Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/PRBonn/rko_lio.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-17 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| rko_lio | 0.2.0 |
README
RKO-LIO
Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modelling
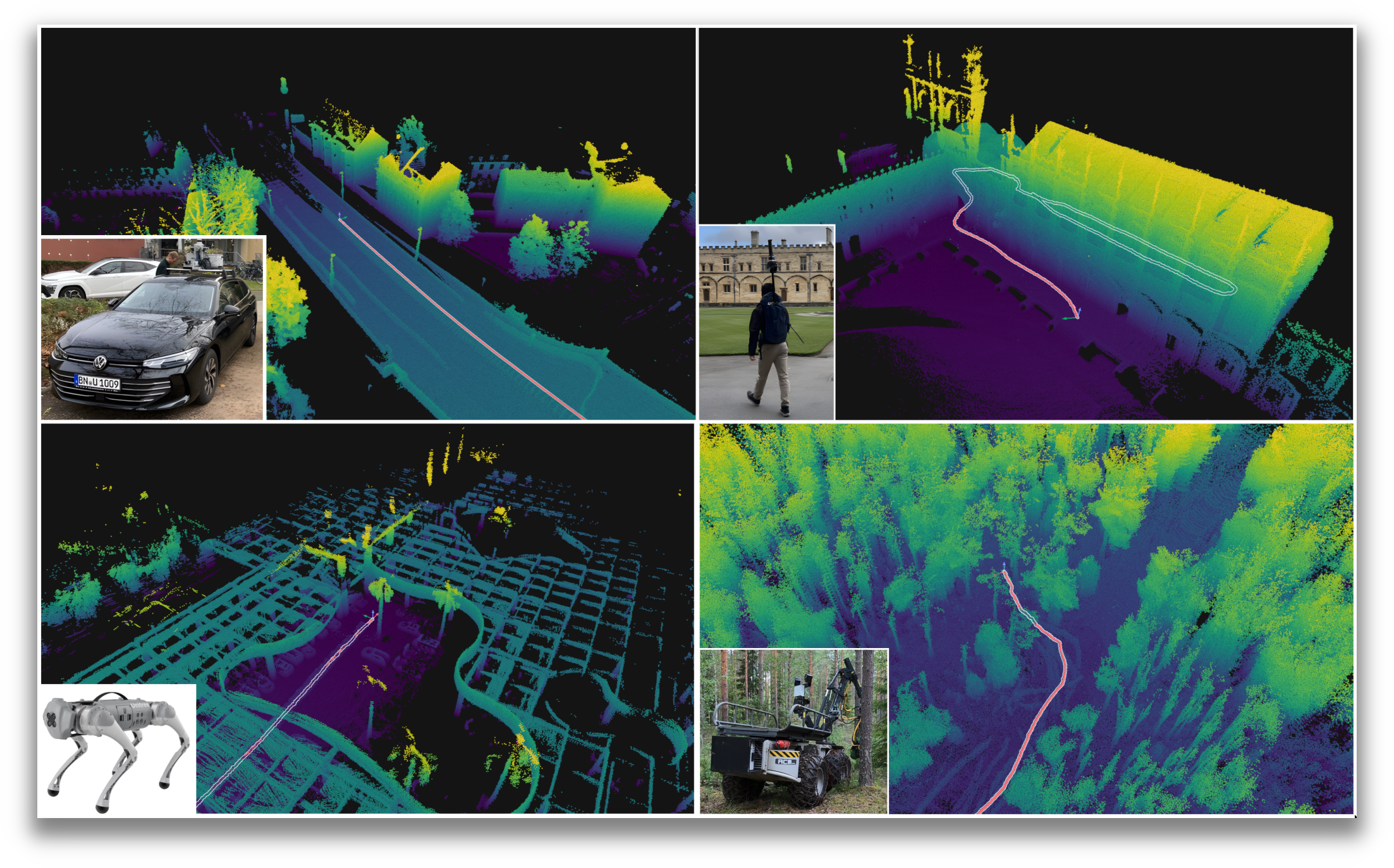
Four different platforms, four different environments, one odometry system
Quick Start
Assuming you have a rosbag (ros1/ros2) which contains a TF tree, you can run RKO-LIO through
pip install rko_lio rosbags rerun-sdk
# data path should be a directory with *.bag files (ROS1) or a metadata.yaml (ROS2)
rko_lio -v /path/to/data
Why pip install those three packages?
-
rko_lio-> the odometry package -
rosbags-> required for the rosbag dataloader. Both ros1 and ros2 bags are supported! -
rerun-sdk-> required for the optional visualizer (-vflag)
Check further options for the CLI through rko_lio --help.
More details are available in the Python usage docs.
ROS
Supported distros: Humble, Jazzy, Kilted, Rolling.
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rko-lio
Or if you’d like to build from source, clone the repo into your colcon workspace and
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio # --symlink-install --event-handlers console_direct+
In case you cannot system install the necessary dependencies through rosdep, you can also build the dependencies while building RKO-LIO
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio --cmake-args -DRKO_LIO_FETCH_CONTENT_DEPS=ON
A launch file is provided:
ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py imu_topic:=<topic> lidar_topic:=<topic> base_frame:=base_link
The three parameters above are the minimum you need to specify for the launch file.
Check further launch configuration options through ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py -s
More details are available in the ROS usage docs.
License
This project is free software made available under the MIT license. For details, see the LICENSE file.
Citation
If you found this work useful, please consider leaving a star :star: on this repository and citing our paper:
@article{malladi2025arxiv,
author = {M.V.R. Malladi and T. Guadagnino and L. Lobefaro and C. Stachniss},
title = {A Robust Approach for LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modeling},
journal = {arXiv preprint},
year = {2025},
volume = {arXiv:2509.06593},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06593},
}
RA-L Submission
You can check out the branch ral_submission for the version of the code used for submission to RA-L. Please note that that branch is meant to be an as-is reproduction of the code used during submission and is not supported. The master and release versions are vastly improved, supported, and are the recommended way to use this system.
Acknowledgements
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/PRBonn/rko_lio.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-17 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| rko_lio | 0.2.0 |
README
RKO-LIO
Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modelling

