
|
persist_parameter_server package from persist_parameter_server repopersist_parameter_server |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.0.4 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-01-05 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Tomoya Fujita
Authors
- Tomoya Fujita>
ROS2 Persistent Parameter Server
ROS 2 Persistent Parameter Server, that resides in the ROS 2 system to serve the parameter daemon. The other nodes(e.g the client demo provided in the code) can write/read the parameter in Parameter Server, and Parameter Server is able to store the parameter into the persistent storage which user can specify such as tmpfs, nfs, or disk.
See overview slide deck for general information.
Background
The discussion is opened here, and centralized parameter server is not a good affinity to ROS 2 distributed system architecture. One of the most valuable things about ROS APIs is that we make sure that the messages have specific semantic meaning so that they can’t be misinterpreted. As we develop the ROS 2 tools and best practices we should make sure to bring that same level of rigor to parameters too for greater reusability and correctness.
Although, it is expected to be the following requirement.
- Global configuration that many nodes share (e.g. RTOS priorities, vehicle dimensions, …)
- Generic ROS 2 system property server.
- Persistent storage support to re-initialize the system. parameters are modified in runtime and cache it into persistent volume as well. and next boot or next re-spawn, modified parameter will be loaded at initialization. (parameter lifetime is dependent on use case, sometimes system lifetime, sometimes node lifetime.)
- Using ROS1 based application with Parameter Server.
Overview
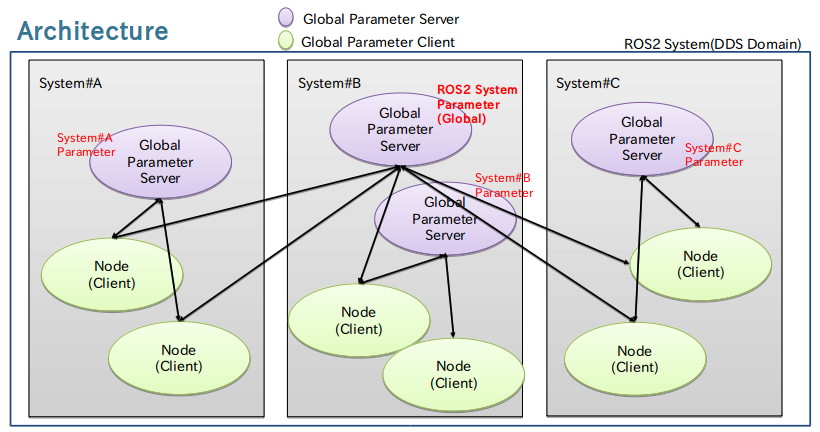
Generally ROS 2 Parameter Server is simple blackboard to write/read parameters on that. The other nodes can write/read the parameter on the server to share them in the ROS 2 system. there is a new concept for “Persistent Parameter” which is described later.
ROS 2 Parameter Server is constructed on ROS parameter API’s, nothing specific API’s are provided to connect to the server from the client. Also, about the security it just relies on ROS 2 security aspect.
Persistent Parameter Registration
Persistent Prefix
persistent parameter must have prefix “persistent”
Scope Overview
parameter server has the following scope for persistent parameter. since parameter server is built on top of ROS 2 Parameter API, parameter server supports “persistent” parameter based on /parameter_events topic.
| Category | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter API | YES | ROS 2 Parameter Client API supported, since this activity can be detected via /parameter_events. |
| Persistent Parameter File | YES | parameter server dedicated argument to specify the file to load as parameters. in addition, all of the persistent parameters will be stored into this file during shutdown. e.g) –file-path /tmp/parameter_server.yaml |
| Parameter Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args -p persistent.some_int:=42 some_int cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since this cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Parameter File Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args –params-file ./parameters_via_cli.yaml same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Launch Parameter | NO | e.g) ros2 launch persist_parameter_server parameter_server.launch.py same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
Configurable Options
-
Node Name
Since ROS 2 parameter is owned by node, node name will be needed to access the parameters, this is designed to clarify semantics for the parameters and owners. Node name will be “parameter_server” if node name is not specifies. so the other nodes can use “parameter_server” as well to access in the same system Parameter Server. If there must exist multiple parameter servers, these parameter servers need to specify a different node name, such as “parameter_server_[special_string]”, please notice that ROS 2 node name can only contains alphanumerics and ‘_’.
-
Persistent Volume
Definition of “Persistent” is different from user and use cases, so it should be configurable to set the path to store the persistent –file-path FILE_PATH parameter. Expecting if the parameter’s lifespan is system boot, path would be “/tmp” because user wants a fresh start via reboot. Or maybe physical persistent volume is chosen if users want to keep the parameter into the hardware storage. At the initialization time, Parameter Server will load the parameters from the storage which is specified by user.
-
Storing Period
It sets the interval for periodically saving parameters to the file system, and that setting the value to 0 disables periodic storing.
-
Node Options
there are three important options:
- allow_undeclared_parameters: (default true)
- automatically_declare_parameters_from_overrides: (default true)
- allow_dynamic_typing: (default false) all of the configuration options will be passed via arguments as following.
| Options | CLI | File truncated at 100 lines [see the full file](https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server/tree/rolling/./README.md)
|---|
Changelog for package persist_parameter_server
1.0.4 (2025-12-20)
-
fix: save floats in explicit float notation (#67)
* fix: save floats in explicit float notation YAML only has the concept of scalar values. So a value of '1' could be an integer, float or string. ros2_persist_parameter_server relies on being able to differentiate if something is a float or integer based on the representation of numbers. Floating numbers must be written such that they can not be mistaken as integers. This is comparable to how many programming languages assume '1' is an integer and '1.0' is a floating point number. The library yaml-cpp exports a float without the distinguishing feature required for ros2_persist_parameter_server. To fix this we manually convert the double into a string representation and ensure that a '.0' extension will be added when required. Note to future maintainer. The current yaml-cpp branch has a YAML::FpToString function which is better suited than using std::stringstream but is not available in the current yaml-cpp release.
- fix: enforce a dot as decimal point
- refactor convertDoubleToString function.
- add test case to make sure double type can be handled.
- remove this problem from known issue description in README.md.
- skil auto-genrated CHANGELOG.rst from codespell checker.
* use std::abs instead of c abs(). ---------Co-authored-by: Tomoya Fujita <<Tomoya.Fujita@sony.com>>
-
Contributors: Simon Gene Gottlieb
1.0.3 (2025-12-08)
- update pdf and html presentation slides.
- Contributors: Tomoya Fujita
1.0.2 (2025-10-21)
- Update package name in script and document
- Change package name for other configuration files
- Use a set of CMakeLists.txt and package.xml files for server and test
- update README for additional service interfaces. (#60)
- Added ros2 service call to manually trigger yaml save (#38)
- remove ament_target_dependencies deprecation warnings. (#59)
- a few follow-ups after https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_p… (#56)
- Fix/dynamic typing (#37)
- add tutorial video from The Construct.
- declare dependencies to boost dev libraries (#55)
- update markdown presenation.
- add kubernetes examples and docs. (#54)
- add JP markdown presentation for possible ROSCon JP 2025 LT. (#53)
- enable Gemini CLI workflow. (#51)
- remove ros signing key temporary workaround. (#48)
- enable builtin dictionaries with custom ones. (#47)
- support codespell github action. (#46)
- Support Kilted Kaiju. (#43)
- Remove use of ament_target_dependencies. (#42)
- perform periodic storing of the yaml file. (#36)
- add nightly workflow files for each distribution. (#34)
- add system test to github workflow for all distributions. (#32)
- fix github workflow target branch, should be rolling. (#30)
- docker images release and build script, and doc update. (#29)
- fix overview html markdown link.
- Iron Irwini is End of Life.
- add overview slide deck link on top.
- Blank issue enabled for miscellaneous issues. (#27)
- cosmetic fix for github issue template files.
- update issue templates and configuration.
- Mirror rolling to master branch.
- Signal(SIGINT) needs to be injected to the server executable. (#25)
- add jazzy to the presentation slides.
- Jazzy support (#23)
- update README and remove deprecation.
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_cmake | |
| launch_ros | |
| ament_cmake_pytest | |
| ament_lint_auto | |
| ament_lint_common | |
| launch | |
| rclcpp | |
| rclcpp_components | |
| rcutils | |
| rmw | |
| rmw_implementation_cmake | |
| std_msgs | |
| std_srvs | |
| yaml_cpp_vendor |
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged persist_parameter_server at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
persist_parameter_server package from persist_parameter_server repopersist_parameter_server |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.0.4 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-01-05 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Tomoya Fujita
Authors
- Tomoya Fujita>
ROS2 Persistent Parameter Server
ROS 2 Persistent Parameter Server, that resides in the ROS 2 system to serve the parameter daemon. The other nodes(e.g the client demo provided in the code) can write/read the parameter in Parameter Server, and Parameter Server is able to store the parameter into the persistent storage which user can specify such as tmpfs, nfs, or disk.
See overview slide deck for general information.
Background
The discussion is opened here, and centralized parameter server is not a good affinity to ROS 2 distributed system architecture. One of the most valuable things about ROS APIs is that we make sure that the messages have specific semantic meaning so that they can’t be misinterpreted. As we develop the ROS 2 tools and best practices we should make sure to bring that same level of rigor to parameters too for greater reusability and correctness.
Although, it is expected to be the following requirement.
- Global configuration that many nodes share (e.g. RTOS priorities, vehicle dimensions, …)
- Generic ROS 2 system property server.
- Persistent storage support to re-initialize the system. parameters are modified in runtime and cache it into persistent volume as well. and next boot or next re-spawn, modified parameter will be loaded at initialization. (parameter lifetime is dependent on use case, sometimes system lifetime, sometimes node lifetime.)
- Using ROS1 based application with Parameter Server.
Overview

Generally ROS 2 Parameter Server is simple blackboard to write/read parameters on that. The other nodes can write/read the parameter on the server to share them in the ROS 2 system. there is a new concept for “Persistent Parameter” which is described later.
ROS 2 Parameter Server is constructed on ROS parameter API’s, nothing specific API’s are provided to connect to the server from the client. Also, about the security it just relies on ROS 2 security aspect.
Persistent Parameter Registration
Persistent Prefix
persistent parameter must have prefix “persistent”
Scope Overview
parameter server has the following scope for persistent parameter. since parameter server is built on top of ROS 2 Parameter API, parameter server supports “persistent” parameter based on /parameter_events topic.
| Category | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter API | YES | ROS 2 Parameter Client API supported, since this activity can be detected via /parameter_events. |
| Persistent Parameter File | YES | parameter server dedicated argument to specify the file to load as parameters. in addition, all of the persistent parameters will be stored into this file during shutdown. e.g) –file-path /tmp/parameter_server.yaml |
| Parameter Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args -p persistent.some_int:=42 some_int cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since this cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Parameter File Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args –params-file ./parameters_via_cli.yaml same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Launch Parameter | NO | e.g) ros2 launch persist_parameter_server parameter_server.launch.py same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
Configurable Options
-
Node Name
Since ROS 2 parameter is owned by node, node name will be needed to access the parameters, this is designed to clarify semantics for the parameters and owners. Node name will be “parameter_server” if node name is not specifies. so the other nodes can use “parameter_server” as well to access in the same system Parameter Server. If there must exist multiple parameter servers, these parameter servers need to specify a different node name, such as “parameter_server_[special_string]”, please notice that ROS 2 node name can only contains alphanumerics and ‘_’.
-
Persistent Volume
Definition of “Persistent” is different from user and use cases, so it should be configurable to set the path to store the persistent –file-path FILE_PATH parameter. Expecting if the parameter’s lifespan is system boot, path would be “/tmp” because user wants a fresh start via reboot. Or maybe physical persistent volume is chosen if users want to keep the parameter into the hardware storage. At the initialization time, Parameter Server will load the parameters from the storage which is specified by user.
-
Storing Period
It sets the interval for periodically saving parameters to the file system, and that setting the value to 0 disables periodic storing.
-
Node Options
there are three important options:
- allow_undeclared_parameters: (default true)
- automatically_declare_parameters_from_overrides: (default true)
- allow_dynamic_typing: (default false) all of the configuration options will be passed via arguments as following.
| Options | CLI | File truncated at 100 lines [see the full file](https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server/tree/rolling/./README.md)
|---|
Changelog for package persist_parameter_server
1.0.4 (2025-12-20)
-
fix: save floats in explicit float notation (#67)
* fix: save floats in explicit float notation YAML only has the concept of scalar values. So a value of '1' could be an integer, float or string. ros2_persist_parameter_server relies on being able to differentiate if something is a float or integer based on the representation of numbers. Floating numbers must be written such that they can not be mistaken as integers. This is comparable to how many programming languages assume '1' is an integer and '1.0' is a floating point number. The library yaml-cpp exports a float without the distinguishing feature required for ros2_persist_parameter_server. To fix this we manually convert the double into a string representation and ensure that a '.0' extension will be added when required. Note to future maintainer. The current yaml-cpp branch has a YAML::FpToString function which is better suited than using std::stringstream but is not available in the current yaml-cpp release.
- fix: enforce a dot as decimal point
- refactor convertDoubleToString function.
- add test case to make sure double type can be handled.
- remove this problem from known issue description in README.md.
- skil auto-genrated CHANGELOG.rst from codespell checker.
* use std::abs instead of c abs(). ---------Co-authored-by: Tomoya Fujita <<Tomoya.Fujita@sony.com>>
-
Contributors: Simon Gene Gottlieb
1.0.3 (2025-12-08)
- update pdf and html presentation slides.
- Contributors: Tomoya Fujita
1.0.2 (2025-10-21)
- Update package name in script and document
- Change package name for other configuration files
- Use a set of CMakeLists.txt and package.xml files for server and test
- update README for additional service interfaces. (#60)
- Added ros2 service call to manually trigger yaml save (#38)
- remove ament_target_dependencies deprecation warnings. (#59)
- a few follow-ups after https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_p… (#56)
- Fix/dynamic typing (#37)
- add tutorial video from The Construct.
- declare dependencies to boost dev libraries (#55)
- update markdown presenation.
- add kubernetes examples and docs. (#54)
- add JP markdown presentation for possible ROSCon JP 2025 LT. (#53)
- enable Gemini CLI workflow. (#51)
- remove ros signing key temporary workaround. (#48)
- enable builtin dictionaries with custom ones. (#47)
- support codespell github action. (#46)
- Support Kilted Kaiju. (#43)
- Remove use of ament_target_dependencies. (#42)
- perform periodic storing of the yaml file. (#36)
- add nightly workflow files for each distribution. (#34)
- add system test to github workflow for all distributions. (#32)
- fix github workflow target branch, should be rolling. (#30)
- docker images release and build script, and doc update. (#29)
- fix overview html markdown link.
- Iron Irwini is End of Life.
- add overview slide deck link on top.
- Blank issue enabled for miscellaneous issues. (#27)
- cosmetic fix for github issue template files.
- update issue templates and configuration.
- Mirror rolling to master branch.
- Signal(SIGINT) needs to be injected to the server executable. (#25)
- add jazzy to the presentation slides.
- Jazzy support (#23)
- update README and remove deprecation.
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_cmake | |
| launch_ros | |
| ament_cmake_pytest | |
| ament_lint_auto | |
| ament_lint_common | |
| launch | |
| rclcpp | |
| rclcpp_components | |
| rcutils | |
| rmw | |
| rmw_implementation_cmake | |
| std_msgs | |
| std_srvs | |
| yaml_cpp_vendor |
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged persist_parameter_server at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
persist_parameter_server package from persist_parameter_server repopersist_parameter_server |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.0.4 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-01-05 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Tomoya Fujita
Authors
- Tomoya Fujita>
ROS2 Persistent Parameter Server
ROS 2 Persistent Parameter Server, that resides in the ROS 2 system to serve the parameter daemon. The other nodes(e.g the client demo provided in the code) can write/read the parameter in Parameter Server, and Parameter Server is able to store the parameter into the persistent storage which user can specify such as tmpfs, nfs, or disk.
See overview slide deck for general information.
Background
The discussion is opened here, and centralized parameter server is not a good affinity to ROS 2 distributed system architecture. One of the most valuable things about ROS APIs is that we make sure that the messages have specific semantic meaning so that they can’t be misinterpreted. As we develop the ROS 2 tools and best practices we should make sure to bring that same level of rigor to parameters too for greater reusability and correctness.
Although, it is expected to be the following requirement.
- Global configuration that many nodes share (e.g. RTOS priorities, vehicle dimensions, …)
- Generic ROS 2 system property server.
- Persistent storage support to re-initialize the system. parameters are modified in runtime and cache it into persistent volume as well. and next boot or next re-spawn, modified parameter will be loaded at initialization. (parameter lifetime is dependent on use case, sometimes system lifetime, sometimes node lifetime.)
- Using ROS1 based application with Parameter Server.
Overview

