce it. Furthermore, when data recordings collected in field tests as ROS-bags are re-played, then the results are often surprisingly different due to non-determinism of process scheduling.
Manually setting up a particular execution order of subscriptions and publishing topics as well as defining use-case specific priorities of the corresponding Linux processes is always possible. However, this approach is error-prone, difficult to extend and requires an in-depth knowledge of the deployed ROS 2 packages in the system.
Therefore the goal of the Executor in micro-ROS is to support roboticists with practical and easy-to-use real-time mechanisms which provide solutions for:
- Deterministic execution
- Real-time guarantees
- Integration of real-time and non real-time functionalities on one platform
- Specific support for RTOS and microcontrollers
In ROS 1 a network thread is responsible for receiving all messages and putting them into a FIFO queue (in roscpp). That is, all callbacks were called in a FIFO manner, without any execution management. With the introduction of DDS (data distribution service) in ROS 2, the messages are buffered in DDS. In ROS 2, an Executor concept was introduced to support execution management. At the rcl-layer, a wait-set is configured with handles to be received and in a second step, the handles are taken from the DDS-queue. A handle is a generic term defined in rcl-layer for timers, subscriptions, services, clients and guard conditions.
The standard implementation of the ROS 2 Executor for the C++ API (rclcpp) has, however, certain unusual features, like precedence of timers over all other DDS handles, non-preemptive round-robin scheduling for non-timer handles and considering only one input data for each handle (even if multiple could be available). These features have the consequence, that in certain situations the standard rclcpp Executor is not deterministic and it makes guaranteeing real-time requirements very hard [CB2019]. We have not looked at the ROS 2 Executor implementation for Python Frontend (rclpy) because we consider a micro-controllers platform, on which typically C or C++ appliations will run.
Given the goals for a Real-Time Executor and the limitations of the ROS 2 standard rclcpp Executor, the challenges are:
- to develop an adequate and well-defined scheduling mechanisms for the ROS 2 framework and the real-time operating system (RTOS)
- to define an easy-to-use interface for ROS developers
- to model requirements (like latencies, determinism in subsystems)
- mapping of ROS 2 framework and operating system schedulers (semi-automated and optimized mapping is desired as well as generic, well-understood framework mechanisms)
Our approach is to provide a real-time-capable Executor for the rcl+rclc layer (as described in section Introduction to Client Library.) in the C programming language .
As the first step, we propose the rclc Executor for the rcl-layer in C programming language with several new features to support real-time and deterministic execution: It supports 1.) user-defined static sequential execution, 2) conditional execution semantics, 3) multi-threaded execution with scheduling configuration, and 4) logical execution semantics (LET). Sequential execution refers to the runtime behavior, that all callbacks are executed in a pre-defined order independent of the arrival time of messages. Conditional execution is available with a trigger condition which enables typical processing patterns in robotics (which are analyzed in detail in section Analysis of processing patterns. Configuration of scheduling parameters for multi-threaded application accomplishes prioritized execution. The logical execution time concept (LET) provides data synchronization for fixed periodic task scheduling of embedded applications.
Beyond the advanced execution management mechanisms for micro-ROS, we also contributed to improving and extending the Executor concept in rclcpp for standard ROS 2: the callback group-level Executor. It is not a new Executor but rather a refinement of the ROS 2 Executor API allowing to prioritize a group of callbacks which is not possible with the ROS 2 default Executor in its current Galactic release.
Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
ROS 2 allows to bundle multiple nodes in one operating system process. To coordinate the execution of the callbacks of the nodes of a process, the Executor concept was introduced in rclcpp (and also in rclpy).
The ROS 2 design defines one Executor (instance of rclcpp::executor::Executor) per process, which is typically created either in a custom main function or by the launch system. The Executor coordinates the execution of all callbacks issued by these nodes by checking for available work (timers, services, messages, subscriptions, etc.) from the DDS queue and dispatching it to one or more threads, implemented in SingleThreadedExecutor and MultiThreadedExecutor, respectively.
The dispatching mechanism resembles the ROS 1 spin thread behavior: the Executor looks up the wait sets, which notifies it of any pending callback in the DDS queue. If there are multiple pending callbacks, the ROS 2 Executor executes them in an in the order as they were registered at the Executor.
Architecture
The following diagram depicts the relevant classes of the standard ROS 2 Executor implementation:

Note that an Executor instance maintains weak pointers to the NodeBaseInterfaces of the nodes only. Therefore, nodes can be destroyed safely, without notifying the Executor.
Also, the Executor does not maintain an explicit callback queue, but relies on the queue mechanism of the underlying DDS implementation as illustrated in the following sequence diagram:

The Executor concept, however, does not provide means for prioritization or categorization of the incoming callback calls. Moreover, it does not leverage the real-time characteristics of the underlying operating-system scheduler to have finer control on the order of executions. The overall implication of this behavior is that time-critical callbacks could suffer possible deadline misses and a degraded performance since they are serviced later than non-critical callbacks. Additionally, due to the FIFO mechanism, it is difficult to determine usable bounds on the worst-case latency that each callback execution may incur.
Scheduling Semantics
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package rclc
4.0.2 (2023-03-22)
- Drop build dependency on std_msgs (backport #314) (#315)
- Updated <ros-tooling/setup-ros@0.4.2> and <ros-tooling/action-ros-ci@0.2.7> (#318) (#320)
- Removed build status for Galactic in README (EOL November 2022) (#321) (#322)
- Update documentation about number_of_handles (#326) (#327)
4.0.1 (2022-07-20)
- updated documentation bloom build status table (#291) (#292)
- updated os-version to ubuntu-22.04 (#295)
- [rolling] updated ros-tooling versions (backport #289) (#297)
- improved doxygen-generated API documentation (#301) (#302)
4.0.0 (2022-04-28)
- updated version for Humble release
3.0.8 (2022-04-14)
- Remove duplicate typedefs. (#249)
- Add rmw dependencies due to EventsExecutor PR in rcl (#255)
- Fix action client & server deallocation (#257)
- updated documentation: build status for Rolling (#266)
- Update action client goal callback signature (#282)
- Upgrade parameters (#274)
3.0.7 (2022-02-17)
- Fix enum naming for avoid collision (#242)
- Added dependency for package performance-test-fixture (#245)
3.0.6 (2022-01-25)
- executor ignore canceled timers (#220)
- uddated documentation README.md (#229)
- resolved error in unit test see issue #230 (#231)
- Add thread dependency to examples (Rolling) (#237) (resolves in this package only cpplint errors)
3.0.5 (2021-11-23)
- Fix data_available reset for timer (backport #215) (#217)
3.0.4 (2021-11-17)
- Ignoring unsuccessful SERVICE_TAKE (#175)
- Add rclc_parameter Quality Declaration (#144)
- use-ros2-testing (#185)
- Fix: printf in executor spin (#195)
- Fix init options handling (#202) (#205)
- Remove init options from support (#203)
- RCLC Actions Implementation (#170)
- Add rcl_action as build export dependency (#211)
3.0.3 (2021-07-28)
- Checking for valid ROS context in spin_some
- Refactoring executor (removing callback_type)
- Fixing codecov config
3.0.2 (2021-07-26)
- Updated codecov to ignore test folders
- Updated bloom release status table
3.0.1 (2021-07-17)
- Added rclc_parameter package
- Added quality of service entity creation API
- Added executor prepare API
- Added support for removing subscription from executor
- Added support for subscription with context
- Added quality declaration statement
- Updated compatability function for sleep
- Removed duplicate NOTICE files
2.0.0 (2021-04-23)
- Added codecov support
- New API of rcl_lifecycle in Rolling required major version bump
1.0.1 (2021-03-29)
- Windows port
- Compatibility sleep function (Windows, POSIX-OS)
- Fixed RCL lifecycle API change for Rolling
1.0.0 (2021-03-04)
- Service callbacks with context
- Fixed minor issues unit tests
- Upgraded setup_ros action (ci jobs)
- Removed Eloquent from ci jobs
0.1.7 (2021-01-20)
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged rclc at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
rclc package from rclc reporclc rclc_examples rclc_lifecycle rclc_parameter |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 4.0.2 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros2/rclc.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble |
| Last Updated | 2025-11-18 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Jan Staschulat
- Eugenio Collado
- Carlos Espinoza
Authors
- Jan Staschulat
- William Woodall
The rclc package
Table of contents
- Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
- Analysis of processing patterns
- rclc Executor
- Callback-group-level Executor
- Related Work
- References
Introduction
Predictable execution under given real-time constraints is a crucial requirement for many robotic applications. While the service-based paradigm of ROS allows a fast integration of many different functionalities, it does not provide sufficient control over the execution management. For example, there are no mechanisms to enforce a certain execution order of callbacks within a node. Also the execution order of multiple nodes is essential for control applications in mobile robotics. Cause-effect-chains comprising of sensor acquisition, evaluation of data and actuation control should be mapped to ROS nodes executed in this order, however there are no explicit mechanisms to enforce it. Furthermore, when data recordings collected in field tests as ROS-bags are re-played, then the results are often surprisingly different due to non-determinism of process scheduling.
Manually setting up a particular execution order of subscriptions and publishing topics as well as defining use-case specific priorities of the corresponding Linux processes is always possible. However, this approach is error-prone, difficult to extend and requires an in-depth knowledge of the deployed ROS 2 packages in the system.
Therefore the goal of the Executor in micro-ROS is to support roboticists with practical and easy-to-use real-time mechanisms which provide solutions for:
- Deterministic execution
- Real-time guarantees
- Integration of real-time and non real-time functionalities on one platform
- Specific support for RTOS and microcontrollers
In ROS 1 a network thread is responsible for receiving all messages and putting them into a FIFO queue (in roscpp). That is, all callbacks were called in a FIFO manner, without any execution management. With the introduction of DDS (data distribution service) in ROS 2, the messages are buffered in DDS. In ROS 2, an Executor concept was introduced to support execution management. At the rcl-layer, a wait-set is configured with handles to be received and in a second step, the handles are taken from the DDS-queue. A handle is a generic term defined in rcl-layer for timers, subscriptions, services, clients and guard conditions.
The standard implementation of the ROS 2 Executor for the C++ API (rclcpp) has, however, certain unusual features, like precedence of timers over all other DDS handles, non-preemptive round-robin scheduling for non-timer handles and considering only one input data for each handle (even if multiple could be available). These features have the consequence, that in certain situations the standard rclcpp Executor is not deterministic and it makes guaranteeing real-time requirements very hard [CB2019]. We have not looked at the ROS 2 Executor implementation for Python Frontend (rclpy) because we consider a micro-controllers platform, on which typically C or C++ appliations will run.
Given the goals for a Real-Time Executor and the limitations of the ROS 2 standard rclcpp Executor, the challenges are:
- to develop an adequate and well-defined scheduling mechanisms for the ROS 2 framework and the real-time operating system (RTOS)
- to define an easy-to-use interface for ROS developers
- to model requirements (like latencies, determinism in subsystems)
- mapping of ROS 2 framework and operating system schedulers (semi-automated and optimized mapping is desired as well as generic, well-understood framework mechanisms)
Our approach is to provide a real-time-capable Executor for the rcl+rclc layer (as described in section Introduction to Client Library.) in the C programming language .
As the first step, we propose the rclc Executor for the rcl-layer in C programming language with several new features to support real-time and deterministic execution: It supports 1.) user-defined static sequential execution, 2) conditional execution semantics, 3) multi-threaded execution with scheduling configuration, and 4) logical execution semantics (LET). Sequential execution refers to the runtime behavior, that all callbacks are executed in a pre-defined order independent of the arrival time of messages. Conditional execution is available with a trigger condition which enables typical processing patterns in robotics (which are analyzed in detail in section Analysis of processing patterns. Configuration of scheduling parameters for multi-threaded application accomplishes prioritized execution. The logical execution time concept (LET) provides data synchronization for fixed periodic task scheduling of embedded applications.
Beyond the advanced execution management mechanisms for micro-ROS, we also contributed to improving and extending the Executor concept in rclcpp for standard ROS 2: the callback group-level Executor. It is not a new Executor but rather a refinement of the ROS 2 Executor API allowing to prioritize a group of callbacks which is not possible with the ROS 2 default Executor in its current Galactic release.
Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
ROS 2 allows to bundle multiple nodes in one operating system process. To coordinate the execution of the callbacks of the nodes of a process, the Executor concept was introduced in rclcpp (and also in rclpy).
The ROS 2 design defines one Executor (instance of rclcpp::executor::Executor) per process, which is typically created either in a custom main function or by the launch system. The Executor coordinates the execution of all callbacks issued by these nodes by checking for available work (timers, services, messages, subscriptions, etc.) from the DDS queue and dispatching it to one or more threads, implemented in SingleThreadedExecutor and MultiThreadedExecutor, respectively.
The dispatching mechanism resembles the ROS 1 spin thread behavior: the Executor looks up the wait sets, which notifies it of any pending callback in the DDS queue. If there are multiple pending callbacks, the ROS 2 Executor executes them in an in the order as they were registered at the Executor.
Architecture
The following diagram depicts the relevant classes of the standard ROS 2 Executor implementation:

Note that an Executor instance maintains weak pointers to the NodeBaseInterfaces of the nodes only. Therefore, nodes can be destroyed safely, without notifying the Executor.
Also, the Executor does not maintain an explicit callback queue, but relies on the queue mechanism of the underlying DDS implementation as illustrated in the following sequence diagram:

The Executor concept, however, does not provide means for prioritization or categorization of the incoming callback calls. Moreover, it does not leverage the real-time characteristics of the underlying operating-system scheduler to have finer control on the order of executions. The overall implication of this behavior is that time-critical callbacks could suffer possible deadline misses and a degraded performance since they are serviced later than non-critical callbacks. Additionally, due to the FIFO mechanism, it is difficult to determine usable bounds on the worst-case latency that each callback execution may incur.
Scheduling Semantics
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package rclc
4.0.2 (2023-03-22)
- Drop build dependency on std_msgs (backport #314) (#315)
- Updated <ros-tooling/setup-ros@0.4.2> and <ros-tooling/action-ros-ci@0.2.7> (#318) (#320)
- Removed build status for Galactic in README (EOL November 2022) (#321) (#322)
- Update documentation about number_of_handles (#326) (#327)
4.0.1 (2022-07-20)
- updated documentation bloom build status table (#291) (#292)
- updated os-version to ubuntu-22.04 (#295)
- [rolling] updated ros-tooling versions (backport #289) (#297)
- improved doxygen-generated API documentation (#301) (#302)
4.0.0 (2022-04-28)
- updated version for Humble release
3.0.8 (2022-04-14)
- Remove duplicate typedefs. (#249)
- Add rmw dependencies due to EventsExecutor PR in rcl (#255)
- Fix action client & server deallocation (#257)
- updated documentation: build status for Rolling (#266)
- Update action client goal callback signature (#282)
- Upgrade parameters (#274)
3.0.7 (2022-02-17)
- Fix enum naming for avoid collision (#242)
- Added dependency for package performance-test-fixture (#245)
3.0.6 (2022-01-25)
- executor ignore canceled timers (#220)
- uddated documentation README.md (#229)
- resolved error in unit test see issue #230 (#231)
- Add thread dependency to examples (Rolling) (#237) (resolves in this package only cpplint errors)
3.0.5 (2021-11-23)
- Fix data_available reset for timer (backport #215) (#217)
3.0.4 (2021-11-17)
- Ignoring unsuccessful SERVICE_TAKE (#175)
- Add rclc_parameter Quality Declaration (#144)
- use-ros2-testing (#185)
- Fix: printf in executor spin (#195)
- Fix init options handling (#202) (#205)
- Remove init options from support (#203)
- RCLC Actions Implementation (#170)
- Add rcl_action as build export dependency (#211)
3.0.3 (2021-07-28)
- Checking for valid ROS context in spin_some
- Refactoring executor (removing callback_type)
- Fixing codecov config
3.0.2 (2021-07-26)
- Updated codecov to ignore test folders
- Updated bloom release status table
3.0.1 (2021-07-17)
- Added rclc_parameter package
- Added quality of service entity creation API
- Added executor prepare API
- Added support for removing subscription from executor
- Added support for subscription with context
- Added quality declaration statement
- Updated compatability function for sleep
- Removed duplicate NOTICE files
2.0.0 (2021-04-23)
- Added codecov support
- New API of rcl_lifecycle in Rolling required major version bump
1.0.1 (2021-03-29)
- Windows port
- Compatibility sleep function (Windows, POSIX-OS)
- Fixed RCL lifecycle API change for Rolling
1.0.0 (2021-03-04)
- Service callbacks with context
- Fixed minor issues unit tests
- Upgraded setup_ros action (ci jobs)
- Removed Eloquent from ci jobs
0.1.7 (2021-01-20)
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged rclc at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
rclc package from rclc reporclc rclc_examples rclc_lifecycle rclc_parameter |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 6.0.0 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros2/rclc.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2023-06-23 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Jan Staschulat
- Pablo Garrido
Authors
- Jan Staschulat
- William Woodall
The rclc package
Table of contents
- Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
- Analysis of processing patterns
- rclc Executor
- Callback-group-level Executor
- Related Work
- References
Introduction
Predictable execution under given real-time constraints is a crucial requirement for many robotic applications. While the service-based paradigm of ROS allows a fast integration of many different functionalities, it does not provide sufficient control over the execution management. For example, there are no mechanisms to enforce a certain execution order of callbacks within a node. Also the execution order of multiple nodes is essential for control applications in mobile robotics. Cause-effect-chains comprising of sensor acquisition, evaluation of data and actuation control should be mapped to ROS nodes executed in this order, however there are no explicit mechanisms to enforce it. Furthermore, when data recordings collected in field tests as ROS-bags are re-played, then the results are often surprisingly different due to non-determinism of process scheduling.
Manually setting up a particular execution order of subscriptions and publishing topics as well as defining use-case specific priorities of the corresponding Linux processes is always possible. However, this approach is error-prone, difficult to extend and requires an in-depth knowledge of the deployed ROS 2 packages in the system.
Therefore the goal of the Executor in micro-ROS is to support roboticists with practical and easy-to-use real-time mechanisms which provide solutions for:
- Deterministic execution
- Real-time guarantees
- Integration of real-time and non real-time functionalities on one platform
- Specific support for RTOS and microcontrollers
In ROS 1 a network thread is responsible for receiving all messages and putting them into a FIFO queue (in roscpp). That is, all callbacks were called in a FIFO manner, without any execution management. With the introduction of DDS (data distribution service) in ROS 2, the messages are buffered in DDS. In ROS 2, an Executor concept was introduced to support execution management. At the rcl-layer, a wait-set is configured with handles to be received and in a second step, the handles are taken from the DDS-queue. A handle is a generic term defined in rcl-layer for timers, subscriptions, services, clients and guard conditions.
The standard implementation of the ROS 2 Executor for the C++ API (rclcpp) has, however, certain unusual features, like precedence of timers over all other DDS handles, non-preemptive round-robin scheduling for non-timer handles and considering only one input data for each handle (even if multiple could be available). These features have the consequence, that in certain situations the standard rclcpp Executor is not deterministic and it makes guaranteeing real-time requirements very hard [CB2019]. We have not looked at the ROS 2 Executor implementation for Python Frontend (rclpy) because we consider a micro-controllers platform, on which typically C or C++ appliations will run.
Given the goals for a Real-Time Executor and the limitations of the ROS 2 standard rclcpp Executor, the challenges are:
- to develop an adequate and well-defined scheduling mechanisms for the ROS 2 framework and the real-time operating system (RTOS)
- to define an easy-to-use interface for ROS developers
- to model requirements (like latencies, determinism in subsystems)
- mapping of ROS 2 framework and operating system schedulers (semi-automated and optimized mapping is desired as well as generic, well-understood framework mechanisms)
Our approach is to provide a real-time-capable Executor for the rcl+rclc layer (as described in section Introduction to Client Library.) in the C programming language .
As the first step, we propose the rclc Executor for the rcl-layer in C programming language with several new features to support real-time and deterministic execution: It supports 1.) user-defined static sequential execution, 2) conditional execution semantics, 3) multi-threaded execution with scheduling configuration, and 4) logical execution semantics (LET). Sequential execution refers to the runtime behavior, that all callbacks are executed in a pre-defined order independent of the arrival time of messages. Conditional execution is available with a trigger condition which enables typical processing patterns in robotics (which are analyzed in detail in section Analysis of processing patterns. Configuration of scheduling parameters for multi-threaded application accomplishes prioritized execution. The logical execution time concept (LET) provides data synchronization for fixed periodic task scheduling of embedded applications.
Beyond the advanced execution management mechanisms for micro-ROS, we also contributed to improving and extending the Executor concept in rclcpp for standard ROS 2: the callback group-level Executor. It is not a new Executor but rather a refinement of the ROS 2 Executor API allowing to prioritize a group of callbacks which is not possible with the ROS 2 default Executor in its current Galactic release.
Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
ROS 2 allows to bundle multiple nodes in one operating system process. To coordinate the execution of the callbacks of the nodes of a process, the Executor concept was introduced in rclcpp (and also in rclpy).
The ROS 2 design defines one Executor (instance of rclcpp::executor::Executor) per process, which is typically created either in a custom main function or by the launch system. The Executor coordinates the execution of all callbacks issued by these nodes by checking for available work (timers, services, messages, subscriptions, etc.) from the DDS queue and dispatching it to one or more threads, implemented in SingleThreadedExecutor and MultiThreadedExecutor, respectively.
The dispatching mechanism resembles the ROS 1 spin thread behavior: the Executor looks up the wait sets, which notifies it of any pending callback in the DDS queue. If there are multiple pending callbacks, the ROS 2 Executor executes them in an in the order as they were registered at the Executor.
Architecture
The following diagram depicts the relevant classes of the standard ROS 2 Executor implementation:
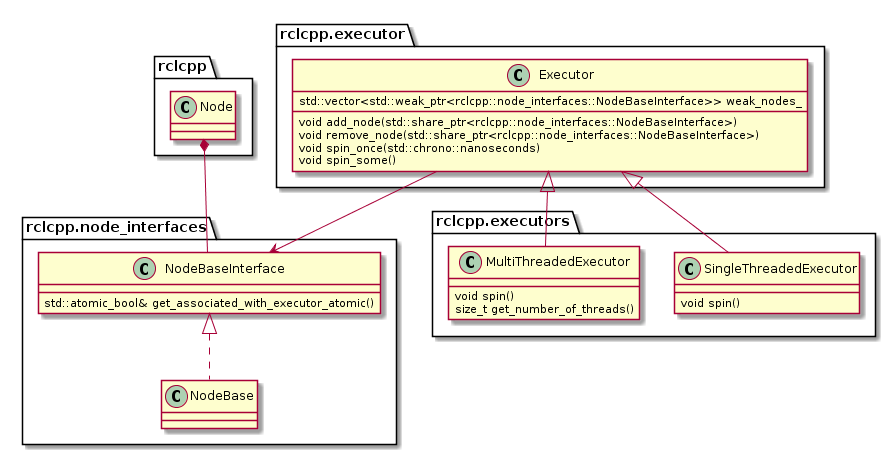
Note that an Executor instance maintains weak pointers to the NodeBaseInterfaces of the nodes only. Therefore, nodes can be destroyed safely, without notifying the Executor.
Also, the Executor does not maintain an explicit callback queue, but relies on the queue mechanism of the underlying DDS implementation as illustrated in the following sequence diagram:
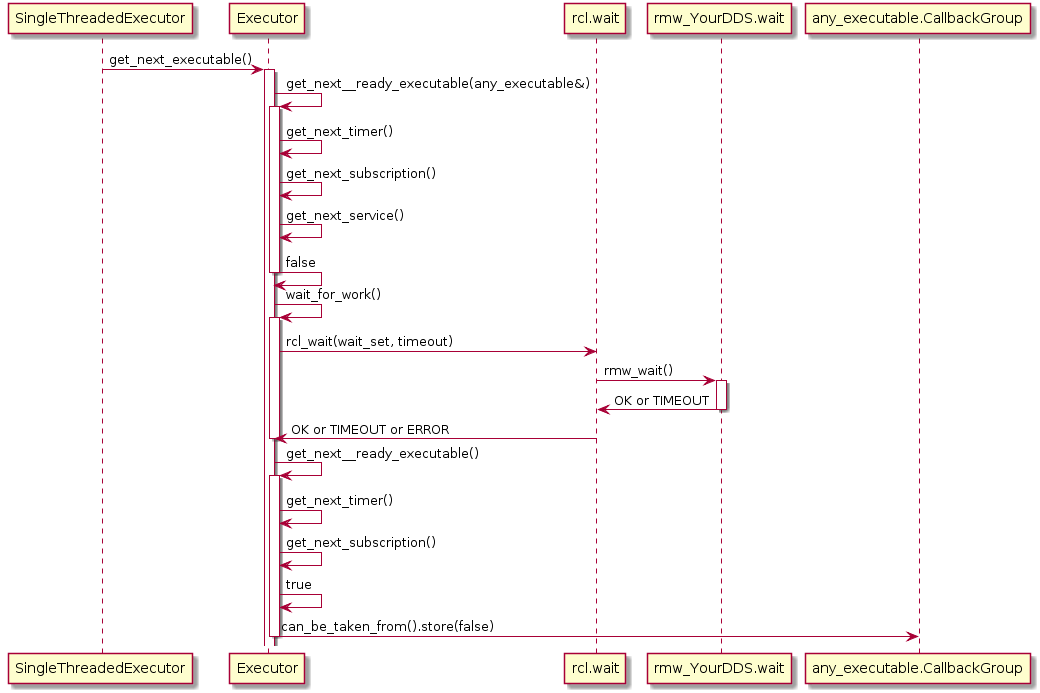
The Executor concept, however, does not provide means for prioritization or categorization of the incoming callback calls. Moreover, it does not leverage the real-time characteristics of the underlying operating-system scheduler to have finer control on the order of executions. The overall implication of this behavior is that time-critical callbacks could suffer possible deadline misses and a degraded performance since they are serviced later than non-critical callbacks. Additionally, due to the FIFO mechanism, it is difficult to determine usable bounds on the worst-case latency that each callback execution may incur.
Scheduling Semantics
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package rclc
6.0.0 (2023-06-15)
- Data structures interfaces for multi-threaded executor (#355)
- update ros-tooling versions (#361)
- updated actions/checkout version (#367)
3.0.9 (2023-03-22)
- Added build status of bloom-releases for Humble distribution (#291)
- [rolling] updated ros-tooling versions (#289)
- github action: updated os-version to ubuntu-22.04 (backport #295) (#296)
- Added documentation (#301)
- Drop build dependency on std_msgs (#314)
- Updated <ros-tooling/setup-ros@0.4.2> and <ros-tooling/action-ros-ci@0.2.7> (#318)
- Removed build status for Galactic in README (EOL November 2022) (#321)
- Update documentation about number_of_handles (#326)
- executor.h: Fix a few docs typos (#338)
3.0.8 (2022-04-14)
- Remove duplicate typedefs. (#249)
- Add rmw dependencies due to EventsExecutor PR in rcl (#255)
- Fix action client & server deallocation (#257)
- updated documentation: build status for Rolling (#266)
- Update action client goal callback signature (#282)
- Upgrade parameters (#274)
3.0.7 (2022-02-17)
- Fix enum naming for avoid collision (#242)
- Added dependency for package performance-test-fixture (#245)
3.0.6 (2022-01-25)
- executor ignore canceled timers (#220)
- uddated documentation README.md (#229)
- resolved error in unit test see issue #230 (#231)
- Add thread dependency to examples (Rolling) (#237) (resolves in this package only cpplint errors)
3.0.5 (2021-11-23)
- Fix data_available reset for timer (backport #215) (#217)
3.0.4 (2021-11-17)
- Ignoring unsuccessful SERVICE_TAKE (#175)
- Add rclc_parameter Quality Declaration (#144)
- use-ros2-testing (#185)
- Fix: printf in executor spin (#195)
- Fix init options handling (#202) (#205)
- Remove init options from support (#203)
- RCLC Actions Implementation (#170)
- Add rcl_action as build export dependency (#211)
3.0.3 (2021-07-28)
- Checking for valid ROS context in spin_some
- Refactoring executor (removing callback_type)
- Fixing codecov config
3.0.2 (2021-07-26)
- Updated codecov to ignore test folders
- Updated bloom release status table
3.0.1 (2021-07-17)
- Added rclc_parameter package
- Added quality of service entity creation API
- Added executor prepare API
- Added support for removing subscription from executor
- Added support for subscription with context
- Added quality declaration statement
- Updated compatability function for sleep
- Removed duplicate NOTICE files
2.0.0 (2021-04-23)
- Added codecov support
- New API of rcl_lifecycle in Rolling required major version bump
1.0.1 (2021-03-29)
- Windows port
- Compatibility sleep function (Windows, POSIX-OS)
- Fixed RCL lifecycle API change for Rolling
1.0.0 (2021-03-04)
- Service callbacks with context
- Fixed minor issues unit tests
- Upgraded setup_ros action (ci jobs)
- Removed Eloquent from ci jobs
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| rclc_examples | |
| rclc_lifecycle | |
| rclc_parameter |
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged rclc at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
rclc package from rclc reporclc rclc_examples rclc_lifecycle |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.0.1 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros2/rclc.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | dashing |
| Last Updated | 2021-07-20 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Jan Staschulat
- Pablo Garrido
Authors
- Jan Staschulat
- William Woodall
The rclc package
Table of Contents
Overview
The rclc-package is a ROS 2 package, which provides convenience functions to create ROS Client Library(RCL) data types and an RCLC-Executor in the C programming language. The convenience functions are a thin API layer on top of RCL-layer to create publishers, subscribers, timers and nodes with a one-liner like in rclcpp. The RCLC-Executor provides an API register subscriptions and timers as well as requesting data from DDS and executing the corresponding callbacks, like the rclcpp Executor for C++. As described in CB2019, it is difficult to reason about end-to-end latencies because of the complex semantics of the rclcpp Executor. Therefore, the RCLC Executor comes with a number of features, which provides mechanisms for deterministic and real-time execution.
The quality declaration is available in QUALITY_DECLARATION.md.
RCLC-Executor
Here we introduce the rclc Executor, which is a ROS 2 Executor implemented based on and for the rcl API, for applications written in the C language. Often embedded applications require real-time to guarantee end-to-end latencies and need deterministic runtime behavior to correctly replay test data. However, this is difficult with the default ROS 2 Executor because of its complex semantics, as discussed in the previous section.
First, we will analyse the requirements for such applications and, secondly, derive simple features for an Executor to enable deterministic and real-time behavior. Then we will present the API of the RCLC-Executor and provide example usages of the RCLC-Executor to address these requirements.
Requirement Analysis
First we discuss a use-case in the embedded domain, in which the time-triggered paradigm is often used to guarantee deterministic and real-time behavior. Then we analyse software design patterns in mobile robotics which enable deterministic behavior.
Real-time embedded application use-case
In embedded systems, real-time behavior is approached by using the time-triggered paradigm, which means that the processes are periodically activated. Processes can be assigned priorities to allow pre-emptions. Figure 1 shows an example, in which three processes with fixed periods are shown. The middle and lower process are preempted multiple times depicted with empty dashed boxes.
Figure 1: Fixed periodic preemptive scheduling
To each process one or multiple tasks can be assigned, as shown in Figure 2. These tasks are executed sequentially, which is often called cooperative scheduling.
Figure 2: Processes with sequentially executed tasks.
While there are different ways to assign priorities to a given number of processes, the rate-monotonic scheduling assignment, in which processes with a shorter period have a higher priority, has been shown optimal if the processor utilization is less than 69% LL1973.
In the last decades many different scheduling approaches have been presented, however fixed-periodic preemptive scheduling is still widely used in embedded real-time systems KZH2015. This becomes also obvious, when looking at the features of current operating systems. Like Linux, real-time operating systems, such as NuttX, Zephyr, FreeRTOS, QNX etc., support fixed-periodic preemptive scheduling and the assignment of priorities, which makes the time-triggered paradigm the dominant design principle in this domain.
However, data consistency is often an issue when preemptive scheduling is used and if data is being shared across multiple processes via global variables. Due to scheduling effects and varying execution times of processes, writing and reading these variables could occur sometimes sooner or later. This results in an latency jitter of update times (the timepoint at which a variable change becomes visible to other processes). Race conditions can occur when multiple processes access a variable at the same time. To solve this problem, the concept of logical-execution time (LET) was introduced in HHK2001, in which communication of data occurs only at pre-defined periodic time instances: Reading data only at the beginning of the period and writing data only at the end of the period. The cost of an additional latency delay is traded for data consistency and reduced jitter. This concept has also recently been applied to automotive applications NSP2018.
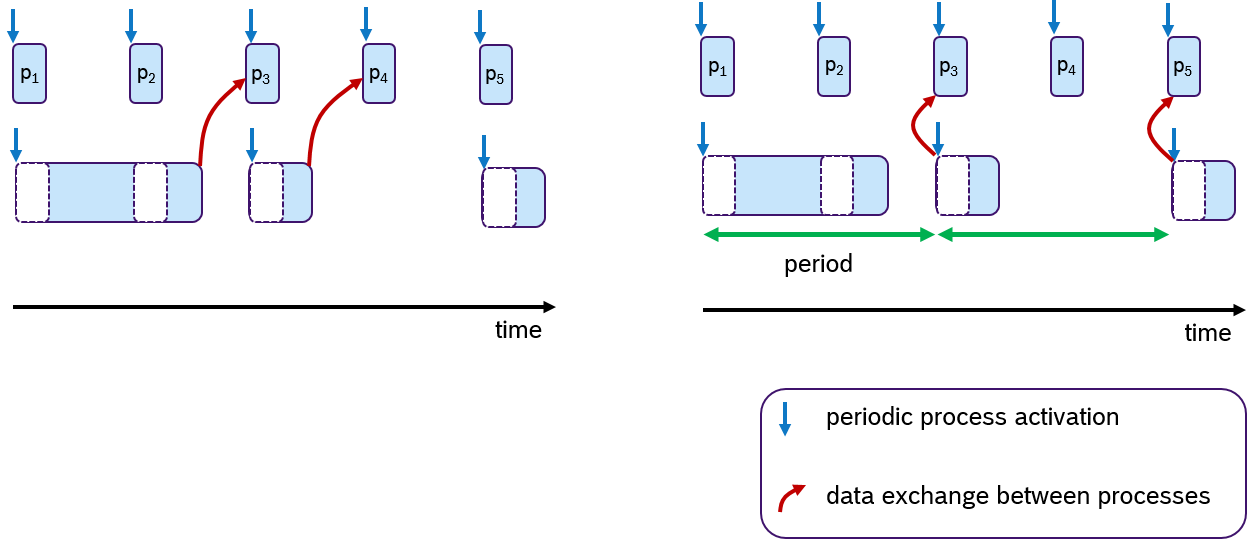
Figure 3: Data communication without and with Logical Execution Time paradigm.
An Example of the LET concept is shown in Figure 3. Assume that two processes are communicating data via one global variable. The timepoint when this data is written is at the end of the processing time. In the default case (left side), the process p3 and p4 receive the update. At the right side of the figure, the same scenario is shown with LET semantics. Here, the data is communicated only at period boundaries. In this case, the lower process communicates at the end of the period, so that always process p3 and p5 receive the new data.
The described embedded use case relies on the following concepts:
- periodic execution of processes
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package rclc
1.0.1 (2021-07-17)
- Updated ci workflow
- Added quality declaration statement
- Updated compatability function for sleep
- Added windows support
- Added codecov support
1.0.0 (2021-03-04)
- Service callbacks with context
- Fixed minor issues unit tests
- Upgraded setup_ros action (ci jobs)
- Removed Eloquent from ci jobs
0.1.7 (2021-01-20)
- Corrected corrupted changelog
0.1.6 (2021-01-20)
- Fixed issues due to Github Action timing delays on cloud build
- Fixed missing package dependency in Github Action for Eloquent
0.1.5 (2020-12-11)