Four different platforms, four different environments, one odometry system
Quick Start
Assuming you have a rosbag (ros1/ros2) which contains a TF tree, you can run RKO-LIO through
pip install rko_lio rosbags rerun-sdk
# data path should be a directory with *.bag files (ROS1) or a metadata.yaml (ROS2)
rko_lio -v /path/to/data
Why pip install those three packages?
-
rko_lio-> the odometry package -
rosbags-> required for the rosbag dataloader. Both ros1 and ros2 bags are supported! -
rerun-sdk-> required for the optional visualizer (-vflag)
Check further options for the CLI through rko_lio --help.
More details are available in the Python usage docs.
ROS
Supported distros: Humble, Jazzy, Kilted, Rolling.
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rko-lio
Or if you’d like to build from source, clone the repo into your colcon workspace and
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio # --symlink-install --event-handlers console_direct+
In case you cannot system install the necessary dependencies through rosdep, you can also build the dependencies while building RKO-LIO
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio --cmake-args -DRKO_LIO_FETCH_CONTENT_DEPS=ON
A launch file is provided:
ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py imu_topic:=<topic> lidar_topic:=<topic> base_frame:=base_link
The three parameters above are the minimum you need to specify for the launch file.
Check further launch configuration options through ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py -s
More details are available in the ROS usage docs.
License
This project is free software made available under the MIT license. For details, see the LICENSE file.
Citation
If you found this work useful, please consider leaving a star :star: on this repository and citing our paper:
@article{malladi2025arxiv,
author = {M.V.R. Malladi and T. Guadagnino and L. Lobefaro and C. Stachniss},
title = {A Robust Approach for LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modeling},
journal = {arXiv preprint},
year = {2025},
volume = {arXiv:2509.06593},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06593},
}
RA-L Submission
You can check out the branch ral_submission for the version of the code used for submission to RA-L. Please note that that branch is meant to be an as-is reproduction of the code used during submission and is not supported. The master and release versions are vastly improved, supported, and are the recommended way to use this system.
Acknowledgements
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/PRBonn/rko_lio.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-17 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| rko_lio | 0.2.0 |
README
RKO-LIO
Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modelling

Four different platforms, four different environments, one odometry system
Quick Start
Assuming you have a rosbag (ros1/ros2) which contains a TF tree, you can run RKO-LIO through
pip install rko_lio rosbags rerun-sdk
# data path should be a directory with *.bag files (ROS1) or a metadata.yaml (ROS2)
rko_lio -v /path/to/data
Why pip install those three packages?
-
rko_lio-> the odometry package -
rosbags-> required for the rosbag dataloader. Both ros1 and ros2 bags are supported! -
rerun-sdk-> required for the optional visualizer (-vflag)
Check further options for the CLI through rko_lio --help.
More details are available in the Python usage docs.
ROS
Supported distros: Humble, Jazzy, Kilted, Rolling.
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rko-lio
Or if you’d like to build from source, clone the repo into your colcon workspace and
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio # --symlink-install --event-handlers console_direct+
In case you cannot system install the necessary dependencies through rosdep, you can also build the dependencies while building RKO-LIO
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio --cmake-args -DRKO_LIO_FETCH_CONTENT_DEPS=ON
A launch file is provided:
ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py imu_topic:=<topic> lidar_topic:=<topic> base_frame:=base_link
The three parameters above are the minimum you need to specify for the launch file.
Check further launch configuration options through ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py -s
More details are available in the ROS usage docs.
License
This project is free software made available under the MIT license. For details, see the LICENSE file.
Citation
If you found this work useful, please consider leaving a star :star: on this repository and citing our paper:
@article{malladi2025arxiv,
author = {M.V.R. Malladi and T. Guadagnino and L. Lobefaro and C. Stachniss},
title = {A Robust Approach for LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modeling},
journal = {arXiv preprint},
year = {2025},
volume = {arXiv:2509.06593},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06593},
}
RA-L Submission
You can check out the branch ral_submission for the version of the code used for submission to RA-L. Please note that that branch is meant to be an as-is reproduction of the code used during submission and is not supported. The master and release versions are vastly improved, supported, and are the recommended way to use this system.
Acknowledgements
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/PRBonn/rko_lio.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-17 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| rko_lio | 0.2.0 |
README
RKO-LIO
Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modelling