Generally ROS 2 Parameter Server is simple blackboard to write/read parameters on that. The other nodes can write/read the parameter on the server to share them in the ROS 2 system. there is a new concept for “Persistent Parameter” which is described later.
ROS 2 Parameter Server is constructed on ROS parameter API’s, nothing specific API’s are provided to connect to the server from the client. Also, about the security it just relies on ROS 2 security aspect.
Persistent Parameter Registration
Persistent Prefix
persistent parameter must have prefix “persistent”
Scope Overview
parameter server has the following scope for persistent parameter. since parameter server is built on top of ROS 2 Parameter API, parameter server supports “persistent” parameter based on /parameter_events topic.
| Category | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter API | YES | ROS 2 Parameter Client API supported, since this activity can be detected via /parameter_events. |
| Persistent Parameter File | YES | parameter server dedicated argument to specify the file to load as parameters. in addition, all of the persistent parameters will be stored into this file during shutdown. e.g) –file-path /tmp/parameter_server.yaml |
| Parameter Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args -p persistent.some_int:=42 some_int cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since this cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Parameter File Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args –params-file ./parameters_via_cli.yaml same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Launch Parameter | NO | e.g) ros2 launch persist_parameter_server parameter_server.launch.py same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
Configurable Options
-
Node Name
Since ROS 2 parameter is owned by node, node name will be needed to access the parameters, this is designed to clarify semantics for the parameters and owners. Node name will be “parameter_server” if node name is not specifies. so the other nodes can use “parameter_server” as well to access in the same system Parameter Server. If there must exist multiple parameter servers, these parameter servers need to specify a different node name, such as “parameter_server_[special_string]”, please notice that ROS 2 node name can only contains alphanumerics and ‘_’.
-
Persistent Volume
Definition of “Persistent” is different from user and use cases, so it should be configurable to set the path to store the persistent –file-path FILE_PATH parameter. Expecting if the parameter’s lifespan is system boot, path would be “/tmp” because user wants a fresh start via reboot. Or maybe physical persistent volume is chosen if users want to keep the parameter into the hardware storage. At the initialization time, Parameter Server will load the parameters from the storage which is specified by user.
-
Storing Period
It sets the interval for periodically saving parameters to the file system, and that setting the value to 0 disables periodic storing.
-
Node Options
there are three important options:
- allow_undeclared_parameters: (default true)
- automatically_declare_parameters_from_overrides: (default true)
- allow_dynamic_typing: (default false) all of the configuration options will be passed via arguments as following.
| Options | CLI | File truncated at 100 lines [see the full file](https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server/tree/rolling/./README.md)
|---|
Changelog for package persist_parameter_server
1.0.4 (2025-12-20)
-
fix: save floats in explicit float notation (#67)
* fix: save floats in explicit float notation YAML only has the concept of scalar values. So a value of '1' could be an integer, float or string. ros2_persist_parameter_server relies on being able to differentiate if something is a float or integer based on the representation of numbers. Floating numbers must be written such that they can not be mistaken as integers. This is comparable to how many programming languages assume '1' is an integer and '1.0' is a floating point number. The library yaml-cpp exports a float without the distinguishing feature required for ros2_persist_parameter_server. To fix this we manually convert the double into a string representation and ensure that a '.0' extension will be added when required. Note to future maintainer. The current yaml-cpp branch has a YAML::FpToString function which is better suited than using std::stringstream but is not available in the current yaml-cpp release.
- fix: enforce a dot as decimal point
- refactor convertDoubleToString function.
- add test case to make sure double type can be handled.
- remove this problem from known issue description in README.md.
- skil auto-genrated CHANGELOG.rst from codespell checker.
* use std::abs instead of c abs(). ---------Co-authored-by: Tomoya Fujita <<Tomoya.Fujita@sony.com>>
-
Contributors: Simon Gene Gottlieb
1.0.3 (2025-12-08)
- update pdf and html presentation slides.
- Contributors: Tomoya Fujita
1.0.2 (2025-10-21)
- Update package name in script and document
- Change package name for other configuration files
- Use a set of CMakeLists.txt and package.xml files for server and test
- update README for additional service interfaces. (#60)
- Added ros2 service call to manually trigger yaml save (#38)
- remove ament_target_dependencies deprecation warnings. (#59)
- a few follow-ups after https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_p… (#56)
- Fix/dynamic typing (#37)
- add tutorial video from The Construct.
- declare dependencies to boost dev libraries (#55)
- update markdown presenation.
- add kubernetes examples and docs. (#54)
- add JP markdown presentation for possible ROSCon JP 2025 LT. (#53)
- enable Gemini CLI workflow. (#51)
- remove ros signing key temporary workaround. (#48)
- enable builtin dictionaries with custom ones. (#47)
- support codespell github action. (#46)
- Support Kilted Kaiju. (#43)
- Remove use of ament_target_dependencies. (#42)
- perform periodic storing of the yaml file. (#36)
- add nightly workflow files for each distribution. (#34)
- add system test to github workflow for all distributions. (#32)
- fix github workflow target branch, should be rolling. (#30)
- docker images release and build script, and doc update. (#29)
- fix overview html markdown link.
- Iron Irwini is End of Life.
- add overview slide deck link on top.
- Blank issue enabled for miscellaneous issues. (#27)
- cosmetic fix for github issue template files.
- update issue templates and configuration.
- Mirror rolling to master branch.
- Signal(SIGINT) needs to be injected to the server executable. (#25)
- add jazzy to the presentation slides.
- Jazzy support (#23)
- update README and remove deprecation.
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_cmake | |
| launch_ros | |
| ament_cmake_pytest | |
| ament_lint_auto | |
| ament_lint_common | |
| launch | |
| rclcpp | |
| rclcpp_components | |
| rcutils | |
| rmw | |
| rmw_implementation_cmake | |
| std_msgs | |
| std_srvs | |
| yaml_cpp_vendor |
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged persist_parameter_server at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
persist_parameter_server package from persist_parameter_server repopersist_parameter_server |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.0.4 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-01-05 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Tomoya Fujita
Authors
- Tomoya Fujita>
ROS2 Persistent Parameter Server
ROS 2 Persistent Parameter Server, that resides in the ROS 2 system to serve the parameter daemon. The other nodes(e.g the client demo provided in the code) can write/read the parameter in Parameter Server, and Parameter Server is able to store the parameter into the persistent storage which user can specify such as tmpfs, nfs, or disk.
See overview slide deck for general information.
Background
The discussion is opened here, and centralized parameter server is not a good affinity to ROS 2 distributed system architecture. One of the most valuable things about ROS APIs is that we make sure that the messages have specific semantic meaning so that they can’t be misinterpreted. As we develop the ROS 2 tools and best practices we should make sure to bring that same level of rigor to parameters too for greater reusability and correctness.
Although, it is expected to be the following requirement.
- Global configuration that many nodes share (e.g. RTOS priorities, vehicle dimensions, …)
- Generic ROS 2 system property server.
- Persistent storage support to re-initialize the system. parameters are modified in runtime and cache it into persistent volume as well. and next boot or next re-spawn, modified parameter will be loaded at initialization. (parameter lifetime is dependent on use case, sometimes system lifetime, sometimes node lifetime.)
- Using ROS1 based application with Parameter Server.
Overview

Generally ROS 2 Parameter Server is simple blackboard to write/read parameters on that. The other nodes can write/read the parameter on the server to share them in the ROS 2 system. there is a new concept for “Persistent Parameter” which is described later.
ROS 2 Parameter Server is constructed on ROS parameter API’s, nothing specific API’s are provided to connect to the server from the client. Also, about the security it just relies on ROS 2 security aspect.
Persistent Parameter Registration
Persistent Prefix
persistent parameter must have prefix “persistent”
Scope Overview
parameter server has the following scope for persistent parameter. since parameter server is built on top of ROS 2 Parameter API, parameter server supports “persistent” parameter based on /parameter_events topic.
| Category | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter API | YES | ROS 2 Parameter Client API supported, since this activity can be detected via /parameter_events. |
| Persistent Parameter File | YES | parameter server dedicated argument to specify the file to load as parameters. in addition, all of the persistent parameters will be stored into this file during shutdown. e.g) –file-path /tmp/parameter_server.yaml |
| Parameter Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args -p persistent.some_int:=42 some_int cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since this cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Parameter File Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args –params-file ./parameters_via_cli.yaml same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Launch Parameter | NO | e.g) ros2 launch persist_parameter_server parameter_server.launch.py same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
Configurable Options
-
Node Name
Since ROS 2 parameter is owned by node, node name will be needed to access the parameters, this is designed to clarify semantics for the parameters and owners. Node name will be “parameter_server” if node name is not specifies. so the other nodes can use “parameter_server” as well to access in the same system Parameter Server. If there must exist multiple parameter servers, these parameter servers need to specify a different node name, such as “parameter_server_[special_string]”, please notice that ROS 2 node name can only contains alphanumerics and ‘_’.
-
Persistent Volume
Definition of “Persistent” is different from user and use cases, so it should be configurable to set the path to store the persistent –file-path FILE_PATH parameter. Expecting if the parameter’s lifespan is system boot, path would be “/tmp” because user wants a fresh start via reboot. Or maybe physical persistent volume is chosen if users want to keep the parameter into the hardware storage. At the initialization time, Parameter Server will load the parameters from the storage which is specified by user.
-
Storing Period
It sets the interval for periodically saving parameters to the file system, and that setting the value to 0 disables periodic storing.
-
Node Options
there are three important options:
- allow_undeclared_parameters: (default true)
- automatically_declare_parameters_from_overrides: (default true)
- allow_dynamic_typing: (default false) all of the configuration options will be passed via arguments as following.
| Options | CLI | File truncated at 100 lines [see the full file](https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server/tree/rolling/./README.md)
|---|
Changelog for package persist_parameter_server
1.0.4 (2025-12-20)
-
fix: save floats in explicit float notation (#67)
* fix: save floats in explicit float notation YAML only has the concept of scalar values. So a value of '1' could be an integer, float or string. ros2_persist_parameter_server relies on being able to differentiate if something is a float or integer based on the representation of numbers. Floating numbers must be written such that they can not be mistaken as integers. This is comparable to how many programming languages assume '1' is an integer and '1.0' is a floating point number. The library yaml-cpp exports a float without the distinguishing feature required for ros2_persist_parameter_server. To fix this we manually convert the double into a string representation and ensure that a '.0' extension will be added when required. Note to future maintainer. The current yaml-cpp branch has a YAML::FpToString function which is better suited than using std::stringstream but is not available in the current yaml-cpp release.
- fix: enforce a dot as decimal point
- refactor convertDoubleToString function.
- add test case to make sure double type can be handled.
- remove this problem from known issue description in README.md.
- skil auto-genrated CHANGELOG.rst from codespell checker.
* use std::abs instead of c abs(). ---------Co-authored-by: Tomoya Fujita <<Tomoya.Fujita@sony.com>>
-
Contributors: Simon Gene Gottlieb
1.0.3 (2025-12-08)
- update pdf and html presentation slides.
- Contributors: Tomoya Fujita
1.0.2 (2025-10-21)
- Update package name in script and document
- Change package name for other configuration files
- Use a set of CMakeLists.txt and package.xml files for server and test
- update README for additional service interfaces. (#60)
- Added ros2 service call to manually trigger yaml save (#38)
- remove ament_target_dependencies deprecation warnings. (#59)
- a few follow-ups after https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_p… (#56)
- Fix/dynamic typing (#37)
- add tutorial video from The Construct.
- declare dependencies to boost dev libraries (#55)
- update markdown presenation.
- add kubernetes examples and docs. (#54)
- add JP markdown presentation for possible ROSCon JP 2025 LT. (#53)
- enable Gemini CLI workflow. (#51)
- remove ros signing key temporary workaround. (#48)
- enable builtin dictionaries with custom ones. (#47)
- support codespell github action. (#46)
- Support Kilted Kaiju. (#43)
- Remove use of ament_target_dependencies. (#42)
- perform periodic storing of the yaml file. (#36)
- add nightly workflow files for each distribution. (#34)
- add system test to github workflow for all distributions. (#32)
- fix github workflow target branch, should be rolling. (#30)
- docker images release and build script, and doc update. (#29)
- fix overview html markdown link.
- Iron Irwini is End of Life.
- add overview slide deck link on top.
- Blank issue enabled for miscellaneous issues. (#27)
- cosmetic fix for github issue template files.
- update issue templates and configuration.
- Mirror rolling to master branch.
- Signal(SIGINT) needs to be injected to the server executable. (#25)
- add jazzy to the presentation slides.
- Jazzy support (#23)
- update README and remove deprecation.
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_cmake | |
| launch_ros | |
| ament_cmake_pytest | |
| ament_lint_auto | |
| ament_lint_common | |
| launch | |
| rclcpp | |
| rclcpp_components | |
| rcutils | |
| rmw | |
| rmw_implementation_cmake | |
| std_msgs | |
| std_srvs | |
| yaml_cpp_vendor |
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged persist_parameter_server at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
persist_parameter_server package from persist_parameter_server repopersist_parameter_server |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.0.4 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-01-05 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Tomoya Fujita
Authors
- Tomoya Fujita>
ROS2 Persistent Parameter Server
ROS 2 Persistent Parameter Server, that resides in the ROS 2 system to serve the parameter daemon. The other nodes(e.g the client demo provided in the code) can write/read the parameter in Parameter Server, and Parameter Server is able to store the parameter into the persistent storage which user can specify such as tmpfs, nfs, or disk.
See overview slide deck for general information.
Background
The discussion is opened here, and centralized parameter server is not a good affinity to ROS 2 distributed system architecture. One of the most valuable things about ROS APIs is that we make sure that the messages have specific semantic meaning so that they can’t be misinterpreted. As we develop the ROS 2 tools and best practices we should make sure to bring that same level of rigor to parameters too for greater reusability and correctness.
Although, it is expected to be the following requirement.
- Global configuration that many nodes share (e.g. RTOS priorities, vehicle dimensions, …)
- Generic ROS 2 system property server.
- Persistent storage support to re-initialize the system. parameters are modified in runtime and cache it into persistent volume as well. and next boot or next re-spawn, modified parameter will be loaded at initialization. (parameter lifetime is dependent on use case, sometimes system lifetime, sometimes node lifetime.)
- Using ROS1 based application with Parameter Server.
Overview