- Added support for services,clients and guard_conditions to rclc executor
- Added table for bloom release status in README file
0.1.4 (2020-11-25)
- Fixed error in bloom release
0.1.3 (2020-11-23)
- Added rclc_lifecycle package
- Change maintainer information
- Minor fixes, updated unit tests
0.1.2 (2020-05-19)
- Fixed compiler errors for bloom release
0.1.1 (2020-05-14)
- Initial release
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| rclc_examples | |
| rclc_lifecycle |
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged rclc at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
rclc package from rclc reporclc rclc_examples rclc_lifecycle rclc_parameter |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 2.0.6 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros2/rclc.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | galactic |
| Last Updated | 2023-01-25 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Jan Staschulat
- Pablo Garrido
Authors
- Jan Staschulat
- William Woodall
The rclc package
Table of contents
- Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
- Analysis of processing patterns
- rclc Executor
- Callback-group-level Executor
- Related Work
- References
Introduction
Predictable execution under given real-time constraints is a crucial requirement for many robotic applications. While the service-based paradigm of ROS allows a fast integration of many different functionalities, it does not provide sufficient control over the execution management. For example, there are no mechanisms to enforce a certain execution order of callbacks within a node. Also the execution order of multiple nodes is essential for control applications in mobile robotics. Cause-effect-chains comprising of sensor acquisition, evaluation of data and actuation control should be mapped to ROS nodes executed in this order, however there are no explicit mechanisms to enforce it. Furthermore, when data recordings collected in field tests as ROS-bags are re-played, then the results are often surprisingly different due to non-determinism of process scheduling.
Manually setting up a particular execution order of subscriptions and publishing topics as well as defining use-case specific priorities of the corresponding Linux processes is always possible. However, this approach is error-prone, difficult to extend and requires an in-depth knowledge of the deployed ROS 2 packages in the system.
Therefore the goal of the Executor in micro-ROS is to support roboticists with practical and easy-to-use real-time mechanisms which provide solutions for:
- Deterministic execution
- Real-time guarantees
- Integration of real-time and non real-time functionalities on one platform
- Specific support for RTOS and microcontrollers
In ROS 1 a network thread is responsible for receiving all messages and putting them into a FIFO queue (in roscpp). That is, all callbacks were called in a FIFO manner, without any execution management. With the introduction of DDS (data distribution service) in ROS 2, the messages are buffered in DDS. In ROS 2, an Executor concept was introduced to support execution management. At the rcl-layer, a wait-set is configured with handles to be received and in a second step, the handles are taken from the DDS-queue. A handle is a generic term defined in rcl-layer for timers, subscriptions, services, clients and guard conditions.
The standard implementation of the ROS 2 Executor for the C++ API (rclcpp) has, however, certain unusual features, like precedence of timers over all other DDS handles, non-preemptive round-robin scheduling for non-timer handles and considering only one input data for each handle (even if multiple could be available). These features have the consequence, that in certain situations the standard rclcpp Executor is not deterministic and it makes guaranteeing real-time requirements very hard [CB2019]. We have not looked at the ROS 2 Executor implementation for Python Frontend (rclpy) because we consider a micro-controllers platform, on which typically C or C++ appliations will run.
Given the goals for a Real-Time Executor and the limitations of the ROS 2 standard rclcpp Executor, the challenges are:
- to develop an adequate and well-defined scheduling mechanisms for the ROS 2 framework and the real-time operating system (RTOS)
- to define an easy-to-use interface for ROS developers
- to model requirements (like latencies, determinism in subsystems)
- mapping of ROS 2 framework and operating system schedulers (semi-automated and optimized mapping is desired as well as generic, well-understood framework mechanisms)
Our approach is to provide a real-time-capable Executor for the rcl+rclc layer (as described in section Introduction to Client Library.) in the C programming language .
As the first step, we propose the rclc Executor for the rcl-layer in C programming language with several new features to support real-time and deterministic execution: It supports 1.) user-defined static sequential execution, 2) conditional execution semantics, 3) multi-threaded execution with scheduling configuration, and 4) logical execution semantics (LET). Sequential execution refers to the runtime behavior, that all callbacks are executed in a pre-defined order independent of the arrival time of messages. Conditional execution is available with a trigger condition which enables typical processing patterns in robotics (which are analyzed in detail in section Analysis of processing patterns. Configuration of scheduling parameters for multi-threaded application accomplishes prioritized execution. The logical execution time concept (LET) provides data synchronization for fixed periodic task scheduling of embedded applications.
Beyond the advanced execution management mechanisms for micro-ROS, we also contributed to improving and extending the Executor concept in rclcpp for standard ROS 2: the callback group-level Executor. It is not a new Executor but rather a refinement of the ROS 2 Executor API allowing to prioritize a group of callbacks which is not possible with the ROS 2 default Executor in its current Galactic release.
Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
ROS 2 allows to bundle multiple nodes in one operating system process. To coordinate the execution of the callbacks of the nodes of a process, the Executor concept was introduced in rclcpp (and also in rclpy).
The ROS 2 design defines one Executor (instance of rclcpp::executor::Executor) per process, which is typically created either in a custom main function or by the launch system. The Executor coordinates the execution of all callbacks issued by these nodes by checking for available work (timers, services, messages, subscriptions, etc.) from the DDS queue and dispatching it to one or more threads, implemented in SingleThreadedExecutor and MultiThreadedExecutor, respectively.
The dispatching mechanism resembles the ROS 1 spin thread behavior: the Executor looks up the wait sets, which notifies it of any pending callback in the DDS queue. If there are multiple pending callbacks, the ROS 2 Executor executes them in an in the order as they were registered at the Executor.
Architecture
The following diagram depicts the relevant classes of the standard ROS 2 Executor implementation:
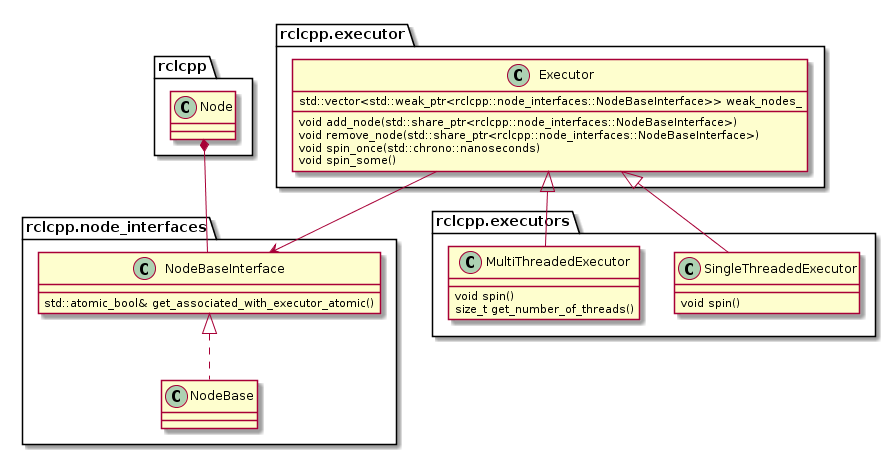
Note that an Executor instance maintains weak pointers to the NodeBaseInterfaces of the nodes only. Therefore, nodes can be destroyed safely, without notifying the Executor.
Also, the Executor does not maintain an explicit callback queue, but relies on the queue mechanism of the underlying DDS implementation as illustrated in the following sequence diagram:
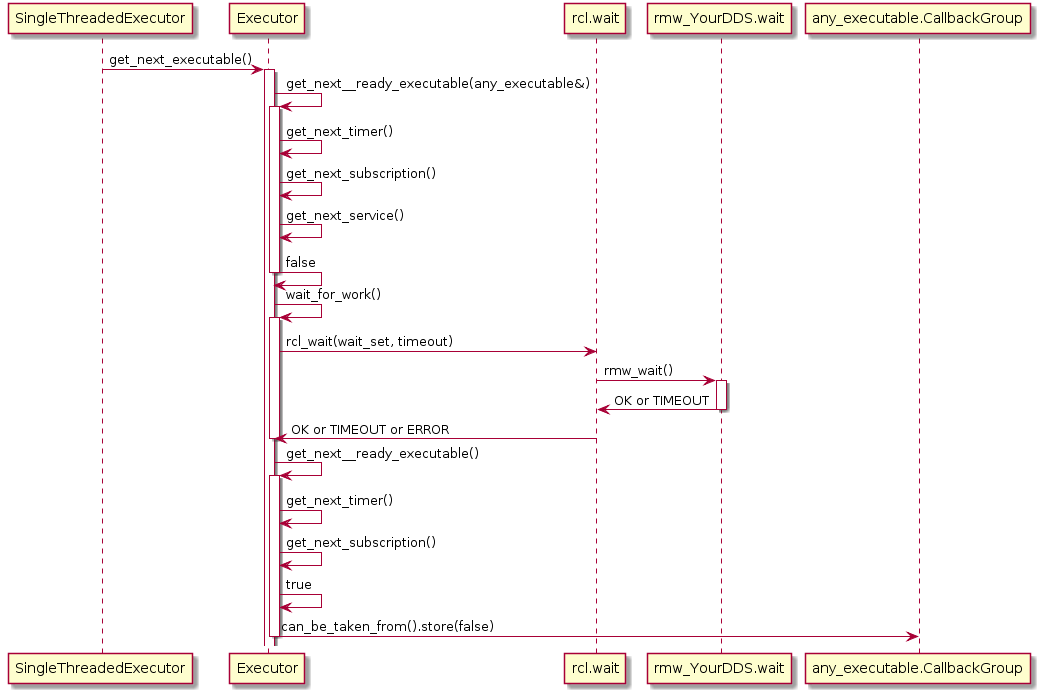
The Executor concept, however, does not provide means for prioritization or categorization of the incoming callback calls. Moreover, it does not leverage the real-time characteristics of the underlying operating-system scheduler to have finer control on the order of executions. The overall implication of this behavior is that time-critical callbacks could suffer possible deadline misses and a degraded performance since they are serviced later than non-critical callbacks. Additionally, due to the FIFO mechanism, it is difficult to determine usable bounds on the worst-case latency that each callback execution may incur.
Scheduling Semantics
In a recent paper [CB2019], the rclcpp Executor has been analyzed in detail and a response time analysis of cause-effect chains has been proposed under reservation-based scheduling. The Executor distinguishes four categories of callbacks: timers, which are triggered by system-level timers, subscribers, which are triggered by new messages on a subscribed topic, services, which are triggered by service requests, and clients, which are triggered by responses to service requests. The Executor is responsible for taking messages from the input queues of the DDS layer and executing the corresponding callback. Since it executes callbacks to completion, it is a non-preemptive scheduler, However it does not consider all ready tasks for execution, but only a snapshot, called readySet. This readySet is updated when the Executor is idle and in this step it interacts with the DDS layer updating the set of ready tasks. Then for every type of task, there are dedicated queues (timers, subscriptions, services, clients) which are processed sequentially. The following undesired properties were pointed out:
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package rclc
2.0.6 (2022-01-25)
- [backport galactic, foxy] data_available optimization (#212)
- Fix data_available reset for timer (#215) (#216)
- Executor ignore canceled timers (#220) (#221)
- Resolved error in unit test see issue #230 (#231) (#232)
- Updated documentation README.md (#229)
2.0.5 (2021-11-08)
- Fix printf in executor spin
- Fix init options handling
2.0.4 (2021-08-19)
- Refactoring: remove callback_type
- Improvement: Checking for valid ROS context in spin_some
- Bug fix: Ignoring unsuccessful SERVICE_TAKE
- Bug fix: Updated ci workflow dependency on galactic
- Improvement: Updated codecov configuration to ignore unit tests
2.0.3 (2021-07-26)
- Updated codecov to ignore test folders
- Updated bloom release status table
2.0.2 (2021-07-17)
- Added rclc_parameter package
- Added quality of service entity creation API
- Addded executor_prepare API
- Added support for removing subscription from executor
- Added support for subscription with context
- Updated compatability function for sleep
- Removed duplicate NOTICE files
2.0.1 (2021-05-28)
- added quality declaration
2.0.0 (2021-04-23)
- added codecov support
- new API of rcl_lifecycle in Rolling required major version bump
1.0.1 (2021-03-29)
- Windows port
- Compatibility sleep function (Windows, POSIX-OS)
- Fixed RCL lifecycle API change for Rolling
1.0.0 (2021-03-04)
- service callbacks with context
- fixed minor issues unit tests
- upgraded setup_ros action (ci jobs)
- removed Eloquent from ci jobs
0.1.7 (2021-01-20)
- Corrected corrupted changelog
0.1.6 (2021-01-20)
- Fixed issues due to Github Action timing delays on cloud build
- Fixed missing package dependency in Github Action for Eloquent
0.1.5 (2020-12-11)
- Added support for services,clients and guard_conditions to rclc executor
- Added table for bloom release status in README file
0.1.4 (2020-11-25)
- Fixed error in bloom release
0.1.3 (2020-11-23)
- Added rclc_lifecycle package
- Change maintainer information
- Minor fixes, updated unit tests
0.1.2 (2020-05-19)
- Fixed compiler errors for bloom release
0.1.1 (2020-05-14)
- Initial release
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged rclc at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
rclc package from rclc reporclc rclc_examples rclc_lifecycle rclc_parameter |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.1.2 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros2/rclc.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | foxy |
| Last Updated | 2023-06-12 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Jan Staschulat
- Pablo Garrido
Authors
- Jan Staschulat
- William Woodall
The rclc package
Table of contents
- Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
- Analysis of processing patterns
- rclc Executor
- Callback-group-level Executor
- Related Work
- References
Introduction
Predictable execution under given real-time constraints is a crucial requirement for many robotic applications. While the service-based paradigm of ROS allows a fast integration of many different functionalities, it does not provide sufficient control over the execution management. For example, there are no mechanisms to enforce a certain execution order of callbacks within a node. Also the execution order of multiple nodes is essential for control applications in mobile robotics. Cause-effect-chains comprising of sensor acquisition, evaluation of data and actuation control should be mapped to ROS nodes executed in this order, however there are no explicit mechanisms to enforce it. Furthermore, when data recordings collected in field tests as ROS-bags are re-played, then the results are often surprisingly different due to non-determinism of process scheduling.
Manually setting up a particular execution order of subscriptions and publishing topics as well as defining use-case specific priorities of the corresponding Linux processes is always possible. However, this approach is error-prone, difficult to extend and requires an in-depth knowledge of the deployed ROS 2 packages in the system.
Therefore the goal of the Executor in micro-ROS is to support roboticists with practical and easy-to-use real-time mechanisms which provide solutions for:
- Deterministic execution
- Real-time guarantees
- Integration of real-time and non real-time functionalities on one platform
- Specific support for RTOS and microcontrollers
In ROS 1 a network thread is responsible for receiving all messages and putting them into a FIFO queue (in roscpp). That is, all callbacks were called in a FIFO manner, without any execution management. With the introduction of DDS (data distribution service) in ROS 2, the messages are buffered in DDS. In ROS 2, an Executor concept was introduced to support execution management. At the rcl-layer, a wait-set is configured with handles to be received and in a second step, the handles are taken from the DDS-queue. A handle is a generic term defined in rcl-layer for timers, subscriptions, services, clients and guard conditions.
The standard implementation of the ROS 2 Executor for the C++ API (rclcpp) has, however, certain unusual features, like precedence of timers over all other DDS handles, non-preemptive round-robin scheduling for non-timer handles and considering only one input data for each handle (even if multiple could be available). These features have the consequence, that in certain situations the standard rclcpp Executor is not deterministic and it makes guaranteeing real-time requirements very hard [CB2019]. We have not looked at the ROS 2 Executor implementation for Python Frontend (rclpy) because we consider a micro-controllers platform, on which typically C or C++ appliations will run.
Given the goals for a Real-Time Executor and the limitations of the ROS 2 standard rclcpp Executor, the challenges are:
- to develop an adequate and well-defined scheduling mechanisms for the ROS 2 framework and the real-time operating system (RTOS)
- to define an easy-to-use interface for ROS developers
- to model requirements (like latencies, determinism in subsystems)
- mapping of ROS 2 framework and operating system schedulers (semi-automated and optimized mapping is desired as well as generic, well-understood framework mechanisms)
Our approach is to provide a real-time-capable Executor for the rcl+rclc layer (as described in section Introduction to Client Library.) in the C programming language .
As the first step, we propose the rclc Executor for the rcl-layer in C programming language with several new features to support real-time and deterministic execution: It supports 1.) user-defined static sequential execution, 2) conditional execution semantics, 3) multi-threaded execution with scheduling configuration, and 4) logical execution semantics (LET). Sequential execution refers to the runtime behavior, that all callbacks are executed in a pre-defined order independent of the arrival time of messages. Conditional execution is available with a trigger condition which enables typical processing patterns in robotics (which are analyzed in detail in section Analysis of processing patterns. Configuration of scheduling parameters for multi-threaded application accomplishes prioritized execution. The logical execution time concept (LET) provides data synchronization for fixed periodic task scheduling of embedded applications.
Beyond the advanced execution management mechanisms for micro-ROS, we also contributed to improving and extending the Executor concept in rclcpp for standard ROS 2: the callback group-level Executor. It is not a new Executor but rather a refinement of the ROS 2 Executor API allowing to prioritize a group of callbacks which is not possible with the ROS 2 default Executor in its current Galactic release.
Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
ROS 2 allows to bundle multiple nodes in one operating system process. To coordinate the execution of the callbacks of the nodes of a process, the Executor concept was introduced in rclcpp (and also in rclpy).
The ROS 2 design defines one Executor (instance of rclcpp::executor::Executor) per process, which is typically created either in a custom main function or by the launch system. The Executor coordinates the execution of all callbacks issued by these nodes by checking for available work (timers, services, messages, subscriptions, etc.) from the DDS queue and dispatching it to one or more threads, implemented in SingleThreadedExecutor and MultiThreadedExecutor, respectively.
The dispatching mechanism resembles the ROS 1 spin thread behavior: the Executor looks up the wait sets, which notifies it of any pending callback in the DDS queue. If there are multiple pending callbacks, the ROS 2 Executor executes them in an in the order as they were registered at the Executor.
Architecture
The following diagram depicts the relevant classes of the standard ROS 2 Executor implementation:
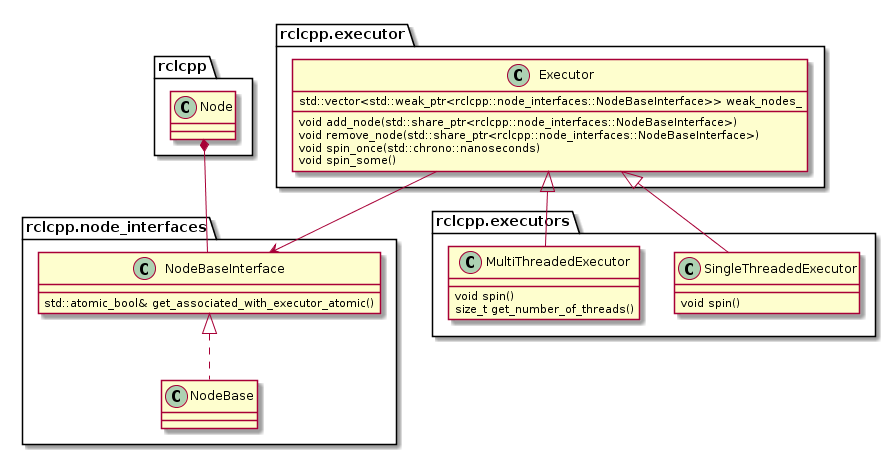
Note that an Executor instance maintains weak pointers to the NodeBaseInterfaces of the nodes only. Therefore, nodes can be destroyed safely, without notifying the Executor.
Also, the Executor does not maintain an explicit callback queue, but relies on the queue mechanism of the underlying DDS implementation as illustrated in the following sequence diagram:
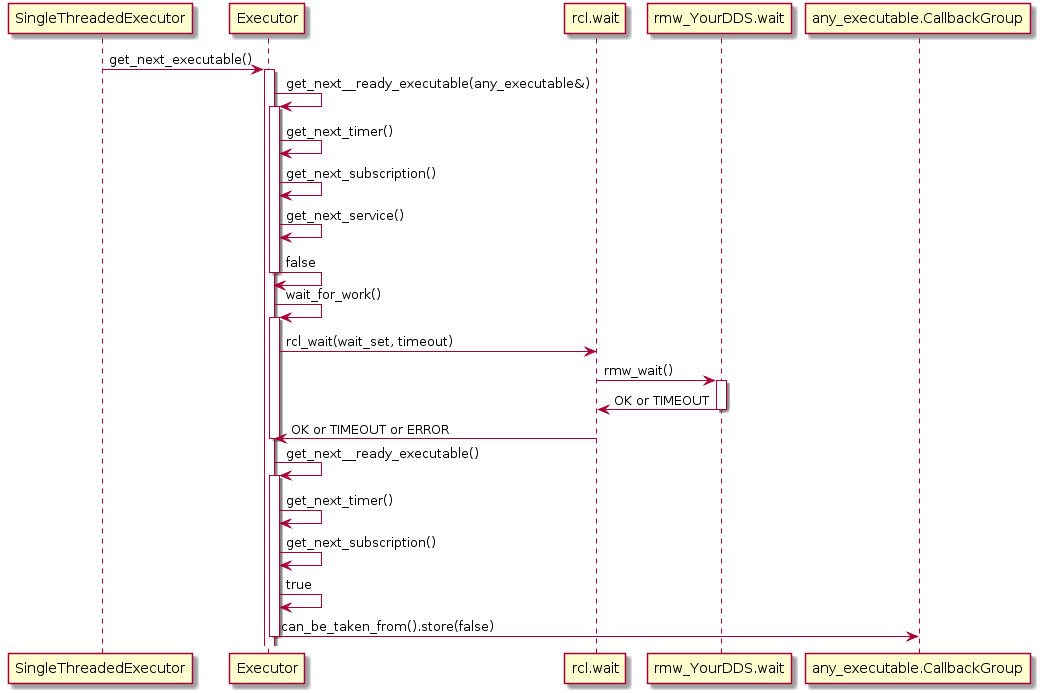
The Executor concept, however, does not provide means for prioritization or categorization of the incoming callback calls. Moreover, it does not leverage the real-time characteristics of the underlying operating-system scheduler to have finer control on the order of executions. The overall implication of this behavior is that time-critical callbacks could suffer possible deadline misses and a degraded performance since they are serviced later than non-critical callbacks. Additionally, due to the FIFO mechanism, it is difficult to determine usable bounds on the worst-case latency that each callback execution may incur.
Scheduling Semantics
In a recent paper [CB2019], the rclcpp Executor has been analyzed in detail and a response time analysis of cause-effect chains has been proposed under reservation-based scheduling. The Executor distinguishes four categories of callbacks: timers, which are triggered by system-level timers, subscribers, which are triggered by new messages on a subscribed topic, services, which are triggered by service requests, and clients, which are triggered by responses to service requests. The Executor is responsible for taking messages from the input queues of the DDS layer and executing the corresponding callback. Since it executes callbacks to completion, it is a non-preemptive scheduler, However it does not consider all ready tasks for execution, but only a snapshot, called readySet. This readySet is updated when the Executor is idle and in this step it interacts with the DDS layer updating the set of ready tasks. Then for every type of task, there are dedicated queues (timers, subscriptions, services, clients) which are processed sequentially. The following undesired properties were pointed out:
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package rclc
1.1.2 (2023-03-31)
- Added build status of bloom-releases for Humble distribution (backport #291) (#294)
- [rolling] updated ros-tooling versions (backport #289) (#299)
- added documentation (#301) (#304)
- Drop build dependency on std_msgs (backport #314) (#317)
- Updated ros-tooling versions (backport #318) (#319)
- removed build status for Galactic distribution in README (backport #321) (#323)
- Update documentation about number_of_handles (#326) (#328)
1.1.1 (2022-03-16)
- Fix enum naming for avoid collision (backport #242) (#243)
- Backport parameters (#263)
1.1.0 (2022-01-25)
- Update codecov to ignore rclc_examples and all test folders (backport #145) (#150)
- Updated table of bloom releases (removed dashing, inserted galactic) (backport #147) (#152)
- Refactor #116 remove callback_type (#154)
- Fix codecov to ignore unit tests and rclc_examples package (backport #155) (#162)
- Feature request: check for valid ros context in spin_some (#165) (#167)
- Ignoring unsuccessful SERVICE_TAKE (#175) (#177)
- Backport windows port of PR #144 (#182)
- Fix: printf in executor spin (#195) (#197)
- Fix init options handling (#202) (#204)
- [backport galactic, foxy] data_available optimization (backport #212) (#213)
- Fix data_available reset for timer (#215)
- Executor ignore canceled timers (#220) (#222)
- Resolved error in unit test see issue #230 (#231) (#233)
- Updated documentation README.md (#234)
1.0.2 (2021-07-17)
- Bumped version (tag with version 1.0.1 already exists)
1.0.1 (2021-07-17)
- Added quality of service entity creation API
- Added executor prepare API
- Added support to add subscription with context to executor
- Added support for removing subscription from executor
- Updated compatability function for sleep
- Added quality declaration statement
- Used executor allocator in spin
1.0.0 (2021-03-04)
- Service callbacks with context
- Fixed minor issues unit tests
- Upgraded setup_ros action (ci jobs)
- Removed Eloquent from ci jobs
0.1.7 (2021-01-20)
- Corrected corrupted changelog
0.1.6 (2021-01-20)
- Fixed issues due to Github Action timing delays on cloud build
- Fixed missing package dependency in Github Action for Eloquent
0.1.5 (2020-12-11)
- Added support for services,clients and guard_conditions to rclc executor
- Added table for bloom release status in README file
0.1.4 (2020-11-25)
- Fixed error in bloom release
0.1.3 (2020-11-23)
- Added rclc_lifecycle package
- Change maintainer information
- Minor fixes, updated unit tests
0.1.2 (2020-05-19)
- Fixed compiler errors for bloom release
0.1.1 (2020-05-14)
- Initial release
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged rclc at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
rclc package from rclc reporclc rclc_examples rclc_lifecycle rclc_parameter |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 5.0.1 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros2/rclc.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | iron |
| Last Updated | 2023-12-14 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Jan Staschulat
- Pablo Garrido
Authors
- Jan Staschulat
- William Woodall
The rclc package
Table of contents
- Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
- Analysis of processing patterns
- rclc Executor
- Callback-group-level Executor
- Related Work
- References
Introduction
Predictable execution under given real-time constraints is a crucial requirement for many robotic applications. While the service-based paradigm of ROS allows a fast integration of many different functionalities, it does not provide sufficient control over the execution management. For example, there are no mechanisms to enforce a certain execution order of callbacks within a node. Also the execution order of multiple nodes is essential for control applications in mobile robotics. Cause-effect-chains comprising of sensor acquisition, evaluation of data and actuation control should be mapped to ROS nodes executed in this order, however there are no explicit mechanisms to enforce it. Furthermore, when data recordings collected in field tests as ROS-bags are re-played, then the results are often surprisingly different due to non-determinism of process scheduling.
Manually setting up a particular execution order of subscriptions and publishing topics as well as defining use-case specific priorities of the corresponding Linux processes is always possible. However, this approach is error-prone, difficult to extend and requires an in-depth knowledge of the deployed ROS 2 packages in the system.
Therefore the goal of the Executor in micro-ROS is to support roboticists with practical and easy-to-use real-time mechanisms which provide solutions for:
- Deterministic execution
- Real-time guarantees
- Integration of real-time and non real-time functionalities on one platform
- Specific support for RTOS and microcontrollers
In ROS 1 a network thread is responsible for receiving all messages and putting them into a FIFO queue (in roscpp). That is, all callbacks were called in a FIFO manner, without any execution management. With the introduction of DDS (data distribution service) in ROS 2, the messages are buffered in DDS. In ROS 2, an Executor concept was introduced to support execution management. At the rcl-layer, a wait-set is configured with handles to be received and in a second step, the handles are taken from the DDS-queue. A handle is a generic term defined in rcl-layer for timers, subscriptions, services, clients and guard conditions.
The standard implementation of the ROS 2 Executor for the C++ API (rclcpp) has, however, certain unusual features, like precedence of timers over all other DDS handles, non-preemptive round-robin scheduling for non-timer handles and considering only one input data for each handle (even if multiple could be available). These features have the consequence, that in certain situations the standard rclcpp Executor is not deterministic and it makes guaranteeing real-time requirements very hard [CB2019]. We have not looked at the ROS 2 Executor implementation for Python Frontend (rclpy) because we consider a micro-controllers platform, on which typically C or C++ appliations will run.
Given the goals for a Real-Time Executor and the limitations of the ROS 2 standard rclcpp Executor, the challenges are:
- to develop an adequate and well-defined scheduling mechanisms for the ROS 2 framework and the real-time operating system (RTOS)
- to define an easy-to-use interface for ROS developers
- to model requirements (like latencies, determinism in subsystems)
- mapping of ROS 2 framework and operating system schedulers (semi-automated and optimized mapping is desired as well as generic, well-understood framework mechanisms)
Our approach is to provide a real-time-capable Executor for the rcl+rclc layer (as described in section Introduction to Client Library.) in the C programming language .
As the first step, we propose the rclc Executor for the rcl-layer in C programming language with several new features to support real-time and deterministic execution: It supports 1.) user-defined static sequential execution, 2) conditional execution semantics, 3) multi-threaded execution with scheduling configuration, and 4) logical execution semantics (LET). Sequential execution refers to the runtime behavior, that all callbacks are executed in a pre-defined order independent of the arrival time of messages. Conditional execution is available with a trigger condition which enables typical processing patterns in robotics (which are analyzed in detail in section Analysis of processing patterns. Configuration of scheduling parameters for multi-threaded application accomplishes prioritized execution. The logical execution time concept (LET) provides data synchronization for fixed periodic task scheduling of embedded applications.
Beyond the advanced execution management mechanisms for micro-ROS, we also contributed to improving and extending the Executor concept in rclcpp for standard ROS 2: the callback group-level Executor. It is not a new Executor but rather a refinement of the ROS 2 Executor API allowing to prioritize a group of callbacks which is not possible with the ROS 2 default Executor in its current Galactic release.
Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
ROS 2 allows to bundle multiple nodes in one operating system process. To coordinate the execution of the callbacks of the nodes of a process, the Executor concept was introduced in rclcpp (and also in rclpy).
The ROS 2 design defines one Executor (instance of rclcpp::executor::Executor) per process, which is typically created either in a custom main function or by the launch system. The Executor coordinates the execution of all callbacks issued by these nodes by checking for available work (timers, services, messages, subscriptions, etc.) from the DDS queue and dispatching it to one or more threads, implemented in SingleThreadedExecutor and MultiThreadedExecutor, respectively.
The dispatching mechanism resembles the ROS 1 spin thread behavior: the Executor looks up the wait sets, which notifies it of any pending callback in the DDS queue. If there are multiple pending callbacks, the ROS 2 Executor executes them in an in the order as they were registered at the Executor.
Architecture
The following diagram depicts the relevant classes of the standard ROS 2 Executor implementation:
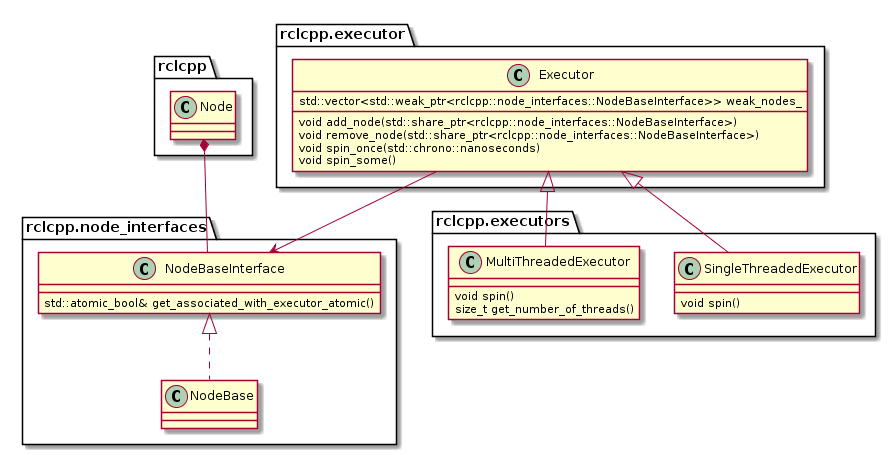
Note that an Executor instance maintains weak pointers to the NodeBaseInterfaces of the nodes only. Therefore, nodes can be destroyed safely, without notifying the Executor.
Also, the Executor does not maintain an explicit callback queue, but relies on the queue mechanism of the underlying DDS implementation as illustrated in the following sequence diagram:
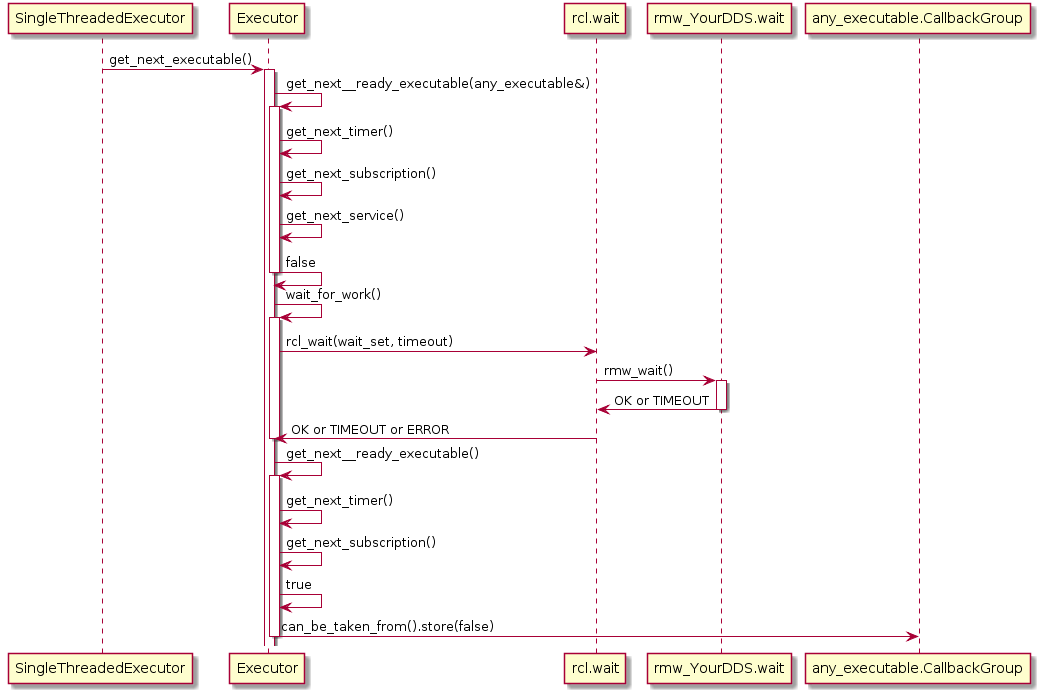
The Executor concept, however, does not provide means for prioritization or categorization of the incoming callback calls. Moreover, it does not leverage the real-time characteristics of the underlying operating-system scheduler to have finer control on the order of executions. The overall implication of this behavior is that time-critical callbacks could suffer possible deadline misses and a degraded performance since they are serviced later than non-critical callbacks. Additionally, due to the FIFO mechanism, it is difficult to determine usable bounds on the worst-case latency that each callback execution may incur.
Scheduling Semantics
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package rclc
5.0.1 (2023-06-15)
- Data structures interfaces for multi-threaded executor (#355)
- Updated ros-tooling versions (#361)
- Updated actions/checkout version (#367)
- Updated branch and distribution name to iron (#371)
3.0.9 (2023-03-22)
- Added build status of bloom-releases for Humble distribution (#291)
- [rolling] updated ros-tooling versions (#289)
- github action: updated os-version to ubuntu-22.04 (backport #295) (#296)
- Added documentation (#301)
- Drop build dependency on std_msgs (#314)
- Updated <ros-tooling/setup-ros@0.4.2> and <ros-tooling/action-ros-ci@0.2.7> (#318)
- Removed build status for Galactic in README (EOL November 2022) (#321)
- Update documentation about number_of_handles (#326)
- executor.h: Fix a few docs typos (#338)
3.0.8 (2022-04-14)
- Remove duplicate typedefs. (#249)
- Add rmw dependencies due to EventsExecutor PR in rcl (#255)
- Fix action client & server deallocation (#257)
- updated documentation: build status for Rolling (#266)
- Update action client goal callback signature (#282)
- Upgrade parameters (#274)
3.0.7 (2022-02-17)
- Fix enum naming for avoid collision (#242)
- Added dependency for package performance-test-fixture (#245)
3.0.6 (2022-01-25)
- executor ignore canceled timers (#220)
- uddated documentation README.md (#229)
- resolved error in unit test see issue #230 (#231)
- Add thread dependency to examples (Rolling) (#237) (resolves in this package only cpplint errors)
3.0.5 (2021-11-23)
- Fix data_available reset for timer (backport #215) (#217)
3.0.4 (2021-11-17)
- Ignoring unsuccessful SERVICE_TAKE (#175)
- Add rclc_parameter Quality Declaration (#144)
- use-ros2-testing (#185)
- Fix: printf in executor spin (#195)
- Fix init options handling (#202) (#205)
- Remove init options from support (#203)
- RCLC Actions Implementation (#170)
- Add rcl_action as build export dependency (#211)
3.0.3 (2021-07-28)
- Checking for valid ROS context in spin_some
- Refactoring executor (removing callback_type)
- Fixing codecov config
3.0.2 (2021-07-26)
- Updated codecov to ignore test folders
- Updated bloom release status table
3.0.1 (2021-07-17)
- Added rclc_parameter package
- Added quality of service entity creation API
- Added executor prepare API
- Added support for removing subscription from executor
- Added support for subscription with context
- Added quality declaration statement
- Updated compatability function for sleep
- Removed duplicate NOTICE files
2.0.0 (2021-04-23)
- Added codecov support
- New API of rcl_lifecycle in Rolling required major version bump
1.0.1 (2021-03-29)
- Windows port
- Compatibility sleep function (Windows, POSIX-OS)
- Fixed RCL lifecycle API change for Rolling
1.0.0 (2021-03-04)
- Service callbacks with context
- Fixed minor issues unit tests
- Upgraded setup_ros action (ci jobs)
- Removed Eloquent from ci jobs
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged rclc at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
rclc package from rclc reporclc rclc_examples rclc_lifecycle rclc_parameter |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 4.0.2 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros2/rclc.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble |
| Last Updated | 2025-11-18 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Jan Staschulat
- Eugenio Collado
- Carlos Espinoza
Authors
- Jan Staschulat
- William Woodall
The rclc package
Table of contents
- Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
- Analysis of processing patterns
- rclc Executor
- Callback-group-level Executor
- Related Work
- References
Introduction
Predictable execution under given real-time constraints is a crucial requirement for many robotic applications. While the service-based paradigm of ROS allows a fast integration of many different functionalities, it does not provide sufficient control over the execution management. For example, there are no mechanisms to enforce a certain execution order of callbacks within a node. Also the execution order of multiple nodes is essential for control applications in mobile robotics. Cause-effect-chains comprising of sensor acquisition, evaluation of data and actuation control should be mapped to ROS nodes executed in this order, however there are no explicit mechanisms to enforce it. Furthermore, when data recordings collected in field tests as ROS-bags are re-played, then the results are often surprisingly different due to non-determinism of process scheduling.
Manually setting up a particular execution order of subscriptions and publishing topics as well as defining use-case specific priorities of the corresponding Linux processes is always possible. However, this approach is error-prone, difficult to extend and requires an in-depth knowledge of the deployed ROS 2 packages in the system.
Therefore the goal of the Executor in micro-ROS is to support roboticists with practical and easy-to-use real-time mechanisms which provide solutions for:
- Deterministic execution
- Real-time guarantees
- Integration of real-time and non real-time functionalities on one platform
- Specific support for RTOS and microcontrollers
In ROS 1 a network thread is responsible for receiving all messages and putting them into a FIFO queue (in roscpp). That is, all callbacks were called in a FIFO manner, without any execution management. With the introduction of DDS (data distribution service) in ROS 2, the messages are buffered in DDS. In ROS 2, an Executor concept was introduced to support execution management. At the rcl-layer, a wait-set is configured with handles to be received and in a second step, the handles are taken from the DDS-queue. A handle is a generic term defined in rcl-layer for timers, subscriptions, services, clients and guard conditions.
The standard implementation of the ROS 2 Executor for the C++ API (rclcpp) has, however, certain unusual features, like precedence of timers over all other DDS handles, non-preemptive round-robin scheduling for non-timer handles and considering only one input data for each handle (even if multiple could be available). These features have the consequence, that in certain situations the standard rclcpp Executor is not deterministic and it makes guaranteeing real-time requirements very hard [CB2019]. We have not looked at the ROS 2 Executor implementation for Python Frontend (rclpy) because we consider a micro-controllers platform, on which typically C or C++ appliations will run.
Given the goals for a Real-Time Executor and the limitations of the ROS 2 standard rclcpp Executor, the challenges are:
- to develop an adequate and well-defined scheduling mechanisms for the ROS 2 framework and the real-time operating system (RTOS)
- to define an easy-to-use interface for ROS developers
- to model requirements (like latencies, determinism in subsystems)
- mapping of ROS 2 framework and operating system schedulers (semi-automated and optimized mapping is desired as well as generic, well-understood framework mechanisms)
Our approach is to provide a real-time-capable Executor for the rcl+rclc layer (as described in section Introduction to Client Library.) in the C programming language .
As the first step, we propose the rclc Executor for the rcl-layer in C programming language with several new features to support real-time and deterministic execution: It supports 1.) user-defined static sequential execution, 2) conditional execution semantics, 3) multi-threaded execution with scheduling configuration, and 4) logical execution semantics (LET). Sequential execution refers to the runtime behavior, that all callbacks are executed in a pre-defined order independent of the arrival time of messages. Conditional execution is available with a trigger condition which enables typical processing patterns in robotics (which are analyzed in detail in section Analysis of processing patterns. Configuration of scheduling parameters for multi-threaded application accomplishes prioritized execution. The logical execution time concept (LET) provides data synchronization for fixed periodic task scheduling of embedded applications.
Beyond the advanced execution management mechanisms for micro-ROS, we also contributed to improving and extending the Executor concept in rclcpp for standard ROS 2: the callback group-level Executor. It is not a new Executor but rather a refinement of the ROS 2 Executor API allowing to prioritize a group of callbacks which is not possible with the ROS 2 default Executor in its current Galactic release.
Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
ROS 2 allows to bundle multiple nodes in one operating system process. To coordinate the execution of the callbacks of the nodes of a process, the Executor concept was introduced in rclcpp (and also in rclpy).
The ROS 2 design defines one Executor (instance of rclcpp::executor::Executor) per process, which is typically created either in a custom main function or by the launch system. The Executor coordinates the execution of all callbacks issued by these nodes by checking for available work (timers, services, messages, subscriptions, etc.) from the DDS queue and dispatching it to one or more threads, implemented in SingleThreadedExecutor and MultiThreadedExecutor, respectively.
The dispatching mechanism resembles the ROS 1 spin thread behavior: the Executor looks up the wait sets, which notifies it of any pending callback in the DDS queue. If there are multiple pending callbacks, the ROS 2 Executor executes them in an in the order as they were registered at the Executor.
Architecture
The following diagram depicts the relevant classes of the standard ROS 2 Executor implementation:

Note that an Executor instance maintains weak pointers to the NodeBaseInterfaces of the nodes only. Therefore, nodes can be destroyed safely, without notifying the Executor.
Also, the Executor does not maintain an explicit callback queue, but relies on the queue mechanism of the underlying DDS implementation as illustrated in the following sequence diagram:

The Executor concept, however, does not provide means for prioritization or categorization of the incoming callback calls. Moreover, it does not leverage the real-time characteristics of the underlying operating-system scheduler to have finer control on the order of executions. The overall implication of this behavior is that time-critical callbacks could suffer possible deadline misses and a degraded performance since they are serviced later than non-critical callbacks. Additionally, due to the FIFO mechanism, it is difficult to determine usable bounds on the worst-case latency that each callback execution may incur.
Scheduling Semantics
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package rclc
4.0.2 (2023-03-22)
- Drop build dependency on std_msgs (backport #314) (#315)
- Updated <ros-tooling/setup-ros@0.4.2> and <ros-tooling/action-ros-ci@0.2.7> (#318) (#320)
- Removed build status for Galactic in README (EOL November 2022) (#321) (#322)
- Update documentation about number_of_handles (#326) (#327)
4.0.1 (2022-07-20)
- updated documentation bloom build status table (#291) (#292)
- updated os-version to ubuntu-22.04 (#295)
- [rolling] updated ros-tooling versions (backport #289) (#297)
- improved doxygen-generated API documentation (#301) (#302)
4.0.0 (2022-04-28)
- updated version for Humble release
3.0.8 (2022-04-14)
- Remove duplicate typedefs. (#249)
- Add rmw dependencies due to EventsExecutor PR in rcl (#255)
- Fix action client & server deallocation (#257)
- updated documentation: build status for Rolling (#266)
- Update action client goal callback signature (#282)
- Upgrade parameters (#274)
3.0.7 (2022-02-17)
- Fix enum naming for avoid collision (#242)
- Added dependency for package performance-test-fixture (#245)
3.0.6 (2022-01-25)
- executor ignore canceled timers (#220)
- uddated documentation README.md (#229)
- resolved error in unit test see issue #230 (#231)
- Add thread dependency to examples (Rolling) (#237) (resolves in this package only cpplint errors)
3.0.5 (2021-11-23)
- Fix data_available reset for timer (backport #215) (#217)
3.0.4 (2021-11-17)
- Ignoring unsuccessful SERVICE_TAKE (#175)
- Add rclc_parameter Quality Declaration (#144)
- use-ros2-testing (#185)
- Fix: printf in executor spin (#195)
- Fix init options handling (#202) (#205)
- Remove init options from support (#203)
- RCLC Actions Implementation (#170)
- Add rcl_action as build export dependency (#211)
3.0.3 (2021-07-28)
- Checking for valid ROS context in spin_some
- Refactoring executor (removing callback_type)
- Fixing codecov config
3.0.2 (2021-07-26)
- Updated codecov to ignore test folders
- Updated bloom release status table
3.0.1 (2021-07-17)
- Added rclc_parameter package
- Added quality of service entity creation API
- Added executor prepare API
- Added support for removing subscription from executor
- Added support for subscription with context
- Added quality declaration statement
- Updated compatability function for sleep
- Removed duplicate NOTICE files
2.0.0 (2021-04-23)
- Added codecov support
- New API of rcl_lifecycle in Rolling required major version bump
1.0.1 (2021-03-29)
- Windows port
- Compatibility sleep function (Windows, POSIX-OS)
- Fixed RCL lifecycle API change for Rolling
1.0.0 (2021-03-04)
- Service callbacks with context
- Fixed minor issues unit tests
- Upgraded setup_ros action (ci jobs)
- Removed Eloquent from ci jobs
0.1.7 (2021-01-20)
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged rclc at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
rclc package from rclc reporclc rclc_examples rclc_lifecycle rclc_parameter |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 4.0.2 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros2/rclc.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble |
| Last Updated | 2025-11-18 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Jan Staschulat
- Eugenio Collado
- Carlos Espinoza
Authors
- Jan Staschulat
- William Woodall
The rclc package
Table of contents
- Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
- Analysis of processing patterns
- rclc Executor
- Callback-group-level Executor
- Related Work
- References
Introduction
Predictable execution under given real-time constraints is a crucial requirement for many robotic applications. While the service-based paradigm of ROS allows a fast integration of many different functionalities, it does not provide sufficient control over the execution management. For example, there are no mechanisms to enforce a certain execution order of callbacks within a node. Also the execution order of multiple nodes is essential for control applications in mobile robotics. Cause-effect-chains comprising of sensor acquisition, evaluation of data and actuation control should be mapped to ROS nodes executed in this order, however there are no explicit mechanisms to enforce it. Furthermore, when data recordings collected in field tests as ROS-bags are re-played, then the results are often surprisingly different due to non-determinism of process scheduling.
Manually setting up a particular execution order of subscriptions and publishing topics as well as defining use-case specific priorities of the corresponding Linux processes is always possible. However, this approach is error-prone, difficult to extend and requires an in-depth knowledge of the deployed ROS 2 packages in the system.
Therefore the goal of the Executor in micro-ROS is to support roboticists with practical and easy-to-use real-time mechanisms which provide solutions for:
- Deterministic execution
- Real-time guarantees
- Integration of real-time and non real-time functionalities on one platform
- Specific support for RTOS and microcontrollers
In ROS 1 a network thread is responsible for receiving all messages and putting them into a FIFO queue (in roscpp). That is, all callbacks were called in a FIFO manner, without any execution management. With the introduction of DDS (data distribution service) in ROS 2, the messages are buffered in DDS. In ROS 2, an Executor concept was introduced to support execution management. At the rcl-layer, a wait-set is configured with handles to be received and in a second step, the handles are taken from the DDS-queue. A handle is a generic term defined in rcl-layer for timers, subscriptions, services, clients and guard conditions.
The standard implementation of the ROS 2 Executor for the C++ API (rclcpp) has, however, certain unusual features, like precedence of timers over all other DDS handles, non-preemptive round-robin scheduling for non-timer handles and considering only one input data for each handle (even if multiple could be available). These features have the consequence, that in certain situations the standard rclcpp Executor is not deterministic and it makes guaranteeing real-time requirements very hard [CB2019]. We have not looked at the ROS 2 Executor implementation for Python Frontend (rclpy) because we consider a micro-controllers platform, on which typically C or C++ appliations will run.
Given the goals for a Real-Time Executor and the limitations of the ROS 2 standard rclcpp Executor, the challenges are:
- to develop an adequate and well-defined scheduling mechanisms for the ROS 2 framework and the real-time operating system (RTOS)
- to define an easy-to-use interface for ROS developers
- to model requirements (like latencies, determinism in subsystems)
- mapping of ROS 2 framework and operating system schedulers (semi-automated and optimized mapping is desired as well as generic, well-understood framework mechanisms)
Our approach is to provide a real-time-capable Executor for the rcl+rclc layer (as described in section Introduction to Client Library.) in the C programming language .
As the first step, we propose the rclc Executor for the rcl-layer in C programming language with several new features to support real-time and deterministic execution: It supports 1.) user-defined static sequential execution, 2) conditional execution semantics, 3) multi-threaded execution with scheduling configuration, and 4) logical execution semantics (LET). Sequential execution refers to the runtime behavior, that all callbacks are executed in a pre-defined order independent of the arrival time of messages. Conditional execution is available with a trigger condition which enables typical processing patterns in robotics (which are analyzed in detail in section Analysis of processing patterns. Configuration of scheduling parameters for multi-threaded application accomplishes prioritized execution. The logical execution time concept (LET) provides data synchronization for fixed periodic task scheduling of embedded applications.
Beyond the advanced execution management mechanisms for micro-ROS, we also contributed to improving and extending the Executor concept in rclcpp for standard ROS 2: the callback group-level Executor. It is not a new Executor but rather a refinement of the ROS 2 Executor API allowing to prioritize a group of callbacks which is not possible with the ROS 2 default Executor in its current Galactic release.
Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
ROS 2 allows to bundle multiple nodes in one operating system process. To coordinate the execution of the callbacks of the nodes of a process, the Executor concept was introduced in rclcpp (and also in rclpy).
The ROS 2 design defines one Executor (instance of rclcpp::executor::Executor) per process, which is typically created either in a custom main function or by the launch system. The Executor coordinates the execution of all callbacks issued by these nodes by checking for available work (timers, services, messages, subscriptions, etc.) from the DDS queue and dispatching it to one or more threads, implemented in SingleThreadedExecutor and MultiThreadedExecutor, respectively.
The dispatching mechanism resembles the ROS 1 spin thread behavior: the Executor looks up the wait sets, which notifies it of any pending callback in the DDS queue. If there are multiple pending callbacks, the ROS 2 Executor executes them in an in the order as they were registered at the Executor.
Architecture
The following diagram depicts the relevant classes of the standard ROS 2 Executor implementation:

Note that an Executor instance maintains weak pointers to the NodeBaseInterfaces of the nodes only. Therefore, nodes can be destroyed safely, without notifying the Executor.
Also, the Executor does not maintain an explicit callback queue, but relies on the queue mechanism of the underlying DDS implementation as illustrated in the following sequence diagram:

The Executor concept, however, does not provide means for prioritization or categorization of the incoming callback calls. Moreover, it does not leverage the real-time characteristics of the underlying operating-system scheduler to have finer control on the order of executions. The overall implication of this behavior is that time-critical callbacks could suffer possible deadline misses and a degraded performance since they are serviced later than non-critical callbacks. Additionally, due to the FIFO mechanism, it is difficult to determine usable bounds on the worst-case latency that each callback execution may incur.
Scheduling Semantics
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package rclc
4.0.2 (2023-03-22)
- Drop build dependency on std_msgs (backport #314) (#315)
- Updated <ros-tooling/setup-ros@0.4.2> and <ros-tooling/action-ros-ci@0.2.7> (#318) (#320)
- Removed build status for Galactic in README (EOL November 2022) (#321) (#322)
- Update documentation about number_of_handles (#326) (#327)
4.0.1 (2022-07-20)
- updated documentation bloom build status table (#291) (#292)
- updated os-version to ubuntu-22.04 (#295)
- [rolling] updated ros-tooling versions (backport #289) (#297)
- improved doxygen-generated API documentation (#301) (#302)
4.0.0 (2022-04-28)
- updated version for Humble release
3.0.8 (2022-04-14)
- Remove duplicate typedefs. (#249)
- Add rmw dependencies due to EventsExecutor PR in rcl (#255)
- Fix action client & server deallocation (#257)
- updated documentation: build status for Rolling (#266)
- Update action client goal callback signature (#282)
- Upgrade parameters (#274)
3.0.7 (2022-02-17)
- Fix enum naming for avoid collision (#242)
- Added dependency for package performance-test-fixture (#245)
3.0.6 (2022-01-25)
- executor ignore canceled timers (#220)
- uddated documentation README.md (#229)
- resolved error in unit test see issue #230 (#231)
- Add thread dependency to examples (Rolling) (#237) (resolves in this package only cpplint errors)
3.0.5 (2021-11-23)
- Fix data_available reset for timer (backport #215) (#217)
3.0.4 (2021-11-17)
- Ignoring unsuccessful SERVICE_TAKE (#175)
- Add rclc_parameter Quality Declaration (#144)
- use-ros2-testing (#185)
- Fix: printf in executor spin (#195)
- Fix init options handling (#202) (#205)
- Remove init options from support (#203)
- RCLC Actions Implementation (#170)
- Add rcl_action as build export dependency (#211)
3.0.3 (2021-07-28)
- Checking for valid ROS context in spin_some
- Refactoring executor (removing callback_type)
- Fixing codecov config
3.0.2 (2021-07-26)
- Updated codecov to ignore test folders
- Updated bloom release status table
3.0.1 (2021-07-17)
- Added rclc_parameter package
- Added quality of service entity creation API
- Added executor prepare API
- Added support for removing subscription from executor
- Added support for subscription with context
- Added quality declaration statement
- Updated compatability function for sleep
- Removed duplicate NOTICE files
2.0.0 (2021-04-23)
- Added codecov support
- New API of rcl_lifecycle in Rolling required major version bump
1.0.1 (2021-03-29)
- Windows port
- Compatibility sleep function (Windows, POSIX-OS)
- Fixed RCL lifecycle API change for Rolling
1.0.0 (2021-03-04)
- Service callbacks with context
- Fixed minor issues unit tests
- Upgraded setup_ros action (ci jobs)
- Removed Eloquent from ci jobs
0.1.7 (2021-01-20)
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged rclc at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
rclc package from rclc reporclc rclc_examples rclc_lifecycle rclc_parameter |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 4.0.2 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros2/rclc.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble |
| Last Updated | 2025-11-18 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Jan Staschulat
- Eugenio Collado
- Carlos Espinoza
Authors
- Jan Staschulat
- William Woodall
The rclc package
Table of contents
- Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
- Analysis of processing patterns
- rclc Executor
- Callback-group-level Executor
- Related Work
- References
Introduction
Predictable execution under given real-time constraints is a crucial requirement for many robotic applications. While the service-based paradigm of ROS allows a fast integration of many different functionalities, it does not provide sufficient control over the execution management. For example, there are no mechanisms to enforce a certain execution order of callbacks within a node. Also the execution order of multiple nodes is essential for control applications in mobile robotics. Cause-effect-chains comprising of sensor acquisition, evaluation of data and actuation control should be mapped to ROS nodes executed in this order, however there are no explicit mechanisms to enforce it. Furthermore, when data recordings collected in field tests as ROS-bags are re-played, then the results are often surprisingly different due to non-determinism of process scheduling.
Manually setting up a particular execution order of subscriptions and publishing topics as well as defining use-case specific priorities of the corresponding Linux processes is always possible. However, this approach is error-prone, difficult to extend and requires an in-depth knowledge of the deployed ROS 2 packages in the system.
Therefore the goal of the Executor in micro-ROS is to support roboticists with practical and easy-to-use real-time mechanisms which provide solutions for:
- Deterministic execution
- Real-time guarantees
- Integration of real-time and non real-time functionalities on one platform
- Specific support for RTOS and microcontrollers
In ROS 1 a network thread is responsible for receiving all messages and putting them into a FIFO queue (in roscpp). That is, all callbacks were called in a FIFO manner, without any execution management. With the introduction of DDS (data distribution service) in ROS 2, the messages are buffered in DDS. In ROS 2, an Executor concept was introduced to support execution management. At the rcl-layer, a wait-set is configured with handles to be received and in a second step, the handles are taken from the DDS-queue. A handle is a generic term defined in rcl-layer for timers, subscriptions, services, clients and guard conditions.
The standard implementation of the ROS 2 Executor for the C++ API (rclcpp) has, however, certain unusual features, like precedence of timers over all other DDS handles, non-preemptive round-robin scheduling for non-timer handles and considering only one input data for each handle (even if multiple could be available). These features have the consequence, that in certain situations the standard rclcpp Executor is not deterministic and it makes guaranteeing real-time requirements very hard [CB2019]. We have not looked at the ROS 2 Executor implementation for Python Frontend (rclpy) because we consider a micro-controllers platform, on which typically C or C++ appliations will run.
Given the goals for a Real-Time Executor and the limitations of the ROS 2 standard rclcpp Executor, the challenges are:
- to develop an adequate and well-defined scheduling mechanisms for the ROS 2 framework and the real-time operating system (RTOS)
- to define an easy-to-use interface for ROS developers
- to model requirements (like latencies, determinism in subsystems)
- mapping of ROS 2 framework and operating system schedulers (semi-automated and optimized mapping is desired as well as generic, well-understood framework mechanisms)
Our approach is to provide a real-time-capable Executor for the rcl+rclc layer (as described in section Introduction to Client Library.) in the C programming language .
As the first step, we propose the rclc Executor for the rcl-layer in C programming language with several new features to support real-time and deterministic execution: It supports 1.) user-defined static sequential execution, 2) conditional execution semantics, 3) multi-threaded execution with scheduling configuration, and 4) logical execution semantics (LET). Sequential execution refers to the runtime behavior, that all callbacks are executed in a pre-defined order independent of the arrival time of messages. Conditional execution is available with a trigger condition which enables typical processing patterns in robotics (which are analyzed in detail in section Analysis of processing patterns. Configuration of scheduling parameters for multi-threaded application accomplishes prioritized execution. The logical execution time concept (LET) provides data synchronization for fixed periodic task scheduling of embedded applications.
Beyond the advanced execution management mechanisms for micro-ROS, we also contributed to improving and extending the Executor concept in rclcpp for standard ROS 2: the callback group-level Executor. It is not a new Executor but rather a refinement of the ROS 2 Executor API allowing to prioritize a group of callbacks which is not possible with the ROS 2 default Executor in its current Galactic release.
Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
ROS 2 allows to bundle multiple nodes in one operating system process. To coordinate the execution of the callbacks of the nodes of a process, the Executor concept was introduced in rclcpp (and also in rclpy).
The ROS 2 design defines one Executor (instance of rclcpp::executor::Executor) per process, which is typically created either in a custom main function or by the launch system. The Executor coordinates the execution of all callbacks issued by these nodes by checking for available work (timers, services, messages, subscriptions, etc.) from the DDS queue and dispatching it to one or more threads, implemented in SingleThreadedExecutor and MultiThreadedExecutor, respectively.
The dispatching mechanism resembles the ROS 1 spin thread behavior: the Executor looks up the wait sets, which notifies it of any pending callback in the DDS queue. If there are multiple pending callbacks, the ROS 2 Executor executes them in an in the order as they were registered at the Executor.
Architecture
The following diagram depicts the relevant classes of the standard ROS 2 Executor implementation:

Note that an Executor instance maintains weak pointers to the NodeBaseInterfaces of the nodes only. Therefore, nodes can be destroyed safely, without notifying the Executor.
Also, the Executor does not maintain an explicit callback queue, but relies on the queue mechanism of the underlying DDS implementation as illustrated in the following sequence diagram:

The Executor concept, however, does not provide means for prioritization or categorization of the incoming callback calls. Moreover, it does not leverage the real-time characteristics of the underlying operating-system scheduler to have finer control on the order of executions. The overall implication of this behavior is that time-critical callbacks could suffer possible deadline misses and a degraded performance since they are serviced later than non-critical callbacks. Additionally, due to the FIFO mechanism, it is difficult to determine usable bounds on the worst-case latency that each callback execution may incur.
Scheduling Semantics
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package rclc
4.0.2 (2023-03-22)
- Drop build dependency on std_msgs (backport #314) (#315)
- Updated <ros-tooling/setup-ros@0.4.2> and <ros-tooling/action-ros-ci@0.2.7> (#318) (#320)
- Removed build status for Galactic in README (EOL November 2022) (#321) (#322)
- Update documentation about number_of_handles (#326) (#327)
4.0.1 (2022-07-20)
- updated documentation bloom build status table (#291) (#292)
- updated os-version to ubuntu-22.04 (#295)
- [rolling] updated ros-tooling versions (backport #289) (#297)
- improved doxygen-generated API documentation (#301) (#302)
4.0.0 (2022-04-28)
- updated version for Humble release
3.0.8 (2022-04-14)
- Remove duplicate typedefs. (#249)
- Add rmw dependencies due to EventsExecutor PR in rcl (#255)
- Fix action client & server deallocation (#257)
- updated documentation: build status for Rolling (#266)
- Update action client goal callback signature (#282)
- Upgrade parameters (#274)
3.0.7 (2022-02-17)
- Fix enum naming for avoid collision (#242)
- Added dependency for package performance-test-fixture (#245)
3.0.6 (2022-01-25)
- executor ignore canceled timers (#220)
- uddated documentation README.md (#229)
- resolved error in unit test see issue #230 (#231)
- Add thread dependency to examples (Rolling) (#237) (resolves in this package only cpplint errors)
3.0.5 (2021-11-23)
- Fix data_available reset for timer (backport #215) (#217)
3.0.4 (2021-11-17)
- Ignoring unsuccessful SERVICE_TAKE (#175)
- Add rclc_parameter Quality Declaration (#144)
- use-ros2-testing (#185)
- Fix: printf in executor spin (#195)
- Fix init options handling (#202) (#205)
- Remove init options from support (#203)
- RCLC Actions Implementation (#170)
- Add rcl_action as build export dependency (#211)
3.0.3 (2021-07-28)
- Checking for valid ROS context in spin_some
- Refactoring executor (removing callback_type)
- Fixing codecov config
3.0.2 (2021-07-26)
- Updated codecov to ignore test folders
- Updated bloom release status table
3.0.1 (2021-07-17)
- Added rclc_parameter package
- Added quality of service entity creation API
- Added executor prepare API
- Added support for removing subscription from executor
- Added support for subscription with context
- Added quality declaration statement
- Updated compatability function for sleep
- Removed duplicate NOTICE files
2.0.0 (2021-04-23)
- Added codecov support
- New API of rcl_lifecycle in Rolling required major version bump
1.0.1 (2021-03-29)
- Windows port
- Compatibility sleep function (Windows, POSIX-OS)
- Fixed RCL lifecycle API change for Rolling
1.0.0 (2021-03-04)
- Service callbacks with context
- Fixed minor issues unit tests
- Upgraded setup_ros action (ci jobs)
- Removed Eloquent from ci jobs
0.1.7 (2021-01-20)
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged rclc at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
rclc package from rclc reporclc rclc_examples rclc_lifecycle rclc_parameter |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 4.0.2 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros2/rclc.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble |
| Last Updated | 2025-11-18 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Jan Staschulat
- Eugenio Collado
- Carlos Espinoza
Authors
- Jan Staschulat
- William Woodall
The rclc package
Table of contents
- Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
- Analysis of processing patterns
- rclc Executor
- Callback-group-level Executor
- Related Work
- References
Introduction
Predictable execution under given real-time constraints is a crucial requirement for many robotic applications. While the service-based paradigm of ROS allows a fast integration of many different functionalities, it does not provide sufficient control over the execution management. For example, there are no mechanisms to enforce a certain execution order of callbacks within a node. Also the execution order of multiple nodes is essential for control applications in mobile robotics. Cause-effect-chains comprising of sensor acquisition, evaluation of data and actuation control should be mapped to ROS nodes executed in this order, however there are no explicit mechanisms to enforce it. Furthermore, when data recordings collected in field tests as ROS-bags are re-played, then the results are often surprisingly different due to non-determinism of process scheduling.
Manually setting up a particular execution order of subscriptions and publishing topics as well as defining use-case specific priorities of the corresponding Linux processes is always possible. However, this approach is error-prone, difficult to extend and requires an in-depth knowledge of the deployed ROS 2 packages in the system.
Therefore the goal of the Executor in micro-ROS is to support roboticists with practical and easy-to-use real-time mechanisms which provide solutions for:
- Deterministic execution
- Real-time guarantees
- Integration of real-time and non real-time functionalities on one platform
- Specific support for RTOS and microcontrollers
In ROS 1 a network thread is responsible for receiving all messages and putting them into a FIFO queue (in roscpp). That is, all callbacks were called in a FIFO manner, without any execution management. With the introduction of DDS (data distribution service) in ROS 2, the messages are buffered in DDS. In ROS 2, an Executor concept was introduced to support execution management. At the rcl-layer, a wait-set is configured with handles to be received and in a second step, the handles are taken from the DDS-queue. A handle is a generic term defined in rcl-layer for timers, subscriptions, services, clients and guard conditions.
The standard implementation of the ROS 2 Executor for the C++ API (rclcpp) has, however, certain unusual features, like precedence of timers over all other DDS handles, non-preemptive round-robin scheduling for non-timer handles and considering only one input data for each handle (even if multiple could be available). These features have the consequence, that in certain situations the standard rclcpp Executor is not deterministic and it makes guaranteeing real-time requirements very hard [CB2019]. We have not looked at the ROS 2 Executor implementation for Python Frontend (rclpy) because we consider a micro-controllers platform, on which typically C or C++ appliations will run.
Given the goals for a Real-Time Executor and the limitations of the ROS 2 standard rclcpp Executor, the challenges are:
- to develop an adequate and well-defined scheduling mechanisms for the ROS 2 framework and the real-time operating system (RTOS)
- to define an easy-to-use interface for ROS developers
- to model requirements (like latencies, determinism in subsystems)
- mapping of ROS 2 framework and operating system schedulers (semi-automated and optimized mapping is desired as well as generic, well-understood framework mechanisms)
Our approach is to provide a real-time-capable Executor for the rcl+rclc layer (as described in section Introduction to Client Library.) in the C programming language .
As the first step, we propose the rclc Executor for the rcl-layer in C programming language with several new features to support real-time and deterministic execution: It supports 1.) user-defined static sequential execution, 2) conditional execution semantics, 3) multi-threaded execution with scheduling configuration, and 4) logical execution semantics (LET). Sequential execution refers to the runtime behavior, that all callbacks are executed in a pre-defined order independent of the arrival time of messages. Conditional execution is available with a trigger condition which enables typical processing patterns in robotics (which are analyzed in detail in section Analysis of processing patterns. Configuration of scheduling parameters for multi-threaded application accomplishes prioritized execution. The logical execution time concept (LET) provides data synchronization for fixed periodic task scheduling of embedded applications.
Beyond the advanced execution management mechanisms for micro-ROS, we also contributed to improving and extending the Executor concept in rclcpp for standard ROS 2: the callback group-level Executor. It is not a new Executor but rather a refinement of the ROS 2 Executor API allowing to prioritize a group of callbacks which is not possible with the ROS 2 default Executor in its current Galactic release.
Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
ROS 2 allows to bundle multiple nodes in one operating system process. To coordinate the execution of the callbacks of the nodes of a process, the Executor concept was introduced in rclcpp (and also in rclpy).
The ROS 2 design defines one Executor (instance of rclcpp::executor::Executor) per process, which is typically created either in a custom main function or by the launch system. The Executor coordinates the execution of all callbacks issued by these nodes by checking for available work (timers, services, messages, subscriptions, etc.) from the DDS queue and dispatching it to one or more threads, implemented in SingleThreadedExecutor and MultiThreadedExecutor, respectively.
The dispatching mechanism resembles the ROS 1 spin thread behavior: the Executor looks up the wait sets, which notifies it of any pending callback in the DDS queue. If there are multiple pending callbacks, the ROS 2 Executor executes them in an in the order as they were registered at the Executor.
Architecture
The following diagram depicts the relevant classes of the standard ROS 2 Executor implementation:

Note that an Executor instance maintains weak pointers to the NodeBaseInterfaces of the nodes only. Therefore, nodes can be destroyed safely, without notifying the Executor.
Also, the Executor does not maintain an explicit callback queue, but relies on the queue mechanism of the underlying DDS implementation as illustrated in the following sequence diagram:

The Executor concept, however, does not provide means for prioritization or categorization of the incoming callback calls. Moreover, it does not leverage the real-time characteristics of the underlying operating-system scheduler to have finer control on the order of executions. The overall implication of this behavior is that time-critical callbacks could suffer possible deadline misses and a degraded performance since they are serviced later than non-critical callbacks. Additionally, due to the FIFO mechanism, it is difficult to determine usable bounds on the worst-case latency that each callback execution may incur.
Scheduling Semantics
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package rclc
4.0.2 (2023-03-22)
- Drop build dependency on std_msgs (backport #314) (#315)
- Updated <ros-tooling/setup-ros@0.4.2> and <ros-tooling/action-ros-ci@0.2.7> (#318) (#320)
- Removed build status for Galactic in README (EOL November 2022) (#321) (#322)
- Update documentation about number_of_handles (#326) (#327)
4.0.1 (2022-07-20)
- updated documentation bloom build status table (#291) (#292)
- updated os-version to ubuntu-22.04 (#295)
- [rolling] updated ros-tooling versions (backport #289) (#297)
- improved doxygen-generated API documentation (#301) (#302)
4.0.0 (2022-04-28)
- updated version for Humble release
3.0.8 (2022-04-14)
- Remove duplicate typedefs. (#249)
- Add rmw dependencies due to EventsExecutor PR in rcl (#255)
- Fix action client & server deallocation (#257)
- updated documentation: build status for Rolling (#266)
- Update action client goal callback signature (#282)
- Upgrade parameters (#274)
3.0.7 (2022-02-17)
- Fix enum naming for avoid collision (#242)
- Added dependency for package performance-test-fixture (#245)
3.0.6 (2022-01-25)
- executor ignore canceled timers (#220)
- uddated documentation README.md (#229)
- resolved error in unit test see issue #230 (#231)
- Add thread dependency to examples (Rolling) (#237) (resolves in this package only cpplint errors)
3.0.5 (2021-11-23)
- Fix data_available reset for timer (backport #215) (#217)
3.0.4 (2021-11-17)
- Ignoring unsuccessful SERVICE_TAKE (#175)
- Add rclc_parameter Quality Declaration (#144)
- use-ros2-testing (#185)
- Fix: printf in executor spin (#195)
- Fix init options handling (#202) (#205)
- Remove init options from support (#203)
- RCLC Actions Implementation (#170)
- Add rcl_action as build export dependency (#211)
3.0.3 (2021-07-28)
- Checking for valid ROS context in spin_some
- Refactoring executor (removing callback_type)
- Fixing codecov config
3.0.2 (2021-07-26)
- Updated codecov to ignore test folders
- Updated bloom release status table
3.0.1 (2021-07-17)
- Added rclc_parameter package
- Added quality of service entity creation API
- Added executor prepare API
- Added support for removing subscription from executor
- Added support for subscription with context
- Added quality declaration statement
- Updated compatability function for sleep
- Removed duplicate NOTICE files
2.0.0 (2021-04-23)
- Added codecov support
- New API of rcl_lifecycle in Rolling required major version bump
1.0.1 (2021-03-29)
- Windows port
- Compatibility sleep function (Windows, POSIX-OS)
- Fixed RCL lifecycle API change for Rolling
1.0.0 (2021-03-04)
- Service callbacks with context
- Fixed minor issues unit tests
- Upgraded setup_ros action (ci jobs)
- Removed Eloquent from ci jobs
0.1.7 (2021-01-20)
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged rclc at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
rclc package from rclc reporclc rclc_examples rclc_lifecycle rclc_parameter |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 4.0.2 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros2/rclc.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble |
| Last Updated | 2025-11-18 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Jan Staschulat
- Eugenio Collado
- Carlos Espinoza
Authors
- Jan Staschulat
- William Woodall
The rclc package
Table of contents
- Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
- Analysis of processing patterns
- rclc Executor
- Callback-group-level Executor
- Related Work
- References
Introduction
Predictable execution under given real-time constraints is a crucial requirement for many robotic applications. While the service-based paradigm of ROS allows a fast integration of many different functionalities, it does not provide sufficient control over the execution management. For example, there are no mechanisms to enforce a certain execution order of callbacks within a node. Also the execution order of multiple nodes is essential for control applications in mobile robotics. Cause-effect-chains comprising of sensor acquisition, evaluation of data and actuation control should be mapped to ROS nodes executed in this order, however there are no explicit mechanisms to enforce it. Furthermore, when data recordings collected in field tests as ROS-bags are re-played, then the results are often surprisingly different due to non-determinism of process scheduling.
Manually setting up a particular execution order of subscriptions and publishing topics as well as defining use-case specific priorities of the corresponding Linux processes is always possible. However, this approach is error-prone, difficult to extend and requires an in-depth knowledge of the deployed ROS 2 packages in the system.
Therefore the goal of the Executor in micro-ROS is to support roboticists with practical and easy-to-use real-time mechanisms which provide solutions for:
- Deterministic execution
- Real-time guarantees
- Integration of real-time and non real-time functionalities on one platform
- Specific support for RTOS and microcontrollers
In ROS 1 a network thread is responsible for receiving all messages and putting them into a FIFO queue (in roscpp). That is, all callbacks were called in a FIFO manner, without any execution management. With the introduction of DDS (data distribution service) in ROS 2, the messages are buffered in DDS. In ROS 2, an Executor concept was introduced to support execution management. At the rcl-layer, a wait-set is configured with handles to be received and in a second step, the handles are taken from the DDS-queue. A handle is a generic term defined in rcl-layer for timers, subscriptions, services, clients and guard conditions.
The standard implementation of the ROS 2 Executor for the C++ API (rclcpp) has, however, certain unusual features, like precedence of timers over all other DDS handles, non-preemptive round-robin scheduling for non-timer handles and considering only one input data for each handle (even if multiple could be available). These features have the consequence, that in certain situations the standard rclcpp Executor is not deterministic and it makes guaranteeing real-time requirements very hard [CB2019]. We have not looked at the ROS 2 Executor implementation for Python Frontend (rclpy) because we consider a micro-controllers platform, on which typically C or C++ appliations will run.
Given the goals for a Real-Time Executor and the limitations of the ROS 2 standard rclcpp Executor, the challenges are:
- to develop an adequate and well-defined scheduling mechanisms for the ROS 2 framework and the real-time operating system (RTOS)
- to define an easy-to-use interface for ROS developers
- to model requirements (like latencies, determinism in subsystems)
- mapping of ROS 2 framework and operating system schedulers (semi-automated and optimized mapping is desired as well as generic, well-understood framework mechanisms)
Our approach is to provide a real-time-capable Executor for the rcl+rclc layer (as described in section Introduction to Client Library.) in the C programming language .
As the first step, we propose the rclc Executor for the rcl-layer in C programming language with several new features to support real-time and deterministic execution: It supports 1.) user-defined static sequential execution, 2) conditional execution semantics, 3) multi-threaded execution with scheduling configuration, and 4) logical execution semantics (LET). Sequential execution refers to the runtime behavior, that all callbacks are executed in a pre-defined order independent of the arrival time of messages. Conditional execution is available with a trigger condition which enables typical processing patterns in robotics (which are analyzed in detail in section Analysis of processing patterns. Configuration of scheduling parameters for multi-threaded application accomplishes prioritized execution. The logical execution time concept (LET) provides data synchronization for fixed periodic task scheduling of embedded applications.
Beyond the advanced execution management mechanisms for micro-ROS, we also contributed to improving and extending the Executor concept in rclcpp for standard ROS 2: the callback group-level Executor. It is not a new Executor but rather a refinement of the ROS 2 Executor API allowing to prioritize a group of callbacks which is not possible with the ROS 2 default Executor in its current Galactic release.
Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
ROS 2 allows to bundle multiple nodes in one operating system process. To coordinate the execution of the callbacks of the nodes of a process, the Executor concept was introduced in rclcpp (and also in rclpy).
The ROS 2 design defines one Executor (instance of rclcpp::executor::Executor) per process, which is typically created either in a custom main function or by the launch system. The Executor coordinates the execution of all callbacks issued by these nodes by checking for available work (timers, services, messages, subscriptions, etc.) from the DDS queue and dispatching it to one or more threads, implemented in SingleThreadedExecutor and MultiThreadedExecutor, respectively.
The dispatching mechanism resembles the ROS 1 spin thread behavior: the Executor looks up the wait sets, which notifies it of any pending callback in the DDS queue. If there are multiple pending callbacks, the ROS 2 Executor executes them in an in the order as they were registered at the Executor.
Architecture
The following diagram depicts the relevant classes of the standard ROS 2 Executor implementation:

Note that an Executor instance maintains weak pointers to the NodeBaseInterfaces of the nodes only. Therefore, nodes can be destroyed safely, without notifying the Executor.
Also, the Executor does not maintain an explicit callback queue, but relies on the queue mechanism of the underlying DDS implementation as illustrated in the following sequence diagram:

The Executor concept, however, does not provide means for prioritization or categorization of the incoming callback calls. Moreover, it does not leverage the real-time characteristics of the underlying operating-system scheduler to have finer control on the order of executions. The overall implication of this behavior is that time-critical callbacks could suffer possible deadline misses and a degraded performance since they are serviced later than non-critical callbacks. Additionally, due to the FIFO mechanism, it is difficult to determine usable bounds on the worst-case latency that each callback execution may incur.
Scheduling Semantics
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package rclc
4.0.2 (2023-03-22)
- Drop build dependency on std_msgs (backport #314) (#315)
- Updated <ros-tooling/setup-ros@0.4.2> and <ros-tooling/action-ros-ci@0.2.7> (#318) (#320)
- Removed build status for Galactic in README (EOL November 2022) (#321) (#322)
- Update documentation about number_of_handles (#326) (#327)
4.0.1 (2022-07-20)
- updated documentation bloom build status table (#291) (#292)
- updated os-version to ubuntu-22.04 (#295)
- [rolling] updated ros-tooling versions (backport #289) (#297)
- improved doxygen-generated API documentation (#301) (#302)
4.0.0 (2022-04-28)
- updated version for Humble release
3.0.8 (2022-04-14)
- Remove duplicate typedefs. (#249)
- Add rmw dependencies due to EventsExecutor PR in rcl (#255)
- Fix action client & server deallocation (#257)
- updated documentation: build status for Rolling (#266)
- Update action client goal callback signature (#282)
- Upgrade parameters (#274)
3.0.7 (2022-02-17)
- Fix enum naming for avoid collision (#242)
- Added dependency for package performance-test-fixture (#245)
3.0.6 (2022-01-25)
- executor ignore canceled timers (#220)
- uddated documentation README.md (#229)
- resolved error in unit test see issue #230 (#231)
- Add thread dependency to examples (Rolling) (#237) (resolves in this package only cpplint errors)
3.0.5 (2021-11-23)
- Fix data_available reset for timer (backport #215) (#217)
3.0.4 (2021-11-17)
- Ignoring unsuccessful SERVICE_TAKE (#175)
- Add rclc_parameter Quality Declaration (#144)
- use-ros2-testing (#185)
- Fix: printf in executor spin (#195)
- Fix init options handling (#202) (#205)
- Remove init options from support (#203)
- RCLC Actions Implementation (#170)
- Add rcl_action as build export dependency (#211)
3.0.3 (2021-07-28)
- Checking for valid ROS context in spin_some
- Refactoring executor (removing callback_type)
- Fixing codecov config
3.0.2 (2021-07-26)
- Updated codecov to ignore test folders
- Updated bloom release status table
3.0.1 (2021-07-17)
- Added rclc_parameter package
- Added quality of service entity creation API
- Added executor prepare API
- Added support for removing subscription from executor
- Added support for subscription with context
- Added quality declaration statement
- Updated compatability function for sleep
- Removed duplicate NOTICE files
2.0.0 (2021-04-23)
- Added codecov support
- New API of rcl_lifecycle in Rolling required major version bump
1.0.1 (2021-03-29)
- Windows port
- Compatibility sleep function (Windows, POSIX-OS)
- Fixed RCL lifecycle API change for Rolling
1.0.0 (2021-03-04)
- Service callbacks with context
- Fixed minor issues unit tests
- Upgraded setup_ros action (ci jobs)
- Removed Eloquent from ci jobs
0.1.7 (2021-01-20)
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged rclc at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
rclc package from rclc reporclc rclc_examples rclc_lifecycle rclc_parameter |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 4.0.2 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros2/rclc.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble |
| Last Updated | 2025-11-18 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Jan Staschulat
- Eugenio Collado
- Carlos Espinoza
Authors
- Jan Staschulat
- William Woodall
The rclc package
Table of contents
- Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
- Analysis of processing patterns
- rclc Executor
- Callback-group-level Executor
- Related Work
- References
Introduction
Predictable execution under given real-time constraints is a crucial requirement for many robotic applications. While the service-based paradigm of ROS allows a fast integration of many different functionalities, it does not provide sufficient control over the execution management. For example, there are no mechanisms to enforce a certain execution order of callbacks within a node. Also the execution order of multiple nodes is essential for control applications in mobile robotics. Cause-effect-chains comprising of sensor acquisition, evaluation of data and actuation control should be mapped to ROS nodes executed in this order, however there are no explicit mechanisms to enforce it. Furthermore, when data recordings collected in field tests as ROS-bags are re-played, then the results are often surprisingly different due to non-determinism of process scheduling.
Manually setting up a particular execution order of subscriptions and publishing topics as well as defining use-case specific priorities of the corresponding Linux processes is always possible. However, this approach is error-prone, difficult to extend and requires an in-depth knowledge of the deployed ROS 2 packages in the system.
Therefore the goal of the Executor in micro-ROS is to support roboticists with practical and easy-to-use real-time mechanisms which provide solutions for:
- Deterministic execution
- Real-time guarantees
- Integration of real-time and non real-time functionalities on one platform
- Specific support for RTOS and microcontrollers
In ROS 1 a network thread is responsible for receiving all messages and putting them into a FIFO queue (in roscpp). That is, all callbacks were called in a FIFO manner, without any execution management. With the introduction of DDS (data distribution service) in ROS 2, the messages are buffered in DDS. In ROS 2, an Executor concept was introduced to support execution management. At the rcl-layer, a wait-set is configured with handles to be received and in a second step, the handles are taken from the DDS-queue. A handle is a generic term defined in rcl-layer for timers, subscriptions, services, clients and guard conditions.
The standard implementation of the ROS 2 Executor for the C++ API (rclcpp) has, however, certain unusual features, like precedence of timers over all other DDS handles, non-preemptive round-robin scheduling for non-timer handles and considering only one input data for each handle (even if multiple could be available). These features have the consequence, that in certain situations the standard rclcpp Executor is not deterministic and it makes guaranteeing real-time requirements very hard [CB2019]. We have not looked at the ROS 2 Executor implementation for Python Frontend (rclpy) because we consider a micro-controllers platform, on which typically C or C++ appliations will run.
Given the goals for a Real-Time Executor and the limitations of the ROS 2 standard rclcpp Executor, the challenges are:
- to develop an adequate and well-defined scheduling mechanisms for the ROS 2 framework and the real-time operating system (RTOS)
- to define an easy-to-use interface for ROS developers
- to model requirements (like latencies, determinism in subsystems)
- mapping of ROS 2 framework and operating system schedulers (semi-automated and optimized mapping is desired as well as generic, well-understood framework mechanisms)
Our approach is to provide a real-time-capable Executor for the rcl+rclc layer (as described in section Introduction to Client Library.) in the C programming language .
As the first step, we propose the rclc Executor for the rcl-layer in C programming language with several new features to support real-time and deterministic execution: It supports 1.) user-defined static sequential execution, 2) conditional execution semantics, 3) multi-threaded execution with scheduling configuration, and 4) logical execution semantics (LET). Sequential execution refers to the runtime behavior, that all callbacks are executed in a pre-defined order independent of the arrival time of messages. Conditional execution is available with a trigger condition which enables typical processing patterns in robotics (which are analyzed in detail in section Analysis of processing patterns. Configuration of scheduling parameters for multi-threaded application accomplishes prioritized execution. The logical execution time concept (LET) provides data synchronization for fixed periodic task scheduling of embedded applications.
Beyond the advanced execution management mechanisms for micro-ROS, we also contributed to improving and extending the Executor concept in rclcpp for standard ROS 2: the callback group-level Executor. It is not a new Executor but rather a refinement of the ROS 2 Executor API allowing to prioritize a group of callbacks which is not possible with the ROS 2 default Executor in its current Galactic release.
Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
ROS 2 allows to bundle multiple nodes in one operating system process. To coordinate the execution of the callbacks of the nodes of a process, the Executor concept was introduced in rclcpp (and also in rclpy).
The ROS 2 design defines one Executor (instance of rclcpp::executor::Executor) per process, which is typically created either in a custom main function or by the launch system. The Executor coordinates the execution of all callbacks issued by these nodes by checking for available work (timers, services, messages, subscriptions, etc.) from the DDS queue and dispatching it to one or more threads, implemented in SingleThreadedExecutor and MultiThreadedExecutor, respectively.
The dispatching mechanism resembles the ROS 1 spin thread behavior: the Executor looks up the wait sets, which notifies it of any pending callback in the DDS queue. If there are multiple pending callbacks, the ROS 2 Executor executes them in an in the order as they were registered at the Executor.
Architecture
The following diagram depicts the relevant classes of the standard ROS 2 Executor implementation:

Note that an Executor instance maintains weak pointers to the NodeBaseInterfaces of the nodes only. Therefore, nodes can be destroyed safely, without notifying the Executor.
Also, the Executor does not maintain an explicit callback queue, but relies on the queue mechanism of the underlying DDS implementation as illustrated in the following sequence diagram:

The Executor concept, however, does not provide means for prioritization or categorization of the incoming callback calls. Moreover, it does not leverage the real-time characteristics of the underlying operating-system scheduler to have finer control on the order of executions. The overall implication of this behavior is that time-critical callbacks could suffer possible deadline misses and a degraded performance since they are serviced later than non-critical callbacks. Additionally, due to the FIFO mechanism, it is difficult to determine usable bounds on the worst-case latency that each callback execution may incur.
Scheduling Semantics
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package rclc
4.0.2 (2023-03-22)
- Drop build dependency on std_msgs (backport #314) (#315)
- Updated <ros-tooling/setup-ros@0.4.2> and <ros-tooling/action-ros-ci@0.2.7> (#318) (#320)
- Removed build status for Galactic in README (EOL November 2022) (#321) (#322)
- Update documentation about number_of_handles (#326) (#327)
4.0.1 (2022-07-20)
- updated documentation bloom build status table (#291) (#292)
- updated os-version to ubuntu-22.04 (#295)
- [rolling] updated ros-tooling versions (backport #289) (#297)
- improved doxygen-generated API documentation (#301) (#302)
4.0.0 (2022-04-28)
- updated version for Humble release
3.0.8 (2022-04-14)
- Remove duplicate typedefs. (#249)
- Add rmw dependencies due to EventsExecutor PR in rcl (#255)
- Fix action client & server deallocation (#257)
- updated documentation: build status for Rolling (#266)
- Update action client goal callback signature (#282)
- Upgrade parameters (#274)
3.0.7 (2022-02-17)
- Fix enum naming for avoid collision (#242)
- Added dependency for package performance-test-fixture (#245)
3.0.6 (2022-01-25)
- executor ignore canceled timers (#220)
- uddated documentation README.md (#229)
- resolved error in unit test see issue #230 (#231)
- Add thread dependency to examples (Rolling) (#237) (resolves in this package only cpplint errors)
3.0.5 (2021-11-23)
- Fix data_available reset for timer (backport #215) (#217)
3.0.4 (2021-11-17)
- Ignoring unsuccessful SERVICE_TAKE (#175)
- Add rclc_parameter Quality Declaration (#144)
- use-ros2-testing (#185)
- Fix: printf in executor spin (#195)
- Fix init options handling (#202) (#205)
- Remove init options from support (#203)
- RCLC Actions Implementation (#170)
- Add rcl_action as build export dependency (#211)
3.0.3 (2021-07-28)
- Checking for valid ROS context in spin_some
- Refactoring executor (removing callback_type)
- Fixing codecov config
3.0.2 (2021-07-26)
- Updated codecov to ignore test folders
- Updated bloom release status table
3.0.1 (2021-07-17)
- Added rclc_parameter package
- Added quality of service entity creation API
- Added executor prepare API
- Added support for removing subscription from executor
- Added support for subscription with context
- Added quality declaration statement
- Updated compatability function for sleep
- Removed duplicate NOTICE files
2.0.0 (2021-04-23)
- Added codecov support
- New API of rcl_lifecycle in Rolling required major version bump
1.0.1 (2021-03-29)
- Windows port
- Compatibility sleep function (Windows, POSIX-OS)
- Fixed RCL lifecycle API change for Rolling
1.0.0 (2021-03-04)
- Service callbacks with context
- Fixed minor issues unit tests
- Upgraded setup_ros action (ci jobs)
- Removed Eloquent from ci jobs
0.1.7 (2021-01-20)
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged rclc at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
rclc package from rclc reporclc rclc_examples rclc_lifecycle rclc_parameter |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 4.0.2 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/ros2/rclc.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble |
| Last Updated | 2025-11-18 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Jan Staschulat
- Eugenio Collado
- Carlos Espinoza
Authors
- Jan Staschulat
- William Woodall
The rclc package
Table of contents
- Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
- Analysis of processing patterns
- rclc Executor
- Callback-group-level Executor
- Related Work
- References
Introduction
Predictable execution under given real-time constraints is a crucial requirement for many robotic applications. While the service-based paradigm of ROS allows a fast integration of many different functionalities, it does not provide sufficient control over the execution management. For example, there are no mechanisms to enforce a certain execution order of callbacks within a node. Also the execution order of multiple nodes is essential for control applications in mobile robotics. Cause-effect-chains comprising of sensor acquisition, evaluation of data and actuation control should be mapped to ROS nodes executed in this order, however there are no explicit mechanisms to enforce it. Furthermore, when data recordings collected in field tests as ROS-bags are re-played, then the results are often surprisingly different due to non-determinism of process scheduling.
Manually setting up a particular execution order of subscriptions and publishing topics as well as defining use-case specific priorities of the corresponding Linux processes is always possible. However, this approach is error-prone, difficult to extend and requires an in-depth knowledge of the deployed ROS 2 packages in the system.
Therefore the goal of the Executor in micro-ROS is to support roboticists with practical and easy-to-use real-time mechanisms which provide solutions for:
- Deterministic execution
- Real-time guarantees
- Integration of real-time and non real-time functionalities on one platform
- Specific support for RTOS and microcontrollers
In ROS 1 a network thread is responsible for receiving all messages and putting them into a FIFO queue (in roscpp). That is, all callbacks were called in a FIFO manner, without any execution management. With the introduction of DDS (data distribution service) in ROS 2, the messages are buffered in DDS. In ROS 2, an Executor concept was introduced to support execution management. At the rcl-layer, a wait-set is configured with handles to be received and in a second step, the handles are taken from the DDS-queue. A handle is a generic term defined in rcl-layer for timers, subscriptions, services, clients and guard conditions.
The standard implementation of the ROS 2 Executor for the C++ API (rclcpp) has, however, certain unusual features, like precedence of timers over all other DDS handles, non-preemptive round-robin scheduling for non-timer handles and considering only one input data for each handle (even if multiple could be available). These features have the consequence, that in certain situations the standard rclcpp Executor is not deterministic and it makes guaranteeing real-time requirements very hard [CB2019]. We have not looked at the ROS 2 Executor implementation for Python Frontend (rclpy) because we consider a micro-controllers platform, on which typically C or C++ appliations will run.
Given the goals for a Real-Time Executor and the limitations of the ROS 2 standard rclcpp Executor, the challenges are:
- to develop an adequate and well-defined scheduling mechanisms for the ROS 2 framework and the real-time operating system (RTOS)
- to define an easy-to-use interface for ROS developers
- to model requirements (like latencies, determinism in subsystems)
- mapping of ROS 2 framework and operating system schedulers (semi-automated and optimized mapping is desired as well as generic, well-understood framework mechanisms)
Our approach is to provide a real-time-capable Executor for the rcl+rclc layer (as described in section Introduction to Client Library.) in the C programming language .
As the first step, we propose the rclc Executor for the rcl-layer in C programming language with several new features to support real-time and deterministic execution: It supports 1.) user-defined static sequential execution, 2) conditional execution semantics, 3) multi-threaded execution with scheduling configuration, and 4) logical execution semantics (LET). Sequential execution refers to the runtime behavior, that all callbacks are executed in a pre-defined order independent of the arrival time of messages. Conditional execution is available with a trigger condition which enables typical processing patterns in robotics (which are analyzed in detail in section Analysis of processing patterns. Configuration of scheduling parameters for multi-threaded application accomplishes prioritized execution. The logical execution time concept (LET) provides data synchronization for fixed periodic task scheduling of embedded applications.
Beyond the advanced execution management mechanisms for micro-ROS, we also contributed to improving and extending the Executor concept in rclcpp for standard ROS 2: the callback group-level Executor. It is not a new Executor but rather a refinement of the ROS 2 Executor API allowing to prioritize a group of callbacks which is not possible with the ROS 2 default Executor in its current Galactic release.
Analysis of rclcpp standard Executor
ROS 2 allows to bundle multiple nodes in one operating system process. To coordinate the execution of the callbacks of the nodes of a process, the Executor concept was introduced in rclcpp (and also in rclpy).
The ROS 2 design defines one Executor (instance of rclcpp::executor::Executor) per process, which is typically created either in a custom main function or by the launch system. The Executor coordinates the execution of all callbacks issued by these nodes by checking for available work (timers, services, messages, subscriptions, etc.) from the DDS queue and dispatching it to one or more threads, implemented in SingleThreadedExecutor and MultiThreadedExecutor, respectively.
The dispatching mechanism resembles the ROS 1 spin thread behavior: the Executor looks up the wait sets, which notifies it of any pending callback in the DDS queue. If there are multiple pending callbacks, the ROS 2 Executor executes them in an in the order as they were registered at the Executor.
Architecture
The following diagram depicts the relevant classes of the standard ROS 2 Executor implementation:

Note that an Executor instance maintains weak pointers to the NodeBaseInterfaces of the nodes only. Therefore, nodes can be destroyed safely, without notifying the Executor.
Also, the Executor does not maintain an explicit callback queue, but relies on the queue mechanism of the underlying DDS implementation as illustrated in the following sequence diagram:

The Executor concept, however, does not provide means for prioritization or categorization of the incoming callback calls. Moreover, it does not leverage the real-time characteristics of the underlying operating-system scheduler to have finer control on the order of executions. The overall implication of this behavior is that time-critical callbacks could suffer possible deadline misses and a degraded performance since they are serviced later than non-critical callbacks. Additionally, due to the FIFO mechanism, it is difficult to determine usable bounds on the worst-case latency that each callback execution may incur.
Scheduling Semantics
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Changelog for package rclc
4.0.2 (2023-03-22)
- Drop build dependency on std_msgs (backport #314) (#315)
- Updated <ros-tooling/setup-ros@0.4.2> and <ros-tooling/action-ros-ci@0.2.7> (#318) (#320)
- Removed build status for Galactic in README (EOL November 2022) (#321) (#322)
- Update documentation about number_of_handles (#326) (#327)
4.0.1 (2022-07-20)
- updated documentation bloom build status table (#291) (#292)
- updated os-version to ubuntu-22.04 (#295)
- [rolling] updated ros-tooling versions (backport #289) (#297)
- improved doxygen-generated API documentation (#301) (#302)
4.0.0 (2022-04-28)
- updated version for Humble release
3.0.8 (2022-04-14)
- Remove duplicate typedefs. (#249)
- Add rmw dependencies due to EventsExecutor PR in rcl (#255)
- Fix action client & server deallocation (#257)
- updated documentation: build status for Rolling (#266)
- Update action client goal callback signature (#282)
- Upgrade parameters (#274)
3.0.7 (2022-02-17)
- Fix enum naming for avoid collision (#242)
- Added dependency for package performance-test-fixture (#245)
3.0.6 (2022-01-25)
- executor ignore canceled timers (#220)
- uddated documentation README.md (#229)
- resolved error in unit test see issue #230 (#231)
- Add thread dependency to examples (Rolling) (#237) (resolves in this package only cpplint errors)
3.0.5 (2021-11-23)
- Fix data_available reset for timer (backport #215) (#217)
3.0.4 (2021-11-17)
- Ignoring unsuccessful SERVICE_TAKE (#175)
- Add rclc_parameter Quality Declaration (#144)
- use-ros2-testing (#185)
- Fix: printf in executor spin (#195)
- Fix init options handling (#202) (#205)
- Remove init options from support (#203)
- RCLC Actions Implementation (#170)
- Add rcl_action as build export dependency (#211)
3.0.3 (2021-07-28)
- Checking for valid ROS context in spin_some
- Refactoring executor (removing callback_type)
- Fixing codecov config
3.0.2 (2021-07-26)
- Updated codecov to ignore test folders
- Updated bloom release status table
3.0.1 (2021-07-17)
- Added rclc_parameter package
- Added quality of service entity creation API
- Added executor prepare API
- Added support for removing subscription from executor
- Added support for subscription with context
- Added quality declaration statement
- Updated compatability function for sleep
- Removed duplicate NOTICE files
2.0.0 (2021-04-23)
- Added codecov support
- New API of rcl_lifecycle in Rolling required major version bump
1.0.1 (2021-03-29)
- Windows port
- Compatibility sleep function (Windows, POSIX-OS)
- Fixed RCL lifecycle API change for Rolling
1.0.0 (2021-03-04)
- Service callbacks with context
- Fixed minor issues unit tests
- Upgraded setup_ros action (ci jobs)
- Removed Eloquent from ci jobs
0.1.7 (2021-01-20)
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file