Four different platforms, four different environments, one odometry system
Quick Start
Assuming you have a rosbag (ros1/ros2) which contains a TF tree, you can run RKO-LIO through
pip install rko_lio rosbags rerun-sdk
# data path should be a directory with *.bag files (ROS1) or a metadata.yaml (ROS2)
rko_lio -v /path/to/data
Why pip install those three packages?
-
rko_lio-> the odometry package -
rosbags-> required for the rosbag dataloader. Both ros1 and ros2 bags are supported! -
rerun-sdk-> required for the optional visualizer (-vflag)
Check further options for the CLI through rko_lio --help.
More details are available in the Python usage docs.
ROS
Supported distros: Humble, Jazzy, Kilted, Rolling.
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rko-lio
Or if you’d like to build from source, clone the repo into your colcon workspace and
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio # --symlink-install --event-handlers console_direct+
In case you cannot system install the necessary dependencies through rosdep, you can also build the dependencies while building RKO-LIO
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio --cmake-args -DRKO_LIO_FETCH_CONTENT_DEPS=ON
A launch file is provided:
ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py imu_topic:=<topic> lidar_topic:=<topic> base_frame:=base_link
The three parameters above are the minimum you need to specify for the launch file.
Check further launch configuration options through ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py -s
More details are available in the ROS usage docs.
License
This project is free software made available under the MIT license. For details, see the LICENSE file.
Citation
If you found this work useful, please consider leaving a star :star: on this repository and citing our paper:
@article{malladi2025arxiv,
author = {M.V.R. Malladi and T. Guadagnino and L. Lobefaro and C. Stachniss},
title = {A Robust Approach for LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modeling},
journal = {arXiv preprint},
year = {2025},
volume = {arXiv:2509.06593},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06593},
}
RA-L Submission
You can check out the branch ral_submission for the version of the code used for submission to RA-L. Please note that that branch is meant to be an as-is reproduction of the code used during submission and is not supported. The master and release versions are vastly improved, supported, and are the recommended way to use this system.
Acknowledgements
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/PRBonn/rko_lio.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-17 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| rko_lio | 0.2.0 |
README
RKO-LIO
Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modelling

Four different platforms, four different environments, one odometry system
Quick Start
Assuming you have a rosbag (ros1/ros2) which contains a TF tree, you can run RKO-LIO through
pip install rko_lio rosbags rerun-sdk
# data path should be a directory with *.bag files (ROS1) or a metadata.yaml (ROS2)
rko_lio -v /path/to/data
Why pip install those three packages?
-
rko_lio-> the odometry package -
rosbags-> required for the rosbag dataloader. Both ros1 and ros2 bags are supported! -
rerun-sdk-> required for the optional visualizer (-vflag)
Check further options for the CLI through rko_lio --help.
More details are available in the Python usage docs.
ROS
Supported distros: Humble, Jazzy, Kilted, Rolling.
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rko-lio
Or if you’d like to build from source, clone the repo into your colcon workspace and
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio # --symlink-install --event-handlers console_direct+
In case you cannot system install the necessary dependencies through rosdep, you can also build the dependencies while building RKO-LIO
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio --cmake-args -DRKO_LIO_FETCH_CONTENT_DEPS=ON
A launch file is provided:
ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py imu_topic:=<topic> lidar_topic:=<topic> base_frame:=base_link
The three parameters above are the minimum you need to specify for the launch file.
Check further launch configuration options through ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py -s
More details are available in the ROS usage docs.
License
This project is free software made available under the MIT license. For details, see the LICENSE file.
Citation
If you found this work useful, please consider leaving a star :star: on this repository and citing our paper:
@article{malladi2025arxiv,
author = {M.V.R. Malladi and T. Guadagnino and L. Lobefaro and C. Stachniss},
title = {A Robust Approach for LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modeling},
journal = {arXiv preprint},
year = {2025},
volume = {arXiv:2509.06593},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06593},
}
RA-L Submission
You can check out the branch ral_submission for the version of the code used for submission to RA-L. Please note that that branch is meant to be an as-is reproduction of the code used during submission and is not supported. The master and release versions are vastly improved, supported, and are the recommended way to use this system.
Acknowledgements
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/PRBonn/rko_lio.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-17 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| rko_lio | 0.2.0 |
README
RKO-LIO
Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modelling

Four different platforms, four different environments, one odometry system
Quick Start
Assuming you have a rosbag (ros1/ros2) which contains a TF tree, you can run RKO-LIO through
pip install rko_lio rosbags rerun-sdk
# data path should be a directory with *.bag files (ROS1) or a metadata.yaml (ROS2)
rko_lio -v /path/to/data
Why pip install those three packages?
-
rko_lio-> the odometry package -
rosbags-> required for the rosbag dataloader. Both ros1 and ros2 bags are supported! -
rerun-sdk-> required for the optional visualizer (-vflag)
Check further options for the CLI through rko_lio --help.
More details are available in the Python usage docs.
ROS
Supported distros: Humble, Jazzy, Kilted, Rolling.
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rko-lio
Or if you’d like to build from source, clone the repo into your colcon workspace and
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio # --symlink-install --event-handlers console_direct+
In case you cannot system install the necessary dependencies through rosdep, you can also build the dependencies while building RKO-LIO
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio --cmake-args -DRKO_LIO_FETCH_CONTENT_DEPS=ON
A launch file is provided:
ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py imu_topic:=<topic> lidar_topic:=<topic> base_frame:=base_link
The three parameters above are the minimum you need to specify for the launch file.
Check further launch configuration options through ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py -s
More details are available in the ROS usage docs.
License
This project is free software made available under the MIT license. For details, see the LICENSE file.
Citation
If you found this work useful, please consider leaving a star :star: on this repository and citing our paper:
@article{malladi2025arxiv,
author = {M.V.R. Malladi and T. Guadagnino and L. Lobefaro and C. Stachniss},
title = {A Robust Approach for LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modeling},
journal = {arXiv preprint},
year = {2025},
volume = {arXiv:2509.06593},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06593},
}
RA-L Submission
You can check out the branch ral_submission for the version of the code used for submission to RA-L. Please note that that branch is meant to be an as-is reproduction of the code used during submission and is not supported. The master and release versions are vastly improved, supported, and are the recommended way to use this system.
Acknowledgements
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/PRBonn/rko_lio.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-17 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| rko_lio | 0.2.0 |
README
RKO-LIO
Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modelling