Generally ROS 2 Parameter Server is simple blackboard to write/read parameters on that. The other nodes can write/read the parameter on the server to share them in the ROS 2 system. there is a new concept for “Persistent Parameter” which is described later.
ROS 2 Parameter Server is constructed on ROS parameter API’s, nothing specific API’s are provided to connect to the server from the client. Also, about the security it just relies on ROS 2 security aspect.
Persistent Parameter Registration
Persistent Prefix
persistent parameter must have prefix “persistent”
Scope Overview
parameter server has the following scope for persistent parameter. since parameter server is built on top of ROS 2 Parameter API, parameter server supports “persistent” parameter based on /parameter_events topic.
| Category | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter API | YES | ROS 2 Parameter Client API supported, since this activity can be detected via /parameter_events. |
| Persistent Parameter File | YES | parameter server dedicated argument to specify the file to load as parameters. in addition, all of the persistent parameters will be stored into this file during shutdown. e.g) –file-path /tmp/parameter_server.yaml |
| Parameter Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args -p persistent.some_int:=42 some_int cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since this cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Parameter File Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args –params-file ./parameters_via_cli.yaml same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Launch Parameter | NO | e.g) ros2 launch persist_parameter_server parameter_server.launch.py same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
Configurable Options
-
Node Name
Since ROS 2 parameter is owned by node, node name will be needed to access the parameters, this is designed to clarify semantics for the parameters and owners. Node name will be “parameter_server” if node name is not specifies. so the other nodes can use “parameter_server” as well to access in the same system Parameter Server. If there must exist multiple parameter servers, these parameter servers need to specify a different node name, such as “parameter_server_[special_string]”, please notice that ROS 2 node name can only contains alphanumerics and ‘_’.
-
Persistent Volume
Definition of “Persistent” is different from user and use cases, so it should be configurable to set the path to store the persistent –file-path FILE_PATH parameter. Expecting if the parameter’s lifespan is system boot, path would be “/tmp” because user wants a fresh start via reboot. Or maybe physical persistent volume is chosen if users want to keep the parameter into the hardware storage. At the initialization time, Parameter Server will load the parameters from the storage which is specified by user.
-
Storing Period
It sets the interval for periodically saving parameters to the file system, and that setting the value to 0 disables periodic storing.
-
Node Options
there are three important options:
- allow_undeclared_parameters: (default true)
- automatically_declare_parameters_from_overrides: (default true)
- allow_dynamic_typing: (default false) all of the configuration options will be passed via arguments as following.
| Options | CLI | File truncated at 100 lines [see the full file](https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server/tree/rolling/./README.md)
|---|
Changelog for package persist_parameter_server
1.0.4 (2025-12-20)
-
fix: save floats in explicit float notation (#67)
* fix: save floats in explicit float notation YAML only has the concept of scalar values. So a value of '1' could be an integer, float or string. ros2_persist_parameter_server relies on being able to differentiate if something is a float or integer based on the representation of numbers. Floating numbers must be written such that they can not be mistaken as integers. This is comparable to how many programming languages assume '1' is an integer and '1.0' is a floating point number. The library yaml-cpp exports a float without the distinguishing feature required for ros2_persist_parameter_server. To fix this we manually convert the double into a string representation and ensure that a '.0' extension will be added when required. Note to future maintainer. The current yaml-cpp branch has a YAML::FpToString function which is better suited than using std::stringstream but is not available in the current yaml-cpp release.
- fix: enforce a dot as decimal point
- refactor convertDoubleToString function.
- add test case to make sure double type can be handled.
- remove this problem from known issue description in README.md.
- skil auto-genrated CHANGELOG.rst from codespell checker.
* use std::abs instead of c abs(). ---------Co-authored-by: Tomoya Fujita <<Tomoya.Fujita@sony.com>>
-
Contributors: Simon Gene Gottlieb
1.0.3 (2025-12-08)
- update pdf and html presentation slides.
- Contributors: Tomoya Fujita
1.0.2 (2025-10-21)
- Update package name in script and document
- Change package name for other configuration files
- Use a set of CMakeLists.txt and package.xml files for server and test
- update README for additional service interfaces. (#60)
- Added ros2 service call to manually trigger yaml save (#38)
- remove ament_target_dependencies deprecation warnings. (#59)
- a few follow-ups after https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_p… (#56)
- Fix/dynamic typing (#37)
- add tutorial video from The Construct.
- declare dependencies to boost dev libraries (#55)
- update markdown presenation.
- add kubernetes examples and docs. (#54)
- add JP markdown presentation for possible ROSCon JP 2025 LT. (#53)
- enable Gemini CLI workflow. (#51)
- remove ros signing key temporary workaround. (#48)
- enable builtin dictionaries with custom ones. (#47)
- support codespell github action. (#46)
- Support Kilted Kaiju. (#43)
- Remove use of ament_target_dependencies. (#42)
- perform periodic storing of the yaml file. (#36)
- add nightly workflow files for each distribution. (#34)
- add system test to github workflow for all distributions. (#32)
- fix github workflow target branch, should be rolling. (#30)
- docker images release and build script, and doc update. (#29)
- fix overview html markdown link.
- Iron Irwini is End of Life.
- add overview slide deck link on top.
- Blank issue enabled for miscellaneous issues. (#27)
- cosmetic fix for github issue template files.
- update issue templates and configuration.
- Mirror rolling to master branch.
- Signal(SIGINT) needs to be injected to the server executable. (#25)
- add jazzy to the presentation slides.
- Jazzy support (#23)
- update README and remove deprecation.
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_cmake | |
| launch_ros | |
| ament_cmake_pytest | |
| ament_lint_auto | |
| ament_lint_common | |
| launch | |
| rclcpp | |
| rclcpp_components | |
| rcutils | |
| rmw | |
| rmw_implementation_cmake | |
| std_msgs | |
| std_srvs | |
| yaml_cpp_vendor |
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged persist_parameter_server at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
persist_parameter_server package from persist_parameter_server repopersist_parameter_server |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.0.4 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-01-05 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Tomoya Fujita
Authors
- Tomoya Fujita>
ROS2 Persistent Parameter Server
ROS 2 Persistent Parameter Server, that resides in the ROS 2 system to serve the parameter daemon. The other nodes(e.g the client demo provided in the code) can write/read the parameter in Parameter Server, and Parameter Server is able to store the parameter into the persistent storage which user can specify such as tmpfs, nfs, or disk.
See overview slide deck for general information.
Background
The discussion is opened here, and centralized parameter server is not a good affinity to ROS 2 distributed system architecture. One of the most valuable things about ROS APIs is that we make sure that the messages have specific semantic meaning so that they can’t be misinterpreted. As we develop the ROS 2 tools and best practices we should make sure to bring that same level of rigor to parameters too for greater reusability and correctness.
Although, it is expected to be the following requirement.
- Global configuration that many nodes share (e.g. RTOS priorities, vehicle dimensions, …)
- Generic ROS 2 system property server.
- Persistent storage support to re-initialize the system. parameters are modified in runtime and cache it into persistent volume as well. and next boot or next re-spawn, modified parameter will be loaded at initialization. (parameter lifetime is dependent on use case, sometimes system lifetime, sometimes node lifetime.)
- Using ROS1 based application with Parameter Server.
Overview

Generally ROS 2 Parameter Server is simple blackboard to write/read parameters on that. The other nodes can write/read the parameter on the server to share them in the ROS 2 system. there is a new concept for “Persistent Parameter” which is described later.
ROS 2 Parameter Server is constructed on ROS parameter API’s, nothing specific API’s are provided to connect to the server from the client. Also, about the security it just relies on ROS 2 security aspect.
Persistent Parameter Registration
Persistent Prefix
persistent parameter must have prefix “persistent”
Scope Overview
parameter server has the following scope for persistent parameter. since parameter server is built on top of ROS 2 Parameter API, parameter server supports “persistent” parameter based on /parameter_events topic.
| Category | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter API | YES | ROS 2 Parameter Client API supported, since this activity can be detected via /parameter_events. |
| Persistent Parameter File | YES | parameter server dedicated argument to specify the file to load as parameters. in addition, all of the persistent parameters will be stored into this file during shutdown. e.g) –file-path /tmp/parameter_server.yaml |
| Parameter Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args -p persistent.some_int:=42 some_int cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since this cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Parameter File Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args –params-file ./parameters_via_cli.yaml same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Launch Parameter | NO | e.g) ros2 launch persist_parameter_server parameter_server.launch.py same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
Configurable Options
-
Node Name
Since ROS 2 parameter is owned by node, node name will be needed to access the parameters, this is designed to clarify semantics for the parameters and owners. Node name will be “parameter_server” if node name is not specifies. so the other nodes can use “parameter_server” as well to access in the same system Parameter Server. If there must exist multiple parameter servers, these parameter servers need to specify a different node name, such as “parameter_server_[special_string]”, please notice that ROS 2 node name can only contains alphanumerics and ‘_’.
-
Persistent Volume
Definition of “Persistent” is different from user and use cases, so it should be configurable to set the path to store the persistent –file-path FILE_PATH parameter. Expecting if the parameter’s lifespan is system boot, path would be “/tmp” because user wants a fresh start via reboot. Or maybe physical persistent volume is chosen if users want to keep the parameter into the hardware storage. At the initialization time, Parameter Server will load the parameters from the storage which is specified by user.
-
Storing Period
It sets the interval for periodically saving parameters to the file system, and that setting the value to 0 disables periodic storing.
-
Node Options
there are three important options:
- allow_undeclared_parameters: (default true)
- automatically_declare_parameters_from_overrides: (default true)
- allow_dynamic_typing: (default false) all of the configuration options will be passed via arguments as following.
| Options | CLI | File truncated at 100 lines [see the full file](https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server/tree/rolling/./README.md)
|---|
Changelog for package persist_parameter_server
1.0.4 (2025-12-20)
-
fix: save floats in explicit float notation (#67)
* fix: save floats in explicit float notation YAML only has the concept of scalar values. So a value of '1' could be an integer, float or string. ros2_persist_parameter_server relies on being able to differentiate if something is a float or integer based on the representation of numbers. Floating numbers must be written such that they can not be mistaken as integers. This is comparable to how many programming languages assume '1' is an integer and '1.0' is a floating point number. The library yaml-cpp exports a float without the distinguishing feature required for ros2_persist_parameter_server. To fix this we manually convert the double into a string representation and ensure that a '.0' extension will be added when required. Note to future maintainer. The current yaml-cpp branch has a YAML::FpToString function which is better suited than using std::stringstream but is not available in the current yaml-cpp release.
- fix: enforce a dot as decimal point
- refactor convertDoubleToString function.
- add test case to make sure double type can be handled.
- remove this problem from known issue description in README.md.
- skil auto-genrated CHANGELOG.rst from codespell checker.
* use std::abs instead of c abs(). ---------Co-authored-by: Tomoya Fujita <<Tomoya.Fujita@sony.com>>
-
Contributors: Simon Gene Gottlieb
1.0.3 (2025-12-08)
- update pdf and html presentation slides.
- Contributors: Tomoya Fujita
1.0.2 (2025-10-21)
- Update package name in script and document
- Change package name for other configuration files
- Use a set of CMakeLists.txt and package.xml files for server and test
- update README for additional service interfaces. (#60)
- Added ros2 service call to manually trigger yaml save (#38)
- remove ament_target_dependencies deprecation warnings. (#59)
- a few follow-ups after https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_p… (#56)
- Fix/dynamic typing (#37)
- add tutorial video from The Construct.
- declare dependencies to boost dev libraries (#55)
- update markdown presenation.
- add kubernetes examples and docs. (#54)
- add JP markdown presentation for possible ROSCon JP 2025 LT. (#53)
- enable Gemini CLI workflow. (#51)
- remove ros signing key temporary workaround. (#48)
- enable builtin dictionaries with custom ones. (#47)
- support codespell github action. (#46)
- Support Kilted Kaiju. (#43)
- Remove use of ament_target_dependencies. (#42)
- perform periodic storing of the yaml file. (#36)
- add nightly workflow files for each distribution. (#34)
- add system test to github workflow for all distributions. (#32)
- fix github workflow target branch, should be rolling. (#30)
- docker images release and build script, and doc update. (#29)
- fix overview html markdown link.
- Iron Irwini is End of Life.
- add overview slide deck link on top.
- Blank issue enabled for miscellaneous issues. (#27)
- cosmetic fix for github issue template files.
- update issue templates and configuration.
- Mirror rolling to master branch.
- Signal(SIGINT) needs to be injected to the server executable. (#25)
- add jazzy to the presentation slides.
- Jazzy support (#23)
- update README and remove deprecation.
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_cmake | |
| launch_ros | |
| ament_cmake_pytest | |
| ament_lint_auto | |
| ament_lint_common | |
| launch | |
| rclcpp | |
| rclcpp_components | |
| rcutils | |
| rmw | |
| rmw_implementation_cmake | |
| std_msgs | |
| std_srvs | |
| yaml_cpp_vendor |
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged persist_parameter_server at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
persist_parameter_server package from persist_parameter_server repopersist_parameter_server |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.0.4 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-01-05 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Tomoya Fujita
Authors
- Tomoya Fujita>
ROS2 Persistent Parameter Server
ROS 2 Persistent Parameter Server, that resides in the ROS 2 system to serve the parameter daemon. The other nodes(e.g the client demo provided in the code) can write/read the parameter in Parameter Server, and Parameter Server is able to store the parameter into the persistent storage which user can specify such as tmpfs, nfs, or disk.
See overview slide deck for general information.
Background
The discussion is opened here, and centralized parameter server is not a good affinity to ROS 2 distributed system architecture. One of the most valuable things about ROS APIs is that we make sure that the messages have specific semantic meaning so that they can’t be misinterpreted. As we develop the ROS 2 tools and best practices we should make sure to bring that same level of rigor to parameters too for greater reusability and correctness.
Although, it is expected to be the following requirement.
- Global configuration that many nodes share (e.g. RTOS priorities, vehicle dimensions, …)
- Generic ROS 2 system property server.
- Persistent storage support to re-initialize the system. parameters are modified in runtime and cache it into persistent volume as well. and next boot or next re-spawn, modified parameter will be loaded at initialization. (parameter lifetime is dependent on use case, sometimes system lifetime, sometimes node lifetime.)
- Using ROS1 based application with Parameter Server.
Overview

Generally ROS 2 Parameter Server is simple blackboard to write/read parameters on that. The other nodes can write/read the parameter on the server to share them in the ROS 2 system. there is a new concept for “Persistent Parameter” which is described later.
ROS 2 Parameter Server is constructed on ROS parameter API’s, nothing specific API’s are provided to connect to the server from the client. Also, about the security it just relies on ROS 2 security aspect.
Persistent Parameter Registration
Persistent Prefix
persistent parameter must have prefix “persistent”
Scope Overview
parameter server has the following scope for persistent parameter. since parameter server is built on top of ROS 2 Parameter API, parameter server supports “persistent” parameter based on /parameter_events topic.
| Category | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter API | YES | ROS 2 Parameter Client API supported, since this activity can be detected via /parameter_events. |
| Persistent Parameter File | YES | parameter server dedicated argument to specify the file to load as parameters. in addition, all of the persistent parameters will be stored into this file during shutdown. e.g) –file-path /tmp/parameter_server.yaml |
| Parameter Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args -p persistent.some_int:=42 some_int cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since this cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Parameter File Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args –params-file ./parameters_via_cli.yaml same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Launch Parameter | NO | e.g) ros2 launch persist_parameter_server parameter_server.launch.py same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
Configurable Options
-
Node Name
Since ROS 2 parameter is owned by node, node name will be needed to access the parameters, this is designed to clarify semantics for the parameters and owners. Node name will be “parameter_server” if node name is not specifies. so the other nodes can use “parameter_server” as well to access in the same system Parameter Server. If there must exist multiple parameter servers, these parameter servers need to specify a different node name, such as “parameter_server_[special_string]”, please notice that ROS 2 node name can only contains alphanumerics and ‘_’.
-
Persistent Volume
Definition of “Persistent” is different from user and use cases, so it should be configurable to set the path to store the persistent –file-path FILE_PATH parameter. Expecting if the parameter’s lifespan is system boot, path would be “/tmp” because user wants a fresh start via reboot. Or maybe physical persistent volume is chosen if users want to keep the parameter into the hardware storage. At the initialization time, Parameter Server will load the parameters from the storage which is specified by user.
-
Storing Period
It sets the interval for periodically saving parameters to the file system, and that setting the value to 0 disables periodic storing.
-
Node Options
there are three important options:
- allow_undeclared_parameters: (default true)
- automatically_declare_parameters_from_overrides: (default true)
- allow_dynamic_typing: (default false) all of the configuration options will be passed via arguments as following.
| Options | CLI | File truncated at 100 lines [see the full file](https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server/tree/rolling/./README.md)
|---|
Changelog for package persist_parameter_server
1.0.4 (2025-12-20)
-
fix: save floats in explicit float notation (#67)
* fix: save floats in explicit float notation YAML only has the concept of scalar values. So a value of '1' could be an integer, float or string. ros2_persist_parameter_server relies on being able to differentiate if something is a float or integer based on the representation of numbers. Floating numbers must be written such that they can not be mistaken as integers. This is comparable to how many programming languages assume '1' is an integer and '1.0' is a floating point number. The library yaml-cpp exports a float without the distinguishing feature required for ros2_persist_parameter_server. To fix this we manually convert the double into a string representation and ensure that a '.0' extension will be added when required. Note to future maintainer. The current yaml-cpp branch has a YAML::FpToString function which is better suited than using std::stringstream but is not available in the current yaml-cpp release.
- fix: enforce a dot as decimal point
- refactor convertDoubleToString function.
- add test case to make sure double type can be handled.
- remove this problem from known issue description in README.md.
- skil auto-genrated CHANGELOG.rst from codespell checker.
* use std::abs instead of c abs(). ---------Co-authored-by: Tomoya Fujita <<Tomoya.Fujita@sony.com>>
-
Contributors: Simon Gene Gottlieb
1.0.3 (2025-12-08)
- update pdf and html presentation slides.
- Contributors: Tomoya Fujita
1.0.2 (2025-10-21)
- Update package name in script and document
- Change package name for other configuration files
- Use a set of CMakeLists.txt and package.xml files for server and test
- update README for additional service interfaces. (#60)
- Added ros2 service call to manually trigger yaml save (#38)
- remove ament_target_dependencies deprecation warnings. (#59)
- a few follow-ups after https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_p… (#56)
- Fix/dynamic typing (#37)
- add tutorial video from The Construct.
- declare dependencies to boost dev libraries (#55)
- update markdown presenation.
- add kubernetes examples and docs. (#54)
- add JP markdown presentation for possible ROSCon JP 2025 LT. (#53)
- enable Gemini CLI workflow. (#51)
- remove ros signing key temporary workaround. (#48)
- enable builtin dictionaries with custom ones. (#47)
- support codespell github action. (#46)
- Support Kilted Kaiju. (#43)
- Remove use of ament_target_dependencies. (#42)
- perform periodic storing of the yaml file. (#36)
- add nightly workflow files for each distribution. (#34)
- add system test to github workflow for all distributions. (#32)
- fix github workflow target branch, should be rolling. (#30)
- docker images release and build script, and doc update. (#29)
- fix overview html markdown link.
- Iron Irwini is End of Life.
- add overview slide deck link on top.
- Blank issue enabled for miscellaneous issues. (#27)
- cosmetic fix for github issue template files.
- update issue templates and configuration.
- Mirror rolling to master branch.
- Signal(SIGINT) needs to be injected to the server executable. (#25)
- add jazzy to the presentation slides.
- Jazzy support (#23)
- update README and remove deprecation.
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_cmake | |
| launch_ros | |
| ament_cmake_pytest | |
| ament_lint_auto | |
| ament_lint_common | |
| launch | |
| rclcpp | |
| rclcpp_components | |
| rcutils | |
| rmw | |
| rmw_implementation_cmake | |
| std_msgs | |
| std_srvs | |
| yaml_cpp_vendor |
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged persist_parameter_server at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
persist_parameter_server package from persist_parameter_server repopersist_parameter_server |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.0.4 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-01-05 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Tomoya Fujita
Authors
- Tomoya Fujita>
ROS2 Persistent Parameter Server
ROS 2 Persistent Parameter Server, that resides in the ROS 2 system to serve the parameter daemon. The other nodes(e.g the client demo provided in the code) can write/read the parameter in Parameter Server, and Parameter Server is able to store the parameter into the persistent storage which user can specify such as tmpfs, nfs, or disk.
See overview slide deck for general information.
Background
The discussion is opened here, and centralized parameter server is not a good affinity to ROS 2 distributed system architecture. One of the most valuable things about ROS APIs is that we make sure that the messages have specific semantic meaning so that they can’t be misinterpreted. As we develop the ROS 2 tools and best practices we should make sure to bring that same level of rigor to parameters too for greater reusability and correctness.
Although, it is expected to be the following requirement.
- Global configuration that many nodes share (e.g. RTOS priorities, vehicle dimensions, …)
- Generic ROS 2 system property server.
- Persistent storage support to re-initialize the system. parameters are modified in runtime and cache it into persistent volume as well. and next boot or next re-spawn, modified parameter will be loaded at initialization. (parameter lifetime is dependent on use case, sometimes system lifetime, sometimes node lifetime.)
- Using ROS1 based application with Parameter Server.
Overview