Four different platforms, four different environments, one odometry system
Quick Start
Assuming you have a rosbag (ros1/ros2) which contains a TF tree, you can run RKO-LIO through
pip install rko_lio rosbags rerun-sdk
# data path should be a directory with *.bag files (ROS1) or a metadata.yaml (ROS2)
rko_lio -v /path/to/data
Why pip install those three packages?
-
rko_lio-> the odometry package -
rosbags-> required for the rosbag dataloader. Both ros1 and ros2 bags are supported! -
rerun-sdk-> required for the optional visualizer (-vflag)
Check further options for the CLI through rko_lio --help.
More details are available in the Python usage docs.
ROS
Supported distros: Humble, Jazzy, Kilted, Rolling.
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rko-lio
Or if you’d like to build from source, clone the repo into your colcon workspace and
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio # --symlink-install --event-handlers console_direct+
In case you cannot system install the necessary dependencies through rosdep, you can also build the dependencies while building RKO-LIO
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio --cmake-args -DRKO_LIO_FETCH_CONTENT_DEPS=ON
A launch file is provided:
ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py imu_topic:=<topic> lidar_topic:=<topic> base_frame:=base_link
The three parameters above are the minimum you need to specify for the launch file.
Check further launch configuration options through ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py -s
More details are available in the ROS usage docs.
License
This project is free software made available under the MIT license. For details, see the LICENSE file.
Citation
If you found this work useful, please consider leaving a star :star: on this repository and citing our paper:
@article{malladi2025arxiv,
author = {M.V.R. Malladi and T. Guadagnino and L. Lobefaro and C. Stachniss},
title = {A Robust Approach for LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modeling},
journal = {arXiv preprint},
year = {2025},
volume = {arXiv:2509.06593},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06593},
}
RA-L Submission
You can check out the branch ral_submission for the version of the code used for submission to RA-L. Please note that that branch is meant to be an as-is reproduction of the code used during submission and is not supported. The master and release versions are vastly improved, supported, and are the recommended way to use this system.
Acknowledgements
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/PRBonn/rko_lio.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-17 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| rko_lio | 0.2.0 |
README
RKO-LIO
Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modelling

Four different platforms, four different environments, one odometry system
Quick Start
Assuming you have a rosbag (ros1/ros2) which contains a TF tree, you can run RKO-LIO through
pip install rko_lio rosbags rerun-sdk
# data path should be a directory with *.bag files (ROS1) or a metadata.yaml (ROS2)
rko_lio -v /path/to/data
Why pip install those three packages?
-
rko_lio-> the odometry package -
rosbags-> required for the rosbag dataloader. Both ros1 and ros2 bags are supported! -
rerun-sdk-> required for the optional visualizer (-vflag)
Check further options for the CLI through rko_lio --help.
More details are available in the Python usage docs.
ROS
Supported distros: Humble, Jazzy, Kilted, Rolling.
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rko-lio
Or if you’d like to build from source, clone the repo into your colcon workspace and
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio # --symlink-install --event-handlers console_direct+
In case you cannot system install the necessary dependencies through rosdep, you can also build the dependencies while building RKO-LIO
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio --cmake-args -DRKO_LIO_FETCH_CONTENT_DEPS=ON
A launch file is provided:
ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py imu_topic:=<topic> lidar_topic:=<topic> base_frame:=base_link
The three parameters above are the minimum you need to specify for the launch file.
Check further launch configuration options through ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py -s
More details are available in the ROS usage docs.
License
This project is free software made available under the MIT license. For details, see the LICENSE file.
Citation
If you found this work useful, please consider leaving a star :star: on this repository and citing our paper:
@article{malladi2025arxiv,
author = {M.V.R. Malladi and T. Guadagnino and L. Lobefaro and C. Stachniss},
title = {A Robust Approach for LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modeling},
journal = {arXiv preprint},
year = {2025},
volume = {arXiv:2509.06593},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06593},
}
RA-L Submission
You can check out the branch ral_submission for the version of the code used for submission to RA-L. Please note that that branch is meant to be an as-is reproduction of the code used during submission and is not supported. The master and release versions are vastly improved, supported, and are the recommended way to use this system.
Acknowledgements
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/PRBonn/rko_lio.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-17 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| rko_lio | 0.2.0 |
README
RKO-LIO
Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modelling

Four different platforms, four different environments, one odometry system
Quick Start
Assuming you have a rosbag (ros1/ros2) which contains a TF tree, you can run RKO-LIO through
pip install rko_lio rosbags rerun-sdk
# data path should be a directory with *.bag files (ROS1) or a metadata.yaml (ROS2)
rko_lio -v /path/to/data
Why pip install those three packages?
-
rko_lio-> the odometry package -
rosbags-> required for the rosbag dataloader. Both ros1 and ros2 bags are supported! -
rerun-sdk-> required for the optional visualizer (-vflag)
Check further options for the CLI through rko_lio --help.
More details are available in the Python usage docs.
ROS
Supported distros: Humble, Jazzy, Kilted, Rolling.
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rko-lio
Or if you’d like to build from source, clone the repo into your colcon workspace and
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio # --symlink-install --event-handlers console_direct+
In case you cannot system install the necessary dependencies through rosdep, you can also build the dependencies while building RKO-LIO
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio --cmake-args -DRKO_LIO_FETCH_CONTENT_DEPS=ON
A launch file is provided:
ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py imu_topic:=<topic> lidar_topic:=<topic> base_frame:=base_link
The three parameters above are the minimum you need to specify for the launch file.
Check further launch configuration options through ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py -s
More details are available in the ROS usage docs.
License
This project is free software made available under the MIT license. For details, see the LICENSE file.
Citation
If you found this work useful, please consider leaving a star :star: on this repository and citing our paper:
@article{malladi2025arxiv,
author = {M.V.R. Malladi and T. Guadagnino and L. Lobefaro and C. Stachniss},
title = {A Robust Approach for LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modeling},
journal = {arXiv preprint},
year = {2025},
volume = {arXiv:2509.06593},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06593},
}
RA-L Submission
You can check out the branch ral_submission for the version of the code used for submission to RA-L. Please note that that branch is meant to be an as-is reproduction of the code used during submission and is not supported. The master and release versions are vastly improved, supported, and are the recommended way to use this system.
Acknowledgements
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/PRBonn/rko_lio.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-17 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| rko_lio | 0.2.0 |
README
RKO-LIO
Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modelling

Four different platforms, four different environments, one odometry system
Quick Start
Assuming you have a rosbag (ros1/ros2) which contains a TF tree, you can run RKO-LIO through
pip install rko_lio rosbags rerun-sdk
# data path should be a directory with *.bag files (ROS1) or a metadata.yaml (ROS2)
rko_lio -v /path/to/data
Why pip install those three packages?
-
rko_lio-> the odometry package -
rosbags-> required for the rosbag dataloader. Both ros1 and ros2 bags are supported! -
rerun-sdk-> required for the optional visualizer (-vflag)
Check further options for the CLI through rko_lio --help.
More details are available in the Python usage docs.
ROS
Supported distros: Humble, Jazzy, Kilted, Rolling.
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rko-lio
Or if you’d like to build from source, clone the repo into your colcon workspace and
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio # --symlink-install --event-handlers console_direct+
In case you cannot system install the necessary dependencies through rosdep, you can also build the dependencies while building RKO-LIO
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio --cmake-args -DRKO_LIO_FETCH_CONTENT_DEPS=ON
A launch file is provided:
ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py imu_topic:=<topic> lidar_topic:=<topic> base_frame:=base_link
The three parameters above are the minimum you need to specify for the launch file.
Check further launch configuration options through ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py -s
More details are available in the ROS usage docs.
License
This project is free software made available under the MIT license. For details, see the LICENSE file.
Citation
If you found this work useful, please consider leaving a star :star: on this repository and citing our paper:
@article{malladi2025arxiv,
author = {M.V.R. Malladi and T. Guadagnino and L. Lobefaro and C. Stachniss},
title = {A Robust Approach for LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modeling},
journal = {arXiv preprint},
year = {2025},
volume = {arXiv:2509.06593},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06593},
}
RA-L Submission
You can check out the branch ral_submission for the version of the code used for submission to RA-L. Please note that that branch is meant to be an as-is reproduction of the code used during submission and is not supported. The master and release versions are vastly improved, supported, and are the recommended way to use this system.
Acknowledgements
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/PRBonn/rko_lio.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-17 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| rko_lio | 0.2.0 |
README
RKO-LIO
Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modelling

Four different platforms, four different environments, one odometry system
Quick Start
Assuming you have a rosbag (ros1/ros2) which contains a TF tree, you can run RKO-LIO through
pip install rko_lio rosbags rerun-sdk
# data path should be a directory with *.bag files (ROS1) or a metadata.yaml (ROS2)
rko_lio -v /path/to/data
Why pip install those three packages?
-
rko_lio-> the odometry package -
rosbags-> required for the rosbag dataloader. Both ros1 and ros2 bags are supported! -
rerun-sdk-> required for the optional visualizer (-vflag)
Check further options for the CLI through rko_lio --help.
More details are available in the Python usage docs.
ROS
Supported distros: Humble, Jazzy, Kilted, Rolling.
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rko-lio
Or if you’d like to build from source, clone the repo into your colcon workspace and
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio # --symlink-install --event-handlers console_direct+
In case you cannot system install the necessary dependencies through rosdep, you can also build the dependencies while building RKO-LIO
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio --cmake-args -DRKO_LIO_FETCH_CONTENT_DEPS=ON
A launch file is provided:
ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py imu_topic:=<topic> lidar_topic:=<topic> base_frame:=base_link
The three parameters above are the minimum you need to specify for the launch file.
Check further launch configuration options through ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py -s
More details are available in the ROS usage docs.
License
This project is free software made available under the MIT license. For details, see the LICENSE file.
Citation
If you found this work useful, please consider leaving a star :star: on this repository and citing our paper:
@article{malladi2025arxiv,
author = {M.V.R. Malladi and T. Guadagnino and L. Lobefaro and C. Stachniss},
title = {A Robust Approach for LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modeling},
journal = {arXiv preprint},
year = {2025},
volume = {arXiv:2509.06593},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06593},
}
RA-L Submission
You can check out the branch ral_submission for the version of the code used for submission to RA-L. Please note that that branch is meant to be an as-is reproduction of the code used during submission and is not supported. The master and release versions are vastly improved, supported, and are the recommended way to use this system.
Acknowledgements
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/PRBonn/rko_lio.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-17 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| rko_lio | 0.2.0 |
README
RKO-LIO
Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modelling