Generally ROS 2 Parameter Server is simple blackboard to write/read parameters on that. The other nodes can write/read the parameter on the server to share them in the ROS 2 system. there is a new concept for “Persistent Parameter” which is described later.
ROS 2 Parameter Server is constructed on ROS parameter API’s, nothing specific API’s are provided to connect to the server from the client. Also, about the security it just relies on ROS 2 security aspect.
Persistent Parameter Registration
Persistent Prefix
persistent parameter must have prefix “persistent”
Scope Overview
parameter server has the following scope for persistent parameter. since parameter server is built on top of ROS 2 Parameter API, parameter server supports “persistent” parameter based on /parameter_events topic.
| Category | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter API | YES | ROS 2 Parameter Client API supported, since this activity can be detected via /parameter_events. |
| Persistent Parameter File | YES | parameter server dedicated argument to specify the file to load as parameters. in addition, all of the persistent parameters will be stored into this file during shutdown. e.g) –file-path /tmp/parameter_server.yaml |
| Parameter Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args -p persistent.some_int:=42 some_int cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since this cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Parameter File Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args –params-file ./parameters_via_cli.yaml same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Launch Parameter | NO | e.g) ros2 launch persist_parameter_server parameter_server.launch.py same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
Configurable Options
-
Node Name
Since ROS 2 parameter is owned by node, node name will be needed to access the parameters, this is designed to clarify semantics for the parameters and owners. Node name will be “parameter_server” if node name is not specifies. so the other nodes can use “parameter_server” as well to access in the same system Parameter Server. If there must exist multiple parameter servers, these parameter servers need to specify a different node name, such as “parameter_server_[special_string]”, please notice that ROS 2 node name can only contains alphanumerics and ‘_’.
-
Persistent Volume
Definition of “Persistent” is different from user and use cases, so it should be configurable to set the path to store the persistent –file-path FILE_PATH parameter. Expecting if the parameter’s lifespan is system boot, path would be “/tmp” because user wants a fresh start via reboot. Or maybe physical persistent volume is chosen if users want to keep the parameter into the hardware storage. At the initialization time, Parameter Server will load the parameters from the storage which is specified by user.
-
Storing Period
It sets the interval for periodically saving parameters to the file system, and that setting the value to 0 disables periodic storing.
-
Node Options
there are three important options:
- allow_undeclared_parameters: (default true)
- automatically_declare_parameters_from_overrides: (default true)
- allow_dynamic_typing: (default false) all of the configuration options will be passed via arguments as following.
| Options | CLI | File truncated at 100 lines [see the full file](https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server/tree/rolling/./README.md)
|---|
Changelog for package persist_parameter_server
1.0.4 (2025-12-20)
-
fix: save floats in explicit float notation (#67)
* fix: save floats in explicit float notation YAML only has the concept of scalar values. So a value of '1' could be an integer, float or string. ros2_persist_parameter_server relies on being able to differentiate if something is a float or integer based on the representation of numbers. Floating numbers must be written such that they can not be mistaken as integers. This is comparable to how many programming languages assume '1' is an integer and '1.0' is a floating point number. The library yaml-cpp exports a float without the distinguishing feature required for ros2_persist_parameter_server. To fix this we manually convert the double into a string representation and ensure that a '.0' extension will be added when required. Note to future maintainer. The current yaml-cpp branch has a YAML::FpToString function which is better suited than using std::stringstream but is not available in the current yaml-cpp release.
- fix: enforce a dot as decimal point
- refactor convertDoubleToString function.
- add test case to make sure double type can be handled.
- remove this problem from known issue description in README.md.
- skil auto-genrated CHANGELOG.rst from codespell checker.
* use std::abs instead of c abs(). ---------Co-authored-by: Tomoya Fujita <<Tomoya.Fujita@sony.com>>
-
Contributors: Simon Gene Gottlieb
1.0.3 (2025-12-08)
- update pdf and html presentation slides.
- Contributors: Tomoya Fujita
1.0.2 (2025-10-21)
- Update package name in script and document
- Change package name for other configuration files
- Use a set of CMakeLists.txt and package.xml files for server and test
- update README for additional service interfaces. (#60)
- Added ros2 service call to manually trigger yaml save (#38)
- remove ament_target_dependencies deprecation warnings. (#59)
- a few follow-ups after https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_p… (#56)
- Fix/dynamic typing (#37)
- add tutorial video from The Construct.
- declare dependencies to boost dev libraries (#55)
- update markdown presenation.
- add kubernetes examples and docs. (#54)
- add JP markdown presentation for possible ROSCon JP 2025 LT. (#53)
- enable Gemini CLI workflow. (#51)
- remove ros signing key temporary workaround. (#48)
- enable builtin dictionaries with custom ones. (#47)
- support codespell github action. (#46)
- Support Kilted Kaiju. (#43)
- Remove use of ament_target_dependencies. (#42)
- perform periodic storing of the yaml file. (#36)
- add nightly workflow files for each distribution. (#34)
- add system test to github workflow for all distributions. (#32)
- fix github workflow target branch, should be rolling. (#30)
- docker images release and build script, and doc update. (#29)
- fix overview html markdown link.
- Iron Irwini is End of Life.
- add overview slide deck link on top.
- Blank issue enabled for miscellaneous issues. (#27)
- cosmetic fix for github issue template files.
- update issue templates and configuration.
- Mirror rolling to master branch.
- Signal(SIGINT) needs to be injected to the server executable. (#25)
- add jazzy to the presentation slides.
- Jazzy support (#23)
- update README and remove deprecation.
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_cmake | |
| launch_ros | |
| ament_cmake_pytest | |
| ament_lint_auto | |
| ament_lint_common | |
| launch | |
| rclcpp | |
| rclcpp_components | |
| rcutils | |
| rmw | |
| rmw_implementation_cmake | |
| std_msgs | |
| std_srvs | |
| yaml_cpp_vendor |
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged persist_parameter_server at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
persist_parameter_server package from persist_parameter_server repopersist_parameter_server |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.0.4 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-01-05 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Tomoya Fujita
Authors
- Tomoya Fujita>
ROS2 Persistent Parameter Server
ROS 2 Persistent Parameter Server, that resides in the ROS 2 system to serve the parameter daemon. The other nodes(e.g the client demo provided in the code) can write/read the parameter in Parameter Server, and Parameter Server is able to store the parameter into the persistent storage which user can specify such as tmpfs, nfs, or disk.
See overview slide deck for general information.
Background
The discussion is opened here, and centralized parameter server is not a good affinity to ROS 2 distributed system architecture. One of the most valuable things about ROS APIs is that we make sure that the messages have specific semantic meaning so that they can’t be misinterpreted. As we develop the ROS 2 tools and best practices we should make sure to bring that same level of rigor to parameters too for greater reusability and correctness.
Although, it is expected to be the following requirement.
- Global configuration that many nodes share (e.g. RTOS priorities, vehicle dimensions, …)
- Generic ROS 2 system property server.
- Persistent storage support to re-initialize the system. parameters are modified in runtime and cache it into persistent volume as well. and next boot or next re-spawn, modified parameter will be loaded at initialization. (parameter lifetime is dependent on use case, sometimes system lifetime, sometimes node lifetime.)
- Using ROS1 based application with Parameter Server.
Overview

Generally ROS 2 Parameter Server is simple blackboard to write/read parameters on that. The other nodes can write/read the parameter on the server to share them in the ROS 2 system. there is a new concept for “Persistent Parameter” which is described later.
ROS 2 Parameter Server is constructed on ROS parameter API’s, nothing specific API’s are provided to connect to the server from the client. Also, about the security it just relies on ROS 2 security aspect.
Persistent Parameter Registration
Persistent Prefix
persistent parameter must have prefix “persistent”
Scope Overview
parameter server has the following scope for persistent parameter. since parameter server is built on top of ROS 2 Parameter API, parameter server supports “persistent” parameter based on /parameter_events topic.
| Category | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter API | YES | ROS 2 Parameter Client API supported, since this activity can be detected via /parameter_events. |
| Persistent Parameter File | YES | parameter server dedicated argument to specify the file to load as parameters. in addition, all of the persistent parameters will be stored into this file during shutdown. e.g) –file-path /tmp/parameter_server.yaml |
| Parameter Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args -p persistent.some_int:=42 some_int cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since this cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Parameter File Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args –params-file ./parameters_via_cli.yaml same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Launch Parameter | NO | e.g) ros2 launch persist_parameter_server parameter_server.launch.py same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
Configurable Options
-
Node Name
Since ROS 2 parameter is owned by node, node name will be needed to access the parameters, this is designed to clarify semantics for the parameters and owners. Node name will be “parameter_server” if node name is not specifies. so the other nodes can use “parameter_server” as well to access in the same system Parameter Server. If there must exist multiple parameter servers, these parameter servers need to specify a different node name, such as “parameter_server_[special_string]”, please notice that ROS 2 node name can only contains alphanumerics and ‘_’.
-
Persistent Volume
Definition of “Persistent” is different from user and use cases, so it should be configurable to set the path to store the persistent –file-path FILE_PATH parameter. Expecting if the parameter’s lifespan is system boot, path would be “/tmp” because user wants a fresh start via reboot. Or maybe physical persistent volume is chosen if users want to keep the parameter into the hardware storage. At the initialization time, Parameter Server will load the parameters from the storage which is specified by user.
-
Storing Period
It sets the interval for periodically saving parameters to the file system, and that setting the value to 0 disables periodic storing.
-
Node Options
there are three important options:
- allow_undeclared_parameters: (default true)
- automatically_declare_parameters_from_overrides: (default true)
- allow_dynamic_typing: (default false) all of the configuration options will be passed via arguments as following.
| Options | CLI | File truncated at 100 lines [see the full file](https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server/tree/rolling/./README.md)
|---|
Changelog for package persist_parameter_server
1.0.4 (2025-12-20)
-
fix: save floats in explicit float notation (#67)
* fix: save floats in explicit float notation YAML only has the concept of scalar values. So a value of '1' could be an integer, float or string. ros2_persist_parameter_server relies on being able to differentiate if something is a float or integer based on the representation of numbers. Floating numbers must be written such that they can not be mistaken as integers. This is comparable to how many programming languages assume '1' is an integer and '1.0' is a floating point number. The library yaml-cpp exports a float without the distinguishing feature required for ros2_persist_parameter_server. To fix this we manually convert the double into a string representation and ensure that a '.0' extension will be added when required. Note to future maintainer. The current yaml-cpp branch has a YAML::FpToString function which is better suited than using std::stringstream but is not available in the current yaml-cpp release.
- fix: enforce a dot as decimal point
- refactor convertDoubleToString function.
- add test case to make sure double type can be handled.
- remove this problem from known issue description in README.md.
- skil auto-genrated CHANGELOG.rst from codespell checker.
* use std::abs instead of c abs(). ---------Co-authored-by: Tomoya Fujita <<Tomoya.Fujita@sony.com>>
-
Contributors: Simon Gene Gottlieb
1.0.3 (2025-12-08)
- update pdf and html presentation slides.
- Contributors: Tomoya Fujita
1.0.2 (2025-10-21)
- Update package name in script and document
- Change package name for other configuration files
- Use a set of CMakeLists.txt and package.xml files for server and test
- update README for additional service interfaces. (#60)
- Added ros2 service call to manually trigger yaml save (#38)
- remove ament_target_dependencies deprecation warnings. (#59)
- a few follow-ups after https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_p… (#56)
- Fix/dynamic typing (#37)
- add tutorial video from The Construct.
- declare dependencies to boost dev libraries (#55)
- update markdown presenation.
- add kubernetes examples and docs. (#54)
- add JP markdown presentation for possible ROSCon JP 2025 LT. (#53)
- enable Gemini CLI workflow. (#51)
- remove ros signing key temporary workaround. (#48)
- enable builtin dictionaries with custom ones. (#47)
- support codespell github action. (#46)
- Support Kilted Kaiju. (#43)
- Remove use of ament_target_dependencies. (#42)
- perform periodic storing of the yaml file. (#36)
- add nightly workflow files for each distribution. (#34)
- add system test to github workflow for all distributions. (#32)
- fix github workflow target branch, should be rolling. (#30)
- docker images release and build script, and doc update. (#29)
- fix overview html markdown link.
- Iron Irwini is End of Life.
- add overview slide deck link on top.
- Blank issue enabled for miscellaneous issues. (#27)
- cosmetic fix for github issue template files.
- update issue templates and configuration.
- Mirror rolling to master branch.
- Signal(SIGINT) needs to be injected to the server executable. (#25)
- add jazzy to the presentation slides.
- Jazzy support (#23)
- update README and remove deprecation.
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_cmake | |
| launch_ros | |
| ament_cmake_pytest | |
| ament_lint_auto | |
| ament_lint_common | |
| launch | |
| rclcpp | |
| rclcpp_components | |
| rcutils | |
| rmw | |
| rmw_implementation_cmake | |
| std_msgs | |
| std_srvs | |
| yaml_cpp_vendor |
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged persist_parameter_server at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
persist_parameter_server package from persist_parameter_server repopersist_parameter_server |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.0.4 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-01-05 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Tomoya Fujita
Authors
- Tomoya Fujita>
ROS2 Persistent Parameter Server
ROS 2 Persistent Parameter Server, that resides in the ROS 2 system to serve the parameter daemon. The other nodes(e.g the client demo provided in the code) can write/read the parameter in Parameter Server, and Parameter Server is able to store the parameter into the persistent storage which user can specify such as tmpfs, nfs, or disk.
See overview slide deck for general information.
Background
The discussion is opened here, and centralized parameter server is not a good affinity to ROS 2 distributed system architecture. One of the most valuable things about ROS APIs is that we make sure that the messages have specific semantic meaning so that they can’t be misinterpreted. As we develop the ROS 2 tools and best practices we should make sure to bring that same level of rigor to parameters too for greater reusability and correctness.
Although, it is expected to be the following requirement.
- Global configuration that many nodes share (e.g. RTOS priorities, vehicle dimensions, …)
- Generic ROS 2 system property server.
- Persistent storage support to re-initialize the system. parameters are modified in runtime and cache it into persistent volume as well. and next boot or next re-spawn, modified parameter will be loaded at initialization. (parameter lifetime is dependent on use case, sometimes system lifetime, sometimes node lifetime.)
- Using ROS1 based application with Parameter Server.
Overview