Four different platforms, four different environments, one odometry system
Quick Start
Assuming you have a rosbag (ros1/ros2) which contains a TF tree, you can run RKO-LIO through
pip install rko_lio rosbags rerun-sdk
# data path should be a directory with *.bag files (ROS1) or a metadata.yaml (ROS2)
rko_lio -v /path/to/data
Why pip install those three packages?
-
rko_lio-> the odometry package -
rosbags-> required for the rosbag dataloader. Both ros1 and ros2 bags are supported! -
rerun-sdk-> required for the optional visualizer (-vflag)
Check further options for the CLI through rko_lio --help.
More details are available in the Python usage docs.
ROS
Supported distros: Humble, Jazzy, Kilted, Rolling.
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rko-lio
Or if you’d like to build from source, clone the repo into your colcon workspace and
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio # --symlink-install --event-handlers console_direct+
In case you cannot system install the necessary dependencies through rosdep, you can also build the dependencies while building RKO-LIO
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio --cmake-args -DRKO_LIO_FETCH_CONTENT_DEPS=ON
A launch file is provided:
ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py imu_topic:=<topic> lidar_topic:=<topic> base_frame:=base_link
The three parameters above are the minimum you need to specify for the launch file.
Check further launch configuration options through ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py -s
More details are available in the ROS usage docs.
License
This project is free software made available under the MIT license. For details, see the LICENSE file.
Citation
If you found this work useful, please consider leaving a star :star: on this repository and citing our paper:
@article{malladi2025arxiv,
author = {M.V.R. Malladi and T. Guadagnino and L. Lobefaro and C. Stachniss},
title = {A Robust Approach for LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modeling},
journal = {arXiv preprint},
year = {2025},
volume = {arXiv:2509.06593},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06593},
}
RA-L Submission
You can check out the branch ral_submission for the version of the code used for submission to RA-L. Please note that that branch is meant to be an as-is reproduction of the code used during submission and is not supported. The master and release versions are vastly improved, supported, and are the recommended way to use this system.
Acknowledgements
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/PRBonn/rko_lio.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-17 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| rko_lio | 0.2.0 |
README
RKO-LIO
Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modelling

Four different platforms, four different environments, one odometry system
Quick Start
Assuming you have a rosbag (ros1/ros2) which contains a TF tree, you can run RKO-LIO through
pip install rko_lio rosbags rerun-sdk
# data path should be a directory with *.bag files (ROS1) or a metadata.yaml (ROS2)
rko_lio -v /path/to/data
Why pip install those three packages?
-
rko_lio-> the odometry package -
rosbags-> required for the rosbag dataloader. Both ros1 and ros2 bags are supported! -
rerun-sdk-> required for the optional visualizer (-vflag)
Check further options for the CLI through rko_lio --help.
More details are available in the Python usage docs.
ROS
Supported distros: Humble, Jazzy, Kilted, Rolling.
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rko-lio
Or if you’d like to build from source, clone the repo into your colcon workspace and
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio # --symlink-install --event-handlers console_direct+
In case you cannot system install the necessary dependencies through rosdep, you can also build the dependencies while building RKO-LIO
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio --cmake-args -DRKO_LIO_FETCH_CONTENT_DEPS=ON
A launch file is provided:
ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py imu_topic:=<topic> lidar_topic:=<topic> base_frame:=base_link
The three parameters above are the minimum you need to specify for the launch file.
Check further launch configuration options through ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py -s
More details are available in the ROS usage docs.
License
This project is free software made available under the MIT license. For details, see the LICENSE file.
Citation
If you found this work useful, please consider leaving a star :star: on this repository and citing our paper:
@article{malladi2025arxiv,
author = {M.V.R. Malladi and T. Guadagnino and L. Lobefaro and C. Stachniss},
title = {A Robust Approach for LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modeling},
journal = {arXiv preprint},
year = {2025},
volume = {arXiv:2509.06593},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06593},
}
RA-L Submission
You can check out the branch ral_submission for the version of the code used for submission to RA-L. Please note that that branch is meant to be an as-is reproduction of the code used during submission and is not supported. The master and release versions are vastly improved, supported, and are the recommended way to use this system.
Acknowledgements
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/PRBonn/rko_lio.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-17 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| rko_lio | 0.2.0 |
README
RKO-LIO
Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modelling

Four different platforms, four different environments, one odometry system
Quick Start
Assuming you have a rosbag (ros1/ros2) which contains a TF tree, you can run RKO-LIO through
pip install rko_lio rosbags rerun-sdk
# data path should be a directory with *.bag files (ROS1) or a metadata.yaml (ROS2)
rko_lio -v /path/to/data
Why pip install those three packages?
-
rko_lio-> the odometry package -
rosbags-> required for the rosbag dataloader. Both ros1 and ros2 bags are supported! -
rerun-sdk-> required for the optional visualizer (-vflag)
Check further options for the CLI through rko_lio --help.
More details are available in the Python usage docs.
ROS
Supported distros: Humble, Jazzy, Kilted, Rolling.
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rko-lio
Or if you’d like to build from source, clone the repo into your colcon workspace and
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio # --symlink-install --event-handlers console_direct+
In case you cannot system install the necessary dependencies through rosdep, you can also build the dependencies while building RKO-LIO
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio --cmake-args -DRKO_LIO_FETCH_CONTENT_DEPS=ON
A launch file is provided:
ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py imu_topic:=<topic> lidar_topic:=<topic> base_frame:=base_link
The three parameters above are the minimum you need to specify for the launch file.
Check further launch configuration options through ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py -s
More details are available in the ROS usage docs.
License
This project is free software made available under the MIT license. For details, see the LICENSE file.
Citation
If you found this work useful, please consider leaving a star :star: on this repository and citing our paper:
@article{malladi2025arxiv,
author = {M.V.R. Malladi and T. Guadagnino and L. Lobefaro and C. Stachniss},
title = {A Robust Approach for LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modeling},
journal = {arXiv preprint},
year = {2025},
volume = {arXiv:2509.06593},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06593},
}
RA-L Submission
You can check out the branch ral_submission for the version of the code used for submission to RA-L. Please note that that branch is meant to be an as-is reproduction of the code used during submission and is not supported. The master and release versions are vastly improved, supported, and are the recommended way to use this system.
Acknowledgements
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/PRBonn/rko_lio.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-17 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| rko_lio | 0.2.0 |
README
RKO-LIO
Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modelling

Four different platforms, four different environments, one odometry system
Quick Start
Assuming you have a rosbag (ros1/ros2) which contains a TF tree, you can run RKO-LIO through
pip install rko_lio rosbags rerun-sdk
# data path should be a directory with *.bag files (ROS1) or a metadata.yaml (ROS2)
rko_lio -v /path/to/data
Why pip install those three packages?
-
rko_lio-> the odometry package -
rosbags-> required for the rosbag dataloader. Both ros1 and ros2 bags are supported! -
rerun-sdk-> required for the optional visualizer (-vflag)
Check further options for the CLI through rko_lio --help.
More details are available in the Python usage docs.
ROS
Supported distros: Humble, Jazzy, Kilted, Rolling.
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rko-lio
Or if you’d like to build from source, clone the repo into your colcon workspace and
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio # --symlink-install --event-handlers console_direct+
In case you cannot system install the necessary dependencies through rosdep, you can also build the dependencies while building RKO-LIO
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio --cmake-args -DRKO_LIO_FETCH_CONTENT_DEPS=ON
A launch file is provided:
ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py imu_topic:=<topic> lidar_topic:=<topic> base_frame:=base_link
The three parameters above are the minimum you need to specify for the launch file.
Check further launch configuration options through ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py -s
More details are available in the ROS usage docs.
License
This project is free software made available under the MIT license. For details, see the LICENSE file.
Citation
If you found this work useful, please consider leaving a star :star: on this repository and citing our paper:
@article{malladi2025arxiv,
author = {M.V.R. Malladi and T. Guadagnino and L. Lobefaro and C. Stachniss},
title = {A Robust Approach for LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modeling},
journal = {arXiv preprint},
year = {2025},
volume = {arXiv:2509.06593},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06593},
}
RA-L Submission
You can check out the branch ral_submission for the version of the code used for submission to RA-L. Please note that that branch is meant to be an as-is reproduction of the code used during submission and is not supported. The master and release versions are vastly improved, supported, and are the recommended way to use this system.
Acknowledgements
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/PRBonn/rko_lio.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-17 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| rko_lio | 0.2.0 |
README
RKO-LIO
Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modelling

Four different platforms, four different environments, one odometry system
Quick Start
Assuming you have a rosbag (ros1/ros2) which contains a TF tree, you can run RKO-LIO through
pip install rko_lio rosbags rerun-sdk
# data path should be a directory with *.bag files (ROS1) or a metadata.yaml (ROS2)
rko_lio -v /path/to/data
Why pip install those three packages?
-
rko_lio-> the odometry package -
rosbags-> required for the rosbag dataloader. Both ros1 and ros2 bags are supported! -
rerun-sdk-> required for the optional visualizer (-vflag)
Check further options for the CLI through rko_lio --help.
More details are available in the Python usage docs.
ROS
Supported distros: Humble, Jazzy, Kilted, Rolling.
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rko-lio
Or if you’d like to build from source, clone the repo into your colcon workspace and
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio # --symlink-install --event-handlers console_direct+
In case you cannot system install the necessary dependencies through rosdep, you can also build the dependencies while building RKO-LIO
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio --cmake-args -DRKO_LIO_FETCH_CONTENT_DEPS=ON
A launch file is provided:
ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py imu_topic:=<topic> lidar_topic:=<topic> base_frame:=base_link
The three parameters above are the minimum you need to specify for the launch file.
Check further launch configuration options through ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py -s
More details are available in the ROS usage docs.
License
This project is free software made available under the MIT license. For details, see the LICENSE file.
Citation
If you found this work useful, please consider leaving a star :star: on this repository and citing our paper:
@article{malladi2025arxiv,
author = {M.V.R. Malladi and T. Guadagnino and L. Lobefaro and C. Stachniss},
title = {A Robust Approach for LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modeling},
journal = {arXiv preprint},
year = {2025},
volume = {arXiv:2509.06593},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06593},
}
RA-L Submission
You can check out the branch ral_submission for the version of the code used for submission to RA-L. Please note that that branch is meant to be an as-is reproduction of the code used during submission and is not supported. The master and release versions are vastly improved, supported, and are the recommended way to use this system.
Acknowledgements
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/PRBonn/rko_lio.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-17 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| rko_lio | 0.2.0 |
README
RKO-LIO
Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modelling