Generally ROS 2 Parameter Server is simple blackboard to write/read parameters on that. The other nodes can write/read the parameter on the server to share them in the ROS 2 system. there is a new concept for “Persistent Parameter” which is described later.
ROS 2 Parameter Server is constructed on ROS parameter API’s, nothing specific API’s are provided to connect to the server from the client. Also, about the security it just relies on ROS 2 security aspect.
Persistent Parameter Registration
Persistent Prefix
persistent parameter must have prefix “persistent”
Scope Overview
parameter server has the following scope for persistent parameter. since parameter server is built on top of ROS 2 Parameter API, parameter server supports “persistent” parameter based on /parameter_events topic.
| Category | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter API | YES | ROS 2 Parameter Client API supported, since this activity can be detected via /parameter_events. |
| Persistent Parameter File | YES | parameter server dedicated argument to specify the file to load as parameters. in addition, all of the persistent parameters will be stored into this file during shutdown. e.g) –file-path /tmp/parameter_server.yaml |
| Parameter Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args -p persistent.some_int:=42 some_int cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since this cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Parameter File Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args –params-file ./parameters_via_cli.yaml same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Launch Parameter | NO | e.g) ros2 launch persist_parameter_server parameter_server.launch.py same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
Configurable Options
-
Node Name
Since ROS 2 parameter is owned by node, node name will be needed to access the parameters, this is designed to clarify semantics for the parameters and owners. Node name will be “parameter_server” if node name is not specifies. so the other nodes can use “parameter_server” as well to access in the same system Parameter Server. If there must exist multiple parameter servers, these parameter servers need to specify a different node name, such as “parameter_server_[special_string]”, please notice that ROS 2 node name can only contains alphanumerics and ‘_’.
-
Persistent Volume
Definition of “Persistent” is different from user and use cases, so it should be configurable to set the path to store the persistent –file-path FILE_PATH parameter. Expecting if the parameter’s lifespan is system boot, path would be “/tmp” because user wants a fresh start via reboot. Or maybe physical persistent volume is chosen if users want to keep the parameter into the hardware storage. At the initialization time, Parameter Server will load the parameters from the storage which is specified by user.
-
Storing Period
It sets the interval for periodically saving parameters to the file system, and that setting the value to 0 disables periodic storing.
-
Node Options
there are three important options:
- allow_undeclared_parameters: (default true)
- automatically_declare_parameters_from_overrides: (default true)
- allow_dynamic_typing: (default false) all of the configuration options will be passed via arguments as following.
| Options | CLI | File truncated at 100 lines [see the full file](https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server/tree/rolling/./README.md)
|---|
Changelog for package persist_parameter_server
1.0.4 (2025-12-20)
-
fix: save floats in explicit float notation (#67)
* fix: save floats in explicit float notation YAML only has the concept of scalar values. So a value of '1' could be an integer, float or string. ros2_persist_parameter_server relies on being able to differentiate if something is a float or integer based on the representation of numbers. Floating numbers must be written such that they can not be mistaken as integers. This is comparable to how many programming languages assume '1' is an integer and '1.0' is a floating point number. The library yaml-cpp exports a float without the distinguishing feature required for ros2_persist_parameter_server. To fix this we manually convert the double into a string representation and ensure that a '.0' extension will be added when required. Note to future maintainer. The current yaml-cpp branch has a YAML::FpToString function which is better suited than using std::stringstream but is not available in the current yaml-cpp release.
- fix: enforce a dot as decimal point
- refactor convertDoubleToString function.
- add test case to make sure double type can be handled.
- remove this problem from known issue description in README.md.
- skil auto-genrated CHANGELOG.rst from codespell checker.
* use std::abs instead of c abs(). ---------Co-authored-by: Tomoya Fujita <<Tomoya.Fujita@sony.com>>
-
Contributors: Simon Gene Gottlieb
1.0.3 (2025-12-08)
- update pdf and html presentation slides.
- Contributors: Tomoya Fujita
1.0.2 (2025-10-21)
- Update package name in script and document
- Change package name for other configuration files
- Use a set of CMakeLists.txt and package.xml files for server and test
- update README for additional service interfaces. (#60)
- Added ros2 service call to manually trigger yaml save (#38)
- remove ament_target_dependencies deprecation warnings. (#59)
- a few follow-ups after https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_p… (#56)
- Fix/dynamic typing (#37)
- add tutorial video from The Construct.
- declare dependencies to boost dev libraries (#55)
- update markdown presenation.
- add kubernetes examples and docs. (#54)
- add JP markdown presentation for possible ROSCon JP 2025 LT. (#53)
- enable Gemini CLI workflow. (#51)
- remove ros signing key temporary workaround. (#48)
- enable builtin dictionaries with custom ones. (#47)
- support codespell github action. (#46)
- Support Kilted Kaiju. (#43)
- Remove use of ament_target_dependencies. (#42)
- perform periodic storing of the yaml file. (#36)
- add nightly workflow files for each distribution. (#34)
- add system test to github workflow for all distributions. (#32)
- fix github workflow target branch, should be rolling. (#30)
- docker images release and build script, and doc update. (#29)
- fix overview html markdown link.
- Iron Irwini is End of Life.
- add overview slide deck link on top.
- Blank issue enabled for miscellaneous issues. (#27)
- cosmetic fix for github issue template files.
- update issue templates and configuration.
- Mirror rolling to master branch.
- Signal(SIGINT) needs to be injected to the server executable. (#25)
- add jazzy to the presentation slides.
- Jazzy support (#23)
- update README and remove deprecation.
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_cmake | |
| launch_ros | |
| ament_cmake_pytest | |
| ament_lint_auto | |
| ament_lint_common | |
| launch | |
| rclcpp | |
| rclcpp_components | |
| rcutils | |
| rmw | |
| rmw_implementation_cmake | |
| std_msgs | |
| std_srvs | |
| yaml_cpp_vendor |
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged persist_parameter_server at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
persist_parameter_server package from persist_parameter_server repopersist_parameter_server |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.0.4 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-01-05 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Tomoya Fujita
Authors
- Tomoya Fujita>
ROS2 Persistent Parameter Server
ROS 2 Persistent Parameter Server, that resides in the ROS 2 system to serve the parameter daemon. The other nodes(e.g the client demo provided in the code) can write/read the parameter in Parameter Server, and Parameter Server is able to store the parameter into the persistent storage which user can specify such as tmpfs, nfs, or disk.
See overview slide deck for general information.
Background
The discussion is opened here, and centralized parameter server is not a good affinity to ROS 2 distributed system architecture. One of the most valuable things about ROS APIs is that we make sure that the messages have specific semantic meaning so that they can’t be misinterpreted. As we develop the ROS 2 tools and best practices we should make sure to bring that same level of rigor to parameters too for greater reusability and correctness.
Although, it is expected to be the following requirement.
- Global configuration that many nodes share (e.g. RTOS priorities, vehicle dimensions, …)
- Generic ROS 2 system property server.
- Persistent storage support to re-initialize the system. parameters are modified in runtime and cache it into persistent volume as well. and next boot or next re-spawn, modified parameter will be loaded at initialization. (parameter lifetime is dependent on use case, sometimes system lifetime, sometimes node lifetime.)
- Using ROS1 based application with Parameter Server.
Overview

Generally ROS 2 Parameter Server is simple blackboard to write/read parameters on that. The other nodes can write/read the parameter on the server to share them in the ROS 2 system. there is a new concept for “Persistent Parameter” which is described later.
ROS 2 Parameter Server is constructed on ROS parameter API’s, nothing specific API’s are provided to connect to the server from the client. Also, about the security it just relies on ROS 2 security aspect.
Persistent Parameter Registration
Persistent Prefix
persistent parameter must have prefix “persistent”
Scope Overview
parameter server has the following scope for persistent parameter. since parameter server is built on top of ROS 2 Parameter API, parameter server supports “persistent” parameter based on /parameter_events topic.
| Category | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter API | YES | ROS 2 Parameter Client API supported, since this activity can be detected via /parameter_events. |
| Persistent Parameter File | YES | parameter server dedicated argument to specify the file to load as parameters. in addition, all of the persistent parameters will be stored into this file during shutdown. e.g) –file-path /tmp/parameter_server.yaml |
| Parameter Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args -p persistent.some_int:=42 some_int cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since this cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Parameter File Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args –params-file ./parameters_via_cli.yaml same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Launch Parameter | NO | e.g) ros2 launch persist_parameter_server parameter_server.launch.py same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
Configurable Options
-
Node Name
Since ROS 2 parameter is owned by node, node name will be needed to access the parameters, this is designed to clarify semantics for the parameters and owners. Node name will be “parameter_server” if node name is not specifies. so the other nodes can use “parameter_server” as well to access in the same system Parameter Server. If there must exist multiple parameter servers, these parameter servers need to specify a different node name, such as “parameter_server_[special_string]”, please notice that ROS 2 node name can only contains alphanumerics and ‘_’.
-
Persistent Volume
Definition of “Persistent” is different from user and use cases, so it should be configurable to set the path to store the persistent –file-path FILE_PATH parameter. Expecting if the parameter’s lifespan is system boot, path would be “/tmp” because user wants a fresh start via reboot. Or maybe physical persistent volume is chosen if users want to keep the parameter into the hardware storage. At the initialization time, Parameter Server will load the parameters from the storage which is specified by user.
-
Storing Period
It sets the interval for periodically saving parameters to the file system, and that setting the value to 0 disables periodic storing.
-
Node Options
there are three important options:
- allow_undeclared_parameters: (default true)
- automatically_declare_parameters_from_overrides: (default true)
- allow_dynamic_typing: (default false) all of the configuration options will be passed via arguments as following.
| Options | CLI | File truncated at 100 lines [see the full file](https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server/tree/rolling/./README.md)
|---|
Changelog for package persist_parameter_server
1.0.4 (2025-12-20)
-
fix: save floats in explicit float notation (#67)
* fix: save floats in explicit float notation YAML only has the concept of scalar values. So a value of '1' could be an integer, float or string. ros2_persist_parameter_server relies on being able to differentiate if something is a float or integer based on the representation of numbers. Floating numbers must be written such that they can not be mistaken as integers. This is comparable to how many programming languages assume '1' is an integer and '1.0' is a floating point number. The library yaml-cpp exports a float without the distinguishing feature required for ros2_persist_parameter_server. To fix this we manually convert the double into a string representation and ensure that a '.0' extension will be added when required. Note to future maintainer. The current yaml-cpp branch has a YAML::FpToString function which is better suited than using std::stringstream but is not available in the current yaml-cpp release.
- fix: enforce a dot as decimal point
- refactor convertDoubleToString function.
- add test case to make sure double type can be handled.
- remove this problem from known issue description in README.md.
- skil auto-genrated CHANGELOG.rst from codespell checker.
* use std::abs instead of c abs(). ---------Co-authored-by: Tomoya Fujita <<Tomoya.Fujita@sony.com>>
-
Contributors: Simon Gene Gottlieb
1.0.3 (2025-12-08)
- update pdf and html presentation slides.
- Contributors: Tomoya Fujita
1.0.2 (2025-10-21)
- Update package name in script and document
- Change package name for other configuration files
- Use a set of CMakeLists.txt and package.xml files for server and test
- update README for additional service interfaces. (#60)
- Added ros2 service call to manually trigger yaml save (#38)
- remove ament_target_dependencies deprecation warnings. (#59)
- a few follow-ups after https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_p… (#56)
- Fix/dynamic typing (#37)
- add tutorial video from The Construct.
- declare dependencies to boost dev libraries (#55)
- update markdown presenation.
- add kubernetes examples and docs. (#54)
- add JP markdown presentation for possible ROSCon JP 2025 LT. (#53)
- enable Gemini CLI workflow. (#51)
- remove ros signing key temporary workaround. (#48)
- enable builtin dictionaries with custom ones. (#47)
- support codespell github action. (#46)
- Support Kilted Kaiju. (#43)
- Remove use of ament_target_dependencies. (#42)
- perform periodic storing of the yaml file. (#36)
- add nightly workflow files for each distribution. (#34)
- add system test to github workflow for all distributions. (#32)
- fix github workflow target branch, should be rolling. (#30)
- docker images release and build script, and doc update. (#29)
- fix overview html markdown link.
- Iron Irwini is End of Life.
- add overview slide deck link on top.
- Blank issue enabled for miscellaneous issues. (#27)
- cosmetic fix for github issue template files.
- update issue templates and configuration.
- Mirror rolling to master branch.
- Signal(SIGINT) needs to be injected to the server executable. (#25)
- add jazzy to the presentation slides.
- Jazzy support (#23)
- update README and remove deprecation.
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_cmake | |
| launch_ros | |
| ament_cmake_pytest | |
| ament_lint_auto | |
| ament_lint_common | |
| launch | |
| rclcpp | |
| rclcpp_components | |
| rcutils | |
| rmw | |
| rmw_implementation_cmake | |
| std_msgs | |
| std_srvs | |
| yaml_cpp_vendor |
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged persist_parameter_server at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
persist_parameter_server package from persist_parameter_server repopersist_parameter_server |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.0.4 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-01-05 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Tomoya Fujita
Authors
- Tomoya Fujita>
ROS2 Persistent Parameter Server
ROS 2 Persistent Parameter Server, that resides in the ROS 2 system to serve the parameter daemon. The other nodes(e.g the client demo provided in the code) can write/read the parameter in Parameter Server, and Parameter Server is able to store the parameter into the persistent storage which user can specify such as tmpfs, nfs, or disk.
See overview slide deck for general information.
Background
The discussion is opened here, and centralized parameter server is not a good affinity to ROS 2 distributed system architecture. One of the most valuable things about ROS APIs is that we make sure that the messages have specific semantic meaning so that they can’t be misinterpreted. As we develop the ROS 2 tools and best practices we should make sure to bring that same level of rigor to parameters too for greater reusability and correctness.
Although, it is expected to be the following requirement.
- Global configuration that many nodes share (e.g. RTOS priorities, vehicle dimensions, …)
- Generic ROS 2 system property server.
- Persistent storage support to re-initialize the system. parameters are modified in runtime and cache it into persistent volume as well. and next boot or next re-spawn, modified parameter will be loaded at initialization. (parameter lifetime is dependent on use case, sometimes system lifetime, sometimes node lifetime.)
- Using ROS1 based application with Parameter Server.
Overview

Generally ROS 2 Parameter Server is simple blackboard to write/read parameters on that. The other nodes can write/read the parameter on the server to share them in the ROS 2 system. there is a new concept for “Persistent Parameter” which is described later.
ROS 2 Parameter Server is constructed on ROS parameter API’s, nothing specific API’s are provided to connect to the server from the client. Also, about the security it just relies on ROS 2 security aspect.
Persistent Parameter Registration
Persistent Prefix
persistent parameter must have prefix “persistent”
Scope Overview
parameter server has the following scope for persistent parameter. since parameter server is built on top of ROS 2 Parameter API, parameter server supports “persistent” parameter based on /parameter_events topic.
| Category | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter API | YES | ROS 2 Parameter Client API supported, since this activity can be detected via /parameter_events. |
| Persistent Parameter File | YES | parameter server dedicated argument to specify the file to load as parameters. in addition, all of the persistent parameters will be stored into this file during shutdown. e.g) –file-path /tmp/parameter_server.yaml |
| Parameter Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args -p persistent.some_int:=42 some_int cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since this cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Parameter File Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args –params-file ./parameters_via_cli.yaml same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Launch Parameter | NO | e.g) ros2 launch persist_parameter_server parameter_server.launch.py same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
Configurable Options
-
Node Name
Since ROS 2 parameter is owned by node, node name will be needed to access the parameters, this is designed to clarify semantics for the parameters and owners. Node name will be “parameter_server” if node name is not specifies. so the other nodes can use “parameter_server” as well to access in the same system Parameter Server. If there must exist multiple parameter servers, these parameter servers need to specify a different node name, such as “parameter_server_[special_string]”, please notice that ROS 2 node name can only contains alphanumerics and ‘_’.
-
Persistent Volume
Definition of “Persistent” is different from user and use cases, so it should be configurable to set the path to store the persistent –file-path FILE_PATH parameter. Expecting if the parameter’s lifespan is system boot, path would be “/tmp” because user wants a fresh start via reboot. Or maybe physical persistent volume is chosen if users want to keep the parameter into the hardware storage. At the initialization time, Parameter Server will load the parameters from the storage which is specified by user.
-
Storing Period
It sets the interval for periodically saving parameters to the file system, and that setting the value to 0 disables periodic storing.
-
Node Options
there are three important options:
- allow_undeclared_parameters: (default true)
- automatically_declare_parameters_from_overrides: (default true)
- allow_dynamic_typing: (default false) all of the configuration options will be passed via arguments as following.
| Options | CLI | File truncated at 100 lines [see the full file](https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server/tree/rolling/./README.md)
|---|
Changelog for package persist_parameter_server
1.0.4 (2025-12-20)
-
fix: save floats in explicit float notation (#67)
* fix: save floats in explicit float notation YAML only has the concept of scalar values. So a value of '1' could be an integer, float or string. ros2_persist_parameter_server relies on being able to differentiate if something is a float or integer based on the representation of numbers. Floating numbers must be written such that they can not be mistaken as integers. This is comparable to how many programming languages assume '1' is an integer and '1.0' is a floating point number. The library yaml-cpp exports a float without the distinguishing feature required for ros2_persist_parameter_server. To fix this we manually convert the double into a string representation and ensure that a '.0' extension will be added when required. Note to future maintainer. The current yaml-cpp branch has a YAML::FpToString function which is better suited than using std::stringstream but is not available in the current yaml-cpp release.
- fix: enforce a dot as decimal point
- refactor convertDoubleToString function.
- add test case to make sure double type can be handled.
- remove this problem from known issue description in README.md.
- skil auto-genrated CHANGELOG.rst from codespell checker.
* use std::abs instead of c abs(). ---------Co-authored-by: Tomoya Fujita <<Tomoya.Fujita@sony.com>>
-
Contributors: Simon Gene Gottlieb
1.0.3 (2025-12-08)
- update pdf and html presentation slides.
- Contributors: Tomoya Fujita
1.0.2 (2025-10-21)
- Update package name in script and document
- Change package name for other configuration files
- Use a set of CMakeLists.txt and package.xml files for server and test
- update README for additional service interfaces. (#60)
- Added ros2 service call to manually trigger yaml save (#38)
- remove ament_target_dependencies deprecation warnings. (#59)
- a few follow-ups after https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_p… (#56)
- Fix/dynamic typing (#37)
- add tutorial video from The Construct.
- declare dependencies to boost dev libraries (#55)
- update markdown presenation.
- add kubernetes examples and docs. (#54)
- add JP markdown presentation for possible ROSCon JP 2025 LT. (#53)
- enable Gemini CLI workflow. (#51)
- remove ros signing key temporary workaround. (#48)
- enable builtin dictionaries with custom ones. (#47)
- support codespell github action. (#46)
- Support Kilted Kaiju. (#43)
- Remove use of ament_target_dependencies. (#42)
- perform periodic storing of the yaml file. (#36)
- add nightly workflow files for each distribution. (#34)
- add system test to github workflow for all distributions. (#32)
- fix github workflow target branch, should be rolling. (#30)
- docker images release and build script, and doc update. (#29)
- fix overview html markdown link.
- Iron Irwini is End of Life.
- add overview slide deck link on top.
- Blank issue enabled for miscellaneous issues. (#27)
- cosmetic fix for github issue template files.
- update issue templates and configuration.
- Mirror rolling to master branch.
- Signal(SIGINT) needs to be injected to the server executable. (#25)
- add jazzy to the presentation slides.
- Jazzy support (#23)
- update README and remove deprecation.
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_cmake | |
| launch_ros | |
| ament_cmake_pytest | |
| ament_lint_auto | |
| ament_lint_common | |
| launch | |
| rclcpp | |
| rclcpp_components | |
| rcutils | |
| rmw | |
| rmw_implementation_cmake | |
| std_msgs | |
| std_srvs | |
| yaml_cpp_vendor |
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged persist_parameter_server at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
persist_parameter_server package from persist_parameter_server repopersist_parameter_server |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.0.4 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-01-05 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Tomoya Fujita
Authors
- Tomoya Fujita>
ROS2 Persistent Parameter Server
ROS 2 Persistent Parameter Server, that resides in the ROS 2 system to serve the parameter daemon. The other nodes(e.g the client demo provided in the code) can write/read the parameter in Parameter Server, and Parameter Server is able to store the parameter into the persistent storage which user can specify such as tmpfs, nfs, or disk.
See overview slide deck for general information.
Background
The discussion is opened here, and centralized parameter server is not a good affinity to ROS 2 distributed system architecture. One of the most valuable things about ROS APIs is that we make sure that the messages have specific semantic meaning so that they can’t be misinterpreted. As we develop the ROS 2 tools and best practices we should make sure to bring that same level of rigor to parameters too for greater reusability and correctness.
Although, it is expected to be the following requirement.
- Global configuration that many nodes share (e.g. RTOS priorities, vehicle dimensions, …)
- Generic ROS 2 system property server.
- Persistent storage support to re-initialize the system. parameters are modified in runtime and cache it into persistent volume as well. and next boot or next re-spawn, modified parameter will be loaded at initialization. (parameter lifetime is dependent on use case, sometimes system lifetime, sometimes node lifetime.)
- Using ROS1 based application with Parameter Server.
Overview