Four different platforms, four different environments, one odometry system
Quick Start
Assuming you have a rosbag (ros1/ros2) which contains a TF tree, you can run RKO-LIO through
pip install rko_lio rosbags rerun-sdk
# data path should be a directory with *.bag files (ROS1) or a metadata.yaml (ROS2)
rko_lio -v /path/to/data
Why pip install those three packages?
-
rko_lio-> the odometry package -
rosbags-> required for the rosbag dataloader. Both ros1 and ros2 bags are supported! -
rerun-sdk-> required for the optional visualizer (-vflag)
Check further options for the CLI through rko_lio --help.
More details are available in the Python usage docs.
ROS
Supported distros: Humble, Jazzy, Kilted, Rolling.
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rko-lio
Or if you’d like to build from source, clone the repo into your colcon workspace and
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio # --symlink-install --event-handlers console_direct+
In case you cannot system install the necessary dependencies through rosdep, you can also build the dependencies while building RKO-LIO
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio --cmake-args -DRKO_LIO_FETCH_CONTENT_DEPS=ON
A launch file is provided:
ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py imu_topic:=<topic> lidar_topic:=<topic> base_frame:=base_link
The three parameters above are the minimum you need to specify for the launch file.
Check further launch configuration options through ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py -s
More details are available in the ROS usage docs.
License
This project is free software made available under the MIT license. For details, see the LICENSE file.
Citation
If you found this work useful, please consider leaving a star :star: on this repository and citing our paper:
@article{malladi2025arxiv,
author = {M.V.R. Malladi and T. Guadagnino and L. Lobefaro and C. Stachniss},
title = {A Robust Approach for LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modeling},
journal = {arXiv preprint},
year = {2025},
volume = {arXiv:2509.06593},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06593},
}
RA-L Submission
You can check out the branch ral_submission for the version of the code used for submission to RA-L. Please note that that branch is meant to be an as-is reproduction of the code used during submission and is not supported. The master and release versions are vastly improved, supported, and are the recommended way to use this system.
Acknowledgements
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/PRBonn/rko_lio.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-17 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| rko_lio | 0.2.0 |
README
RKO-LIO
Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modelling

Four different platforms, four different environments, one odometry system
Quick Start
Assuming you have a rosbag (ros1/ros2) which contains a TF tree, you can run RKO-LIO through
pip install rko_lio rosbags rerun-sdk
# data path should be a directory with *.bag files (ROS1) or a metadata.yaml (ROS2)
rko_lio -v /path/to/data
Why pip install those three packages?
-
rko_lio-> the odometry package -
rosbags-> required for the rosbag dataloader. Both ros1 and ros2 bags are supported! -
rerun-sdk-> required for the optional visualizer (-vflag)
Check further options for the CLI through rko_lio --help.
More details are available in the Python usage docs.
ROS
Supported distros: Humble, Jazzy, Kilted, Rolling.
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rko-lio
Or if you’d like to build from source, clone the repo into your colcon workspace and
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio # --symlink-install --event-handlers console_direct+
In case you cannot system install the necessary dependencies through rosdep, you can also build the dependencies while building RKO-LIO
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio --cmake-args -DRKO_LIO_FETCH_CONTENT_DEPS=ON
A launch file is provided:
ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py imu_topic:=<topic> lidar_topic:=<topic> base_frame:=base_link
The three parameters above are the minimum you need to specify for the launch file.
Check further launch configuration options through ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py -s
More details are available in the ROS usage docs.
License
This project is free software made available under the MIT license. For details, see the LICENSE file.
Citation
If you found this work useful, please consider leaving a star :star: on this repository and citing our paper:
@article{malladi2025arxiv,
author = {M.V.R. Malladi and T. Guadagnino and L. Lobefaro and C. Stachniss},
title = {A Robust Approach for LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modeling},
journal = {arXiv preprint},
year = {2025},
volume = {arXiv:2509.06593},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06593},
}
RA-L Submission
You can check out the branch ral_submission for the version of the code used for submission to RA-L. Please note that that branch is meant to be an as-is reproduction of the code used during submission and is not supported. The master and release versions are vastly improved, supported, and are the recommended way to use this system.
Acknowledgements
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING
Repository Summary
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/PRBonn/rko_lio.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2026-02-17 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| rko_lio | 0.2.0 |
README
RKO-LIO
Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modelling

Four different platforms, four different environments, one odometry system
Quick Start
Assuming you have a rosbag (ros1/ros2) which contains a TF tree, you can run RKO-LIO through
pip install rko_lio rosbags rerun-sdk
# data path should be a directory with *.bag files (ROS1) or a metadata.yaml (ROS2)
rko_lio -v /path/to/data
Why pip install those three packages?
-
rko_lio-> the odometry package -
rosbags-> required for the rosbag dataloader. Both ros1 and ros2 bags are supported! -
rerun-sdk-> required for the optional visualizer (-vflag)
Check further options for the CLI through rko_lio --help.
More details are available in the Python usage docs.
ROS
Supported distros: Humble, Jazzy, Kilted, Rolling.
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rko-lio
Or if you’d like to build from source, clone the repo into your colcon workspace and
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio # --symlink-install --event-handlers console_direct+
In case you cannot system install the necessary dependencies through rosdep, you can also build the dependencies while building RKO-LIO
colcon build --packages-select rko_lio --cmake-args -DRKO_LIO_FETCH_CONTENT_DEPS=ON
A launch file is provided:
ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py imu_topic:=<topic> lidar_topic:=<topic> base_frame:=base_link
The three parameters above are the minimum you need to specify for the launch file.
Check further launch configuration options through ros2 launch rko_lio odometry.launch.py -s
More details are available in the ROS usage docs.
License
This project is free software made available under the MIT license. For details, see the LICENSE file.
Citation
If you found this work useful, please consider leaving a star :star: on this repository and citing our paper:
@article{malladi2025arxiv,
author = {M.V.R. Malladi and T. Guadagnino and L. Lobefaro and C. Stachniss},
title = {A Robust Approach for LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Without Sensor-Specific Modeling},
journal = {arXiv preprint},
year = {2025},
volume = {arXiv:2509.06593},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.06593},
}
RA-L Submission
You can check out the branch ral_submission for the version of the code used for submission to RA-L. Please note that that branch is meant to be an as-is reproduction of the code used during submission and is not supported. The master and release versions are vastly improved, supported, and are the recommended way to use this system.
Acknowledgements
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