Generally ROS 2 Parameter Server is simple blackboard to write/read parameters on that. The other nodes can write/read the parameter on the server to share them in the ROS 2 system. there is a new concept for “Persistent Parameter” which is described later.
ROS 2 Parameter Server is constructed on ROS parameter API’s, nothing specific API’s are provided to connect to the server from the client. Also, about the security it just relies on ROS 2 security aspect.
Persistent Parameter Registration
Persistent Prefix
persistent parameter must have prefix “persistent”
Scope Overview
parameter server has the following scope for persistent parameter. since parameter server is built on top of ROS 2 Parameter API, parameter server supports “persistent” parameter based on /parameter_events topic.
| Category | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter API | YES | ROS 2 Parameter Client API supported, since this activity can be detected via /parameter_events. |
| Persistent Parameter File | YES | parameter server dedicated argument to specify the file to load as parameters. in addition, all of the persistent parameters will be stored into this file during shutdown. e.g) –file-path /tmp/parameter_server.yaml |
| Parameter Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args -p persistent.some_int:=42 some_int cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since this cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Parameter File Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args –params-file ./parameters_via_cli.yaml same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Launch Parameter | NO | e.g) ros2 launch persist_parameter_server parameter_server.launch.py same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
Configurable Options
-
Node Name
Since ROS 2 parameter is owned by node, node name will be needed to access the parameters, this is designed to clarify semantics for the parameters and owners. Node name will be “parameter_server” if node name is not specifies. so the other nodes can use “parameter_server” as well to access in the same system Parameter Server. If there must exist multiple parameter servers, these parameter servers need to specify a different node name, such as “parameter_server_[special_string]”, please notice that ROS 2 node name can only contains alphanumerics and ‘_’.
-
Persistent Volume
Definition of “Persistent” is different from user and use cases, so it should be configurable to set the path to store the persistent –file-path FILE_PATH parameter. Expecting if the parameter’s lifespan is system boot, path would be “/tmp” because user wants a fresh start via reboot. Or maybe physical persistent volume is chosen if users want to keep the parameter into the hardware storage. At the initialization time, Parameter Server will load the parameters from the storage which is specified by user.
-
Storing Period
It sets the interval for periodically saving parameters to the file system, and that setting the value to 0 disables periodic storing.
-
Node Options
there are three important options:
- allow_undeclared_parameters: (default true)
- automatically_declare_parameters_from_overrides: (default true)
- allow_dynamic_typing: (default false) all of the configuration options will be passed via arguments as following.
| Options | CLI | File truncated at 100 lines [see the full file](https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server/tree/rolling/./README.md)
|---|
Changelog for package persist_parameter_server
1.0.4 (2025-12-20)
-
fix: save floats in explicit float notation (#67)
* fix: save floats in explicit float notation YAML only has the concept of scalar values. So a value of '1' could be an integer, float or string. ros2_persist_parameter_server relies on being able to differentiate if something is a float or integer based on the representation of numbers. Floating numbers must be written such that they can not be mistaken as integers. This is comparable to how many programming languages assume '1' is an integer and '1.0' is a floating point number. The library yaml-cpp exports a float without the distinguishing feature required for ros2_persist_parameter_server. To fix this we manually convert the double into a string representation and ensure that a '.0' extension will be added when required. Note to future maintainer. The current yaml-cpp branch has a YAML::FpToString function which is better suited than using std::stringstream but is not available in the current yaml-cpp release.
- fix: enforce a dot as decimal point
- refactor convertDoubleToString function.
- add test case to make sure double type can be handled.
- remove this problem from known issue description in README.md.
- skil auto-genrated CHANGELOG.rst from codespell checker.
* use std::abs instead of c abs(). ---------Co-authored-by: Tomoya Fujita <<Tomoya.Fujita@sony.com>>
-
Contributors: Simon Gene Gottlieb
1.0.3 (2025-12-08)
- update pdf and html presentation slides.
- Contributors: Tomoya Fujita
1.0.2 (2025-10-21)
- Update package name in script and document
- Change package name for other configuration files
- Use a set of CMakeLists.txt and package.xml files for server and test
- update README for additional service interfaces. (#60)
- Added ros2 service call to manually trigger yaml save (#38)
- remove ament_target_dependencies deprecation warnings. (#59)
- a few follow-ups after https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_p… (#56)
- Fix/dynamic typing (#37)
- add tutorial video from The Construct.
- declare dependencies to boost dev libraries (#55)
- update markdown presenation.
- add kubernetes examples and docs. (#54)
- add JP markdown presentation for possible ROSCon JP 2025 LT. (#53)
- enable Gemini CLI workflow. (#51)
- remove ros signing key temporary workaround. (#48)
- enable builtin dictionaries with custom ones. (#47)
- support codespell github action. (#46)
- Support Kilted Kaiju. (#43)
- Remove use of ament_target_dependencies. (#42)
- perform periodic storing of the yaml file. (#36)
- add nightly workflow files for each distribution. (#34)
- add system test to github workflow for all distributions. (#32)
- fix github workflow target branch, should be rolling. (#30)
- docker images release and build script, and doc update. (#29)
- fix overview html markdown link.
- Iron Irwini is End of Life.
- add overview slide deck link on top.
- Blank issue enabled for miscellaneous issues. (#27)
- cosmetic fix for github issue template files.
- update issue templates and configuration.
- Mirror rolling to master branch.
- Signal(SIGINT) needs to be injected to the server executable. (#25)
- add jazzy to the presentation slides.
- Jazzy support (#23)
- update README and remove deprecation.
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_cmake | |
| launch_ros | |
| ament_cmake_pytest | |
| ament_lint_auto | |
| ament_lint_common | |
| launch | |
| rclcpp | |
| rclcpp_components | |
| rcutils | |
| rmw | |
| rmw_implementation_cmake | |
| std_msgs | |
| std_srvs | |
| yaml_cpp_vendor |
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged persist_parameter_server at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
persist_parameter_server package from persist_parameter_server repopersist_parameter_server |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.0.4 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-01-05 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Tomoya Fujita
Authors
- Tomoya Fujita>
ROS2 Persistent Parameter Server
ROS 2 Persistent Parameter Server, that resides in the ROS 2 system to serve the parameter daemon. The other nodes(e.g the client demo provided in the code) can write/read the parameter in Parameter Server, and Parameter Server is able to store the parameter into the persistent storage which user can specify such as tmpfs, nfs, or disk.
See overview slide deck for general information.
Background
The discussion is opened here, and centralized parameter server is not a good affinity to ROS 2 distributed system architecture. One of the most valuable things about ROS APIs is that we make sure that the messages have specific semantic meaning so that they can’t be misinterpreted. As we develop the ROS 2 tools and best practices we should make sure to bring that same level of rigor to parameters too for greater reusability and correctness.
Although, it is expected to be the following requirement.
- Global configuration that many nodes share (e.g. RTOS priorities, vehicle dimensions, …)
- Generic ROS 2 system property server.
- Persistent storage support to re-initialize the system. parameters are modified in runtime and cache it into persistent volume as well. and next boot or next re-spawn, modified parameter will be loaded at initialization. (parameter lifetime is dependent on use case, sometimes system lifetime, sometimes node lifetime.)
- Using ROS1 based application with Parameter Server.
Overview

Generally ROS 2 Parameter Server is simple blackboard to write/read parameters on that. The other nodes can write/read the parameter on the server to share them in the ROS 2 system. there is a new concept for “Persistent Parameter” which is described later.
ROS 2 Parameter Server is constructed on ROS parameter API’s, nothing specific API’s are provided to connect to the server from the client. Also, about the security it just relies on ROS 2 security aspect.
Persistent Parameter Registration
Persistent Prefix
persistent parameter must have prefix “persistent”
Scope Overview
parameter server has the following scope for persistent parameter. since parameter server is built on top of ROS 2 Parameter API, parameter server supports “persistent” parameter based on /parameter_events topic.
| Category | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter API | YES | ROS 2 Parameter Client API supported, since this activity can be detected via /parameter_events. |
| Persistent Parameter File | YES | parameter server dedicated argument to specify the file to load as parameters. in addition, all of the persistent parameters will be stored into this file during shutdown. e.g) –file-path /tmp/parameter_server.yaml |
| Parameter Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args -p persistent.some_int:=42 some_int cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since this cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Parameter File Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args –params-file ./parameters_via_cli.yaml same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Launch Parameter | NO | e.g) ros2 launch persist_parameter_server parameter_server.launch.py same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
Configurable Options
-
Node Name
Since ROS 2 parameter is owned by node, node name will be needed to access the parameters, this is designed to clarify semantics for the parameters and owners. Node name will be “parameter_server” if node name is not specifies. so the other nodes can use “parameter_server” as well to access in the same system Parameter Server. If there must exist multiple parameter servers, these parameter servers need to specify a different node name, such as “parameter_server_[special_string]”, please notice that ROS 2 node name can only contains alphanumerics and ‘_’.
-
Persistent Volume
Definition of “Persistent” is different from user and use cases, so it should be configurable to set the path to store the persistent –file-path FILE_PATH parameter. Expecting if the parameter’s lifespan is system boot, path would be “/tmp” because user wants a fresh start via reboot. Or maybe physical persistent volume is chosen if users want to keep the parameter into the hardware storage. At the initialization time, Parameter Server will load the parameters from the storage which is specified by user.
-
Storing Period
It sets the interval for periodically saving parameters to the file system, and that setting the value to 0 disables periodic storing.
-
Node Options
there are three important options:
- allow_undeclared_parameters: (default true)
- automatically_declare_parameters_from_overrides: (default true)
- allow_dynamic_typing: (default false) all of the configuration options will be passed via arguments as following.
| Options | CLI | File truncated at 100 lines [see the full file](https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server/tree/rolling/./README.md)
|---|
Changelog for package persist_parameter_server
1.0.4 (2025-12-20)
-
fix: save floats in explicit float notation (#67)
* fix: save floats in explicit float notation YAML only has the concept of scalar values. So a value of '1' could be an integer, float or string. ros2_persist_parameter_server relies on being able to differentiate if something is a float or integer based on the representation of numbers. Floating numbers must be written such that they can not be mistaken as integers. This is comparable to how many programming languages assume '1' is an integer and '1.0' is a floating point number. The library yaml-cpp exports a float without the distinguishing feature required for ros2_persist_parameter_server. To fix this we manually convert the double into a string representation and ensure that a '.0' extension will be added when required. Note to future maintainer. The current yaml-cpp branch has a YAML::FpToString function which is better suited than using std::stringstream but is not available in the current yaml-cpp release.
- fix: enforce a dot as decimal point
- refactor convertDoubleToString function.
- add test case to make sure double type can be handled.
- remove this problem from known issue description in README.md.
- skil auto-genrated CHANGELOG.rst from codespell checker.
* use std::abs instead of c abs(). ---------Co-authored-by: Tomoya Fujita <<Tomoya.Fujita@sony.com>>
-
Contributors: Simon Gene Gottlieb
1.0.3 (2025-12-08)
- update pdf and html presentation slides.
- Contributors: Tomoya Fujita
1.0.2 (2025-10-21)
- Update package name in script and document
- Change package name for other configuration files
- Use a set of CMakeLists.txt and package.xml files for server and test
- update README for additional service interfaces. (#60)
- Added ros2 service call to manually trigger yaml save (#38)
- remove ament_target_dependencies deprecation warnings. (#59)
- a few follow-ups after https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_p… (#56)
- Fix/dynamic typing (#37)
- add tutorial video from The Construct.
- declare dependencies to boost dev libraries (#55)
- update markdown presenation.
- add kubernetes examples and docs. (#54)
- add JP markdown presentation for possible ROSCon JP 2025 LT. (#53)
- enable Gemini CLI workflow. (#51)
- remove ros signing key temporary workaround. (#48)
- enable builtin dictionaries with custom ones. (#47)
- support codespell github action. (#46)
- Support Kilted Kaiju. (#43)
- Remove use of ament_target_dependencies. (#42)
- perform periodic storing of the yaml file. (#36)
- add nightly workflow files for each distribution. (#34)
- add system test to github workflow for all distributions. (#32)
- fix github workflow target branch, should be rolling. (#30)
- docker images release and build script, and doc update. (#29)
- fix overview html markdown link.
- Iron Irwini is End of Life.
- add overview slide deck link on top.
- Blank issue enabled for miscellaneous issues. (#27)
- cosmetic fix for github issue template files.
- update issue templates and configuration.
- Mirror rolling to master branch.
- Signal(SIGINT) needs to be injected to the server executable. (#25)
- add jazzy to the presentation slides.
- Jazzy support (#23)
- update README and remove deprecation.
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_cmake | |
| launch_ros | |
| ament_cmake_pytest | |
| ament_lint_auto | |
| ament_lint_common | |
| launch | |
| rclcpp | |
| rclcpp_components | |
| rcutils | |
| rmw | |
| rmw_implementation_cmake | |
| std_msgs | |
| std_srvs | |
| yaml_cpp_vendor |
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged persist_parameter_server at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
persist_parameter_server package from persist_parameter_server repopersist_parameter_server |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.0.4 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-01-05 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Tomoya Fujita
Authors
- Tomoya Fujita>
ROS2 Persistent Parameter Server
ROS 2 Persistent Parameter Server, that resides in the ROS 2 system to serve the parameter daemon. The other nodes(e.g the client demo provided in the code) can write/read the parameter in Parameter Server, and Parameter Server is able to store the parameter into the persistent storage which user can specify such as tmpfs, nfs, or disk.
See overview slide deck for general information.
Background
The discussion is opened here, and centralized parameter server is not a good affinity to ROS 2 distributed system architecture. One of the most valuable things about ROS APIs is that we make sure that the messages have specific semantic meaning so that they can’t be misinterpreted. As we develop the ROS 2 tools and best practices we should make sure to bring that same level of rigor to parameters too for greater reusability and correctness.
Although, it is expected to be the following requirement.
- Global configuration that many nodes share (e.g. RTOS priorities, vehicle dimensions, …)
- Generic ROS 2 system property server.
- Persistent storage support to re-initialize the system. parameters are modified in runtime and cache it into persistent volume as well. and next boot or next re-spawn, modified parameter will be loaded at initialization. (parameter lifetime is dependent on use case, sometimes system lifetime, sometimes node lifetime.)
- Using ROS1 based application with Parameter Server.
Overview

Generally ROS 2 Parameter Server is simple blackboard to write/read parameters on that. The other nodes can write/read the parameter on the server to share them in the ROS 2 system. there is a new concept for “Persistent Parameter” which is described later.
ROS 2 Parameter Server is constructed on ROS parameter API’s, nothing specific API’s are provided to connect to the server from the client. Also, about the security it just relies on ROS 2 security aspect.
Persistent Parameter Registration
Persistent Prefix
persistent parameter must have prefix “persistent”
Scope Overview
parameter server has the following scope for persistent parameter. since parameter server is built on top of ROS 2 Parameter API, parameter server supports “persistent” parameter based on /parameter_events topic.
| Category | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter API | YES | ROS 2 Parameter Client API supported, since this activity can be detected via /parameter_events. |
| Persistent Parameter File | YES | parameter server dedicated argument to specify the file to load as parameters. in addition, all of the persistent parameters will be stored into this file during shutdown. e.g) –file-path /tmp/parameter_server.yaml |
| Parameter Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args -p persistent.some_int:=42 some_int cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since this cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Parameter File Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args –params-file ./parameters_via_cli.yaml same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Launch Parameter | NO | e.g) ros2 launch persist_parameter_server parameter_server.launch.py same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
Configurable Options
-
Node Name
Since ROS 2 parameter is owned by node, node name will be needed to access the parameters, this is designed to clarify semantics for the parameters and owners. Node name will be “parameter_server” if node name is not specifies. so the other nodes can use “parameter_server” as well to access in the same system Parameter Server. If there must exist multiple parameter servers, these parameter servers need to specify a different node name, such as “parameter_server_[special_string]”, please notice that ROS 2 node name can only contains alphanumerics and ‘_’.
-
Persistent Volume
Definition of “Persistent” is different from user and use cases, so it should be configurable to set the path to store the persistent –file-path FILE_PATH parameter. Expecting if the parameter’s lifespan is system boot, path would be “/tmp” because user wants a fresh start via reboot. Or maybe physical persistent volume is chosen if users want to keep the parameter into the hardware storage. At the initialization time, Parameter Server will load the parameters from the storage which is specified by user.
-
Storing Period
It sets the interval for periodically saving parameters to the file system, and that setting the value to 0 disables periodic storing.
-
Node Options
there are three important options:
- allow_undeclared_parameters: (default true)
- automatically_declare_parameters_from_overrides: (default true)
- allow_dynamic_typing: (default false) all of the configuration options will be passed via arguments as following.
| Options | CLI | File truncated at 100 lines [see the full file](https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server/tree/rolling/./README.md)
|---|
Changelog for package persist_parameter_server
1.0.4 (2025-12-20)
-
fix: save floats in explicit float notation (#67)
* fix: save floats in explicit float notation YAML only has the concept of scalar values. So a value of '1' could be an integer, float or string. ros2_persist_parameter_server relies on being able to differentiate if something is a float or integer based on the representation of numbers. Floating numbers must be written such that they can not be mistaken as integers. This is comparable to how many programming languages assume '1' is an integer and '1.0' is a floating point number. The library yaml-cpp exports a float without the distinguishing feature required for ros2_persist_parameter_server. To fix this we manually convert the double into a string representation and ensure that a '.0' extension will be added when required. Note to future maintainer. The current yaml-cpp branch has a YAML::FpToString function which is better suited than using std::stringstream but is not available in the current yaml-cpp release.
- fix: enforce a dot as decimal point
- refactor convertDoubleToString function.
- add test case to make sure double type can be handled.
- remove this problem from known issue description in README.md.
- skil auto-genrated CHANGELOG.rst from codespell checker.
* use std::abs instead of c abs(). ---------Co-authored-by: Tomoya Fujita <<Tomoya.Fujita@sony.com>>
-
Contributors: Simon Gene Gottlieb
1.0.3 (2025-12-08)
- update pdf and html presentation slides.
- Contributors: Tomoya Fujita
1.0.2 (2025-10-21)
- Update package name in script and document
- Change package name for other configuration files
- Use a set of CMakeLists.txt and package.xml files for server and test
- update README for additional service interfaces. (#60)
- Added ros2 service call to manually trigger yaml save (#38)
- remove ament_target_dependencies deprecation warnings. (#59)
- a few follow-ups after https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_p… (#56)
- Fix/dynamic typing (#37)
- add tutorial video from The Construct.
- declare dependencies to boost dev libraries (#55)
- update markdown presenation.
- add kubernetes examples and docs. (#54)
- add JP markdown presentation for possible ROSCon JP 2025 LT. (#53)
- enable Gemini CLI workflow. (#51)
- remove ros signing key temporary workaround. (#48)
- enable builtin dictionaries with custom ones. (#47)
- support codespell github action. (#46)
- Support Kilted Kaiju. (#43)
- Remove use of ament_target_dependencies. (#42)
- perform periodic storing of the yaml file. (#36)
- add nightly workflow files for each distribution. (#34)
- add system test to github workflow for all distributions. (#32)
- fix github workflow target branch, should be rolling. (#30)
- docker images release and build script, and doc update. (#29)
- fix overview html markdown link.
- Iron Irwini is End of Life.
- add overview slide deck link on top.
- Blank issue enabled for miscellaneous issues. (#27)
- cosmetic fix for github issue template files.
- update issue templates and configuration.
- Mirror rolling to master branch.
- Signal(SIGINT) needs to be injected to the server executable. (#25)
- add jazzy to the presentation slides.
- Jazzy support (#23)
- update README and remove deprecation.
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_cmake | |
| launch_ros | |
| ament_cmake_pytest | |
| ament_lint_auto | |
| ament_lint_common | |
| launch | |
| rclcpp | |
| rclcpp_components | |
| rcutils | |
| rmw | |
| rmw_implementation_cmake | |
| std_msgs | |
| std_srvs | |
| yaml_cpp_vendor |
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged persist_parameter_server at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
persist_parameter_server package from persist_parameter_server repopersist_parameter_server |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.0.4 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-01-05 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Tomoya Fujita
Authors
- Tomoya Fujita>
ROS2 Persistent Parameter Server
ROS 2 Persistent Parameter Server, that resides in the ROS 2 system to serve the parameter daemon. The other nodes(e.g the client demo provided in the code) can write/read the parameter in Parameter Server, and Parameter Server is able to store the parameter into the persistent storage which user can specify such as tmpfs, nfs, or disk.
See overview slide deck for general information.
Background
The discussion is opened here, and centralized parameter server is not a good affinity to ROS 2 distributed system architecture. One of the most valuable things about ROS APIs is that we make sure that the messages have specific semantic meaning so that they can’t be misinterpreted. As we develop the ROS 2 tools and best practices we should make sure to bring that same level of rigor to parameters too for greater reusability and correctness.
Although, it is expected to be the following requirement.
- Global configuration that many nodes share (e.g. RTOS priorities, vehicle dimensions, …)
- Generic ROS 2 system property server.
- Persistent storage support to re-initialize the system. parameters are modified in runtime and cache it into persistent volume as well. and next boot or next re-spawn, modified parameter will be loaded at initialization. (parameter lifetime is dependent on use case, sometimes system lifetime, sometimes node lifetime.)
- Using ROS1 based application with Parameter Server.
Overview

Generally ROS 2 Parameter Server is simple blackboard to write/read parameters on that. The other nodes can write/read the parameter on the server to share them in the ROS 2 system. there is a new concept for “Persistent Parameter” which is described later.
ROS 2 Parameter Server is constructed on ROS parameter API’s, nothing specific API’s are provided to connect to the server from the client. Also, about the security it just relies on ROS 2 security aspect.
Persistent Parameter Registration
Persistent Prefix
persistent parameter must have prefix “persistent”
Scope Overview
parameter server has the following scope for persistent parameter. since parameter server is built on top of ROS 2 Parameter API, parameter server supports “persistent” parameter based on /parameter_events topic.
| Category | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter API | YES | ROS 2 Parameter Client API supported, since this activity can be detected via /parameter_events. |
| Persistent Parameter File | YES | parameter server dedicated argument to specify the file to load as parameters. in addition, all of the persistent parameters will be stored into this file during shutdown. e.g) –file-path /tmp/parameter_server.yaml |
| Parameter Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args -p persistent.some_int:=42 some_int cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since this cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Parameter File Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args –params-file ./parameters_via_cli.yaml same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Launch Parameter | NO | e.g) ros2 launch persist_parameter_server parameter_server.launch.py same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
Configurable Options
-
Node Name
Since ROS 2 parameter is owned by node, node name will be needed to access the parameters, this is designed to clarify semantics for the parameters and owners. Node name will be “parameter_server” if node name is not specifies. so the other nodes can use “parameter_server” as well to access in the same system Parameter Server. If there must exist multiple parameter servers, these parameter servers need to specify a different node name, such as “parameter_server_[special_string]”, please notice that ROS 2 node name can only contains alphanumerics and ‘_’.
-
Persistent Volume
Definition of “Persistent” is different from user and use cases, so it should be configurable to set the path to store the persistent –file-path FILE_PATH parameter. Expecting if the parameter’s lifespan is system boot, path would be “/tmp” because user wants a fresh start via reboot. Or maybe physical persistent volume is chosen if users want to keep the parameter into the hardware storage. At the initialization time, Parameter Server will load the parameters from the storage which is specified by user.
-
Storing Period
It sets the interval for periodically saving parameters to the file system, and that setting the value to 0 disables periodic storing.
-
Node Options
there are three important options:
- allow_undeclared_parameters: (default true)
- automatically_declare_parameters_from_overrides: (default true)
- allow_dynamic_typing: (default false) all of the configuration options will be passed via arguments as following.
| Options | CLI | File truncated at 100 lines [see the full file](https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server/tree/rolling/./README.md)
|---|
Changelog for package persist_parameter_server
1.0.4 (2025-12-20)
-
fix: save floats in explicit float notation (#67)
* fix: save floats in explicit float notation YAML only has the concept of scalar values. So a value of '1' could be an integer, float or string. ros2_persist_parameter_server relies on being able to differentiate if something is a float or integer based on the representation of numbers. Floating numbers must be written such that they can not be mistaken as integers. This is comparable to how many programming languages assume '1' is an integer and '1.0' is a floating point number. The library yaml-cpp exports a float without the distinguishing feature required for ros2_persist_parameter_server. To fix this we manually convert the double into a string representation and ensure that a '.0' extension will be added when required. Note to future maintainer. The current yaml-cpp branch has a YAML::FpToString function which is better suited than using std::stringstream but is not available in the current yaml-cpp release.
- fix: enforce a dot as decimal point
- refactor convertDoubleToString function.
- add test case to make sure double type can be handled.
- remove this problem from known issue description in README.md.
- skil auto-genrated CHANGELOG.rst from codespell checker.
* use std::abs instead of c abs(). ---------Co-authored-by: Tomoya Fujita <<Tomoya.Fujita@sony.com>>
-
Contributors: Simon Gene Gottlieb
1.0.3 (2025-12-08)
- update pdf and html presentation slides.
- Contributors: Tomoya Fujita
1.0.2 (2025-10-21)
- Update package name in script and document
- Change package name for other configuration files
- Use a set of CMakeLists.txt and package.xml files for server and test
- update README for additional service interfaces. (#60)
- Added ros2 service call to manually trigger yaml save (#38)
- remove ament_target_dependencies deprecation warnings. (#59)
- a few follow-ups after https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_p… (#56)
- Fix/dynamic typing (#37)
- add tutorial video from The Construct.
- declare dependencies to boost dev libraries (#55)
- update markdown presenation.
- add kubernetes examples and docs. (#54)
- add JP markdown presentation for possible ROSCon JP 2025 LT. (#53)
- enable Gemini CLI workflow. (#51)
- remove ros signing key temporary workaround. (#48)
- enable builtin dictionaries with custom ones. (#47)
- support codespell github action. (#46)
- Support Kilted Kaiju. (#43)
- Remove use of ament_target_dependencies. (#42)
- perform periodic storing of the yaml file. (#36)
- add nightly workflow files for each distribution. (#34)
- add system test to github workflow for all distributions. (#32)
- fix github workflow target branch, should be rolling. (#30)
- docker images release and build script, and doc update. (#29)
- fix overview html markdown link.
- Iron Irwini is End of Life.
- add overview slide deck link on top.
- Blank issue enabled for miscellaneous issues. (#27)
- cosmetic fix for github issue template files.
- update issue templates and configuration.
- Mirror rolling to master branch.
- Signal(SIGINT) needs to be injected to the server executable. (#25)
- add jazzy to the presentation slides.
- Jazzy support (#23)
- update README and remove deprecation.
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_cmake | |
| launch_ros | |
| ament_cmake_pytest | |
| ament_lint_auto | |
| ament_lint_common | |
| launch | |
| rclcpp | |
| rclcpp_components | |
| rcutils | |
| rmw | |
| rmw_implementation_cmake | |
| std_msgs | |
| std_srvs | |
| yaml_cpp_vendor |
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged persist_parameter_server at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
persist_parameter_server package from persist_parameter_server repopersist_parameter_server |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.0.4 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-01-05 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Tomoya Fujita
Authors
- Tomoya Fujita>
ROS2 Persistent Parameter Server
ROS 2 Persistent Parameter Server, that resides in the ROS 2 system to serve the parameter daemon. The other nodes(e.g the client demo provided in the code) can write/read the parameter in Parameter Server, and Parameter Server is able to store the parameter into the persistent storage which user can specify such as tmpfs, nfs, or disk.
See overview slide deck for general information.
Background
The discussion is opened here, and centralized parameter server is not a good affinity to ROS 2 distributed system architecture. One of the most valuable things about ROS APIs is that we make sure that the messages have specific semantic meaning so that they can’t be misinterpreted. As we develop the ROS 2 tools and best practices we should make sure to bring that same level of rigor to parameters too for greater reusability and correctness.
Although, it is expected to be the following requirement.
- Global configuration that many nodes share (e.g. RTOS priorities, vehicle dimensions, …)
- Generic ROS 2 system property server.
- Persistent storage support to re-initialize the system. parameters are modified in runtime and cache it into persistent volume as well. and next boot or next re-spawn, modified parameter will be loaded at initialization. (parameter lifetime is dependent on use case, sometimes system lifetime, sometimes node lifetime.)
- Using ROS1 based application with Parameter Server.
Overview

Generally ROS 2 Parameter Server is simple blackboard to write/read parameters on that. The other nodes can write/read the parameter on the server to share them in the ROS 2 system. there is a new concept for “Persistent Parameter” which is described later.
ROS 2 Parameter Server is constructed on ROS parameter API’s, nothing specific API’s are provided to connect to the server from the client. Also, about the security it just relies on ROS 2 security aspect.
Persistent Parameter Registration
Persistent Prefix
persistent parameter must have prefix “persistent”
Scope Overview
parameter server has the following scope for persistent parameter. since parameter server is built on top of ROS 2 Parameter API, parameter server supports “persistent” parameter based on /parameter_events topic.
| Category | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter API | YES | ROS 2 Parameter Client API supported, since this activity can be detected via /parameter_events. |
| Persistent Parameter File | YES | parameter server dedicated argument to specify the file to load as parameters. in addition, all of the persistent parameters will be stored into this file during shutdown. e.g) –file-path /tmp/parameter_server.yaml |
| Parameter Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args -p persistent.some_int:=42 some_int cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since this cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Parameter File Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args –params-file ./parameters_via_cli.yaml same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Launch Parameter | NO | e.g) ros2 launch persist_parameter_server parameter_server.launch.py same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
Configurable Options
-
Node Name
Since ROS 2 parameter is owned by node, node name will be needed to access the parameters, this is designed to clarify semantics for the parameters and owners. Node name will be “parameter_server” if node name is not specifies. so the other nodes can use “parameter_server” as well to access in the same system Parameter Server. If there must exist multiple parameter servers, these parameter servers need to specify a different node name, such as “parameter_server_[special_string]”, please notice that ROS 2 node name can only contains alphanumerics and ‘_’.
-
Persistent Volume
Definition of “Persistent” is different from user and use cases, so it should be configurable to set the path to store the persistent –file-path FILE_PATH parameter. Expecting if the parameter’s lifespan is system boot, path would be “/tmp” because user wants a fresh start via reboot. Or maybe physical persistent volume is chosen if users want to keep the parameter into the hardware storage. At the initialization time, Parameter Server will load the parameters from the storage which is specified by user.
-
Storing Period
It sets the interval for periodically saving parameters to the file system, and that setting the value to 0 disables periodic storing.
-
Node Options
there are three important options:
- allow_undeclared_parameters: (default true)
- automatically_declare_parameters_from_overrides: (default true)
- allow_dynamic_typing: (default false) all of the configuration options will be passed via arguments as following.
| Options | CLI | File truncated at 100 lines [see the full file](https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server/tree/rolling/./README.md)
|---|
Changelog for package persist_parameter_server
1.0.4 (2025-12-20)
-
fix: save floats in explicit float notation (#67)
* fix: save floats in explicit float notation YAML only has the concept of scalar values. So a value of '1' could be an integer, float or string. ros2_persist_parameter_server relies on being able to differentiate if something is a float or integer based on the representation of numbers. Floating numbers must be written such that they can not be mistaken as integers. This is comparable to how many programming languages assume '1' is an integer and '1.0' is a floating point number. The library yaml-cpp exports a float without the distinguishing feature required for ros2_persist_parameter_server. To fix this we manually convert the double into a string representation and ensure that a '.0' extension will be added when required. Note to future maintainer. The current yaml-cpp branch has a YAML::FpToString function which is better suited than using std::stringstream but is not available in the current yaml-cpp release.
- fix: enforce a dot as decimal point
- refactor convertDoubleToString function.
- add test case to make sure double type can be handled.
- remove this problem from known issue description in README.md.
- skil auto-genrated CHANGELOG.rst from codespell checker.
* use std::abs instead of c abs(). ---------Co-authored-by: Tomoya Fujita <<Tomoya.Fujita@sony.com>>
-
Contributors: Simon Gene Gottlieb
1.0.3 (2025-12-08)
- update pdf and html presentation slides.
- Contributors: Tomoya Fujita
1.0.2 (2025-10-21)
- Update package name in script and document
- Change package name for other configuration files
- Use a set of CMakeLists.txt and package.xml files for server and test
- update README for additional service interfaces. (#60)
- Added ros2 service call to manually trigger yaml save (#38)
- remove ament_target_dependencies deprecation warnings. (#59)
- a few follow-ups after https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_p… (#56)
- Fix/dynamic typing (#37)
- add tutorial video from The Construct.
- declare dependencies to boost dev libraries (#55)
- update markdown presenation.
- add kubernetes examples and docs. (#54)
- add JP markdown presentation for possible ROSCon JP 2025 LT. (#53)
- enable Gemini CLI workflow. (#51)
- remove ros signing key temporary workaround. (#48)
- enable builtin dictionaries with custom ones. (#47)
- support codespell github action. (#46)
- Support Kilted Kaiju. (#43)
- Remove use of ament_target_dependencies. (#42)
- perform periodic storing of the yaml file. (#36)
- add nightly workflow files for each distribution. (#34)
- add system test to github workflow for all distributions. (#32)
- fix github workflow target branch, should be rolling. (#30)
- docker images release and build script, and doc update. (#29)
- fix overview html markdown link.
- Iron Irwini is End of Life.
- add overview slide deck link on top.
- Blank issue enabled for miscellaneous issues. (#27)
- cosmetic fix for github issue template files.
- update issue templates and configuration.
- Mirror rolling to master branch.
- Signal(SIGINT) needs to be injected to the server executable. (#25)
- add jazzy to the presentation slides.
- Jazzy support (#23)
- update README and remove deprecation.
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_cmake | |
| launch_ros | |
| ament_cmake_pytest | |
| ament_lint_auto | |
| ament_lint_common | |
| launch | |
| rclcpp | |
| rclcpp_components | |
| rcutils | |
| rmw | |
| rmw_implementation_cmake | |
| std_msgs | |
| std_srvs | |
| yaml_cpp_vendor |
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged persist_parameter_server at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
persist_parameter_server package from persist_parameter_server repopersist_parameter_server |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.0.4 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-01-05 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Tomoya Fujita
Authors
- Tomoya Fujita>
ROS2 Persistent Parameter Server
ROS 2 Persistent Parameter Server, that resides in the ROS 2 system to serve the parameter daemon. The other nodes(e.g the client demo provided in the code) can write/read the parameter in Parameter Server, and Parameter Server is able to store the parameter into the persistent storage which user can specify such as tmpfs, nfs, or disk.
See overview slide deck for general information.
Background
The discussion is opened here, and centralized parameter server is not a good affinity to ROS 2 distributed system architecture. One of the most valuable things about ROS APIs is that we make sure that the messages have specific semantic meaning so that they can’t be misinterpreted. As we develop the ROS 2 tools and best practices we should make sure to bring that same level of rigor to parameters too for greater reusability and correctness.
Although, it is expected to be the following requirement.
- Global configuration that many nodes share (e.g. RTOS priorities, vehicle dimensions, …)
- Generic ROS 2 system property server.
- Persistent storage support to re-initialize the system. parameters are modified in runtime and cache it into persistent volume as well. and next boot or next re-spawn, modified parameter will be loaded at initialization. (parameter lifetime is dependent on use case, sometimes system lifetime, sometimes node lifetime.)
- Using ROS1 based application with Parameter Server.
Overview

Generally ROS 2 Parameter Server is simple blackboard to write/read parameters on that. The other nodes can write/read the parameter on the server to share them in the ROS 2 system. there is a new concept for “Persistent Parameter” which is described later.
ROS 2 Parameter Server is constructed on ROS parameter API’s, nothing specific API’s are provided to connect to the server from the client. Also, about the security it just relies on ROS 2 security aspect.
Persistent Parameter Registration
Persistent Prefix
persistent parameter must have prefix “persistent”
Scope Overview
parameter server has the following scope for persistent parameter. since parameter server is built on top of ROS 2 Parameter API, parameter server supports “persistent” parameter based on /parameter_events topic.
| Category | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter API | YES | ROS 2 Parameter Client API supported, since this activity can be detected via /parameter_events. |
| Persistent Parameter File | YES | parameter server dedicated argument to specify the file to load as parameters. in addition, all of the persistent parameters will be stored into this file during shutdown. e.g) –file-path /tmp/parameter_server.yaml |
| Parameter Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args -p persistent.some_int:=42 some_int cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since this cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Parameter File Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args –params-file ./parameters_via_cli.yaml same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Launch Parameter | NO | e.g) ros2 launch persist_parameter_server parameter_server.launch.py same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
Configurable Options
-
Node Name
Since ROS 2 parameter is owned by node, node name will be needed to access the parameters, this is designed to clarify semantics for the parameters and owners. Node name will be “parameter_server” if node name is not specifies. so the other nodes can use “parameter_server” as well to access in the same system Parameter Server. If there must exist multiple parameter servers, these parameter servers need to specify a different node name, such as “parameter_server_[special_string]”, please notice that ROS 2 node name can only contains alphanumerics and ‘_’.
-
Persistent Volume
Definition of “Persistent” is different from user and use cases, so it should be configurable to set the path to store the persistent –file-path FILE_PATH parameter. Expecting if the parameter’s lifespan is system boot, path would be “/tmp” because user wants a fresh start via reboot. Or maybe physical persistent volume is chosen if users want to keep the parameter into the hardware storage. At the initialization time, Parameter Server will load the parameters from the storage which is specified by user.
-
Storing Period
It sets the interval for periodically saving parameters to the file system, and that setting the value to 0 disables periodic storing.
-
Node Options
there are three important options:
- allow_undeclared_parameters: (default true)
- automatically_declare_parameters_from_overrides: (default true)
- allow_dynamic_typing: (default false) all of the configuration options will be passed via arguments as following.
| Options | CLI | File truncated at 100 lines [see the full file](https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server/tree/rolling/./README.md)
|---|
Changelog for package persist_parameter_server
1.0.4 (2025-12-20)
-
fix: save floats in explicit float notation (#67)
* fix: save floats in explicit float notation YAML only has the concept of scalar values. So a value of '1' could be an integer, float or string. ros2_persist_parameter_server relies on being able to differentiate if something is a float or integer based on the representation of numbers. Floating numbers must be written such that they can not be mistaken as integers. This is comparable to how many programming languages assume '1' is an integer and '1.0' is a floating point number. The library yaml-cpp exports a float without the distinguishing feature required for ros2_persist_parameter_server. To fix this we manually convert the double into a string representation and ensure that a '.0' extension will be added when required. Note to future maintainer. The current yaml-cpp branch has a YAML::FpToString function which is better suited than using std::stringstream but is not available in the current yaml-cpp release.
- fix: enforce a dot as decimal point
- refactor convertDoubleToString function.
- add test case to make sure double type can be handled.
- remove this problem from known issue description in README.md.
- skil auto-genrated CHANGELOG.rst from codespell checker.
* use std::abs instead of c abs(). ---------Co-authored-by: Tomoya Fujita <<Tomoya.Fujita@sony.com>>
-
Contributors: Simon Gene Gottlieb
1.0.3 (2025-12-08)
- update pdf and html presentation slides.
- Contributors: Tomoya Fujita
1.0.2 (2025-10-21)
- Update package name in script and document
- Change package name for other configuration files
- Use a set of CMakeLists.txt and package.xml files for server and test
- update README for additional service interfaces. (#60)
- Added ros2 service call to manually trigger yaml save (#38)
- remove ament_target_dependencies deprecation warnings. (#59)
- a few follow-ups after https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_p… (#56)
- Fix/dynamic typing (#37)
- add tutorial video from The Construct.
- declare dependencies to boost dev libraries (#55)
- update markdown presenation.
- add kubernetes examples and docs. (#54)
- add JP markdown presentation for possible ROSCon JP 2025 LT. (#53)
- enable Gemini CLI workflow. (#51)
- remove ros signing key temporary workaround. (#48)
- enable builtin dictionaries with custom ones. (#47)
- support codespell github action. (#46)
- Support Kilted Kaiju. (#43)
- Remove use of ament_target_dependencies. (#42)
- perform periodic storing of the yaml file. (#36)
- add nightly workflow files for each distribution. (#34)
- add system test to github workflow for all distributions. (#32)
- fix github workflow target branch, should be rolling. (#30)
- docker images release and build script, and doc update. (#29)
- fix overview html markdown link.
- Iron Irwini is End of Life.
- add overview slide deck link on top.
- Blank issue enabled for miscellaneous issues. (#27)
- cosmetic fix for github issue template files.
- update issue templates and configuration.
- Mirror rolling to master branch.
- Signal(SIGINT) needs to be injected to the server executable. (#25)
- add jazzy to the presentation slides.
- Jazzy support (#23)
- update README and remove deprecation.
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_cmake | |
| launch_ros | |
| ament_cmake_pytest | |
| ament_lint_auto | |
| ament_lint_common | |
| launch | |
| rclcpp | |
| rclcpp_components | |
| rcutils | |
| rmw | |
| rmw_implementation_cmake | |
| std_msgs | |
| std_srvs | |
| yaml_cpp_vendor |
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
Launch files
Messages
Services
Plugins
Recent questions tagged persist_parameter_server at Robotics Stack Exchange

|
persist_parameter_server package from persist_parameter_server repopersist_parameter_server |
ROS Distro
|
Package Summary
| Version | 1.0.4 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | rolling |
| Last Updated | 2026-01-05 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Package Description
Maintainers
- Tomoya Fujita
Authors
- Tomoya Fujita>
ROS2 Persistent Parameter Server
ROS 2 Persistent Parameter Server, that resides in the ROS 2 system to serve the parameter daemon. The other nodes(e.g the client demo provided in the code) can write/read the parameter in Parameter Server, and Parameter Server is able to store the parameter into the persistent storage which user can specify such as tmpfs, nfs, or disk.
See overview slide deck for general information.
Background
The discussion is opened here, and centralized parameter server is not a good affinity to ROS 2 distributed system architecture. One of the most valuable things about ROS APIs is that we make sure that the messages have specific semantic meaning so that they can’t be misinterpreted. As we develop the ROS 2 tools and best practices we should make sure to bring that same level of rigor to parameters too for greater reusability and correctness.
Although, it is expected to be the following requirement.
- Global configuration that many nodes share (e.g. RTOS priorities, vehicle dimensions, …)
- Generic ROS 2 system property server.
- Persistent storage support to re-initialize the system. parameters are modified in runtime and cache it into persistent volume as well. and next boot or next re-spawn, modified parameter will be loaded at initialization. (parameter lifetime is dependent on use case, sometimes system lifetime, sometimes node lifetime.)
- Using ROS1 based application with Parameter Server.
Overview

Generally ROS 2 Parameter Server is simple blackboard to write/read parameters on that. The other nodes can write/read the parameter on the server to share them in the ROS 2 system. there is a new concept for “Persistent Parameter” which is described later.
ROS 2 Parameter Server is constructed on ROS parameter API’s, nothing specific API’s are provided to connect to the server from the client. Also, about the security it just relies on ROS 2 security aspect.
Persistent Parameter Registration
Persistent Prefix
persistent parameter must have prefix “persistent”
Scope Overview
parameter server has the following scope for persistent parameter. since parameter server is built on top of ROS 2 Parameter API, parameter server supports “persistent” parameter based on /parameter_events topic.
| Category | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter API | YES | ROS 2 Parameter Client API supported, since this activity can be detected via /parameter_events. |
| Persistent Parameter File | YES | parameter server dedicated argument to specify the file to load as parameters. in addition, all of the persistent parameters will be stored into this file during shutdown. e.g) –file-path /tmp/parameter_server.yaml |
| Parameter Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args -p persistent.some_int:=42 some_int cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since this cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Parameter File Arguments | NO | e.g) –ros-args –params-file ./parameters_via_cli.yaml same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
| Launch Parameter | NO | e.g) ros2 launch persist_parameter_server parameter_server.launch.py same with parameter arguments, cannot be registered as persistent parameter, since these cannot be notified via /parameter_events to parameter server. |
Configurable Options
-
Node Name
Since ROS 2 parameter is owned by node, node name will be needed to access the parameters, this is designed to clarify semantics for the parameters and owners. Node name will be “parameter_server” if node name is not specifies. so the other nodes can use “parameter_server” as well to access in the same system Parameter Server. If there must exist multiple parameter servers, these parameter servers need to specify a different node name, such as “parameter_server_[special_string]”, please notice that ROS 2 node name can only contains alphanumerics and ‘_’.
-
Persistent Volume
Definition of “Persistent” is different from user and use cases, so it should be configurable to set the path to store the persistent –file-path FILE_PATH parameter. Expecting if the parameter’s lifespan is system boot, path would be “/tmp” because user wants a fresh start via reboot. Or maybe physical persistent volume is chosen if users want to keep the parameter into the hardware storage. At the initialization time, Parameter Server will load the parameters from the storage which is specified by user.
-
Storing Period
It sets the interval for periodically saving parameters to the file system, and that setting the value to 0 disables periodic storing.
-
Node Options
there are three important options:
- allow_undeclared_parameters: (default true)
- automatically_declare_parameters_from_overrides: (default true)
- allow_dynamic_typing: (default false) all of the configuration options will be passed via arguments as following.
| Options | CLI | File truncated at 100 lines [see the full file](https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_parameter_server/tree/rolling/./README.md)
|---|
Changelog for package persist_parameter_server
1.0.4 (2025-12-20)
-
fix: save floats in explicit float notation (#67)
* fix: save floats in explicit float notation YAML only has the concept of scalar values. So a value of '1' could be an integer, float or string. ros2_persist_parameter_server relies on being able to differentiate if something is a float or integer based on the representation of numbers. Floating numbers must be written such that they can not be mistaken as integers. This is comparable to how many programming languages assume '1' is an integer and '1.0' is a floating point number. The library yaml-cpp exports a float without the distinguishing feature required for ros2_persist_parameter_server. To fix this we manually convert the double into a string representation and ensure that a '.0' extension will be added when required. Note to future maintainer. The current yaml-cpp branch has a YAML::FpToString function which is better suited than using std::stringstream but is not available in the current yaml-cpp release.
- fix: enforce a dot as decimal point
- refactor convertDoubleToString function.
- add test case to make sure double type can be handled.
- remove this problem from known issue description in README.md.
- skil auto-genrated CHANGELOG.rst from codespell checker.
* use std::abs instead of c abs(). ---------Co-authored-by: Tomoya Fujita <<Tomoya.Fujita@sony.com>>
-
Contributors: Simon Gene Gottlieb
1.0.3 (2025-12-08)
- update pdf and html presentation slides.
- Contributors: Tomoya Fujita
1.0.2 (2025-10-21)
- Update package name in script and document
- Change package name for other configuration files
- Use a set of CMakeLists.txt and package.xml files for server and test
- update README for additional service interfaces. (#60)
- Added ros2 service call to manually trigger yaml save (#38)
- remove ament_target_dependencies deprecation warnings. (#59)
- a few follow-ups after https://github.com/fujitatomoya/ros2_persist_p… (#56)
- Fix/dynamic typing (#37)
- add tutorial video from The Construct.
- declare dependencies to boost dev libraries (#55)
- update markdown presenation.
- add kubernetes examples and docs. (#54)
- add JP markdown presentation for possible ROSCon JP 2025 LT. (#53)
- enable Gemini CLI workflow. (#51)
- remove ros signing key temporary workaround. (#48)
- enable builtin dictionaries with custom ones. (#47)
- support codespell github action. (#46)
- Support Kilted Kaiju. (#43)
- Remove use of ament_target_dependencies. (#42)
- perform periodic storing of the yaml file. (#36)
- add nightly workflow files for each distribution. (#34)
- add system test to github workflow for all distributions. (#32)
- fix github workflow target branch, should be rolling. (#30)
- docker images release and build script, and doc update. (#29)
- fix overview html markdown link.
- Iron Irwini is End of Life.
- add overview slide deck link on top.
- Blank issue enabled for miscellaneous issues. (#27)
- cosmetic fix for github issue template files.
- update issue templates and configuration.
- Mirror rolling to master branch.
- Signal(SIGINT) needs to be injected to the server executable. (#25)
- add jazzy to the presentation slides.
- Jazzy support (#23)
- update README and remove deprecation.
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_cmake | |
| launch_ros | |
| ament_cmake_pytest | |
| ament_lint_auto | |
| ament_lint_common | |
| launch | |
| rclcpp | |
| rclcpp_components | |
| rcutils | |
| rmw | |
| rmw_implementation_cmake | |
| std_msgs | |
| std_srvs | |
| yaml_cpp_vendor